Compare commits
360 Commits
v3.0.0-bet
...
v3.0.0-bet
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
d01fb804a4 | ||
|
|
285835f23a | ||
|
|
b5ac0bd365 | ||
|
|
aef2a52cea | ||
|
|
bc98567f41 | ||
|
|
317bc070e4 | ||
|
|
5a994d9739 | ||
|
|
3ddc2a0e83 | ||
|
|
2c4da93b28 | ||
|
|
cf50eabbab | ||
|
|
bf374a23ab | ||
|
|
223d726280 | ||
|
|
a680e687b5 | ||
|
|
b7d5a6a2a2 | ||
|
|
040893ff22 | ||
|
|
cedd916816 | ||
|
|
45871489d0 | ||
|
|
35a5d0cb3c | ||
|
|
47ee40a3f4 | ||
|
|
25968d43c2 | ||
|
|
9e76c8f4e3 | ||
|
|
3b3b1cecc5 | ||
|
|
6862b43261 | ||
|
|
a3e1856bde | ||
|
|
6612bd1c98 | ||
|
|
ce2ae9561d | ||
|
|
1a03e9ace5 | ||
|
|
e7159c033e | ||
|
|
628749573e | ||
|
|
0920c8a2f0 | ||
|
|
680ed1dec8 | ||
|
|
ddc3ab534e | ||
|
|
7c35e8865c | ||
|
|
8f6cedf67a | ||
|
|
7bb2e3be76 | ||
|
|
78db50a497 | ||
|
|
f36bf5e4e3 | ||
|
|
d10792452f | ||
|
|
c500ac83b2 | ||
|
|
082650c0e2 | ||
|
|
11de4b037d | ||
|
|
0162560996 | ||
|
|
ed0820f6c8 | ||
|
|
e148243260 | ||
|
|
8e56328e63 | ||
|
|
019677b7e6 | ||
|
|
0d31021c25 | ||
|
|
8e9ed2ebe3 | ||
|
|
763a34f19b | ||
|
|
be0462db56 | ||
|
|
6e55a2e52d | ||
|
|
4e127054ca | ||
|
|
27510bb963 | ||
|
|
de45e6094b | ||
|
|
74159de1ec | ||
|
|
ba92d864bb | ||
|
|
0fb14cfebe | ||
|
|
2ada6fc58d | ||
|
|
cb3355b30f | ||
|
|
10c6ffafc3 | ||
|
|
6512d5ce69 | ||
|
|
57fcc9148e | ||
|
|
36f4f23463 | ||
|
|
7b7dc71845 | ||
|
|
ba513d5a97 | ||
|
|
a26d03190e | ||
|
|
9f525621c8 | ||
|
|
7309d474ee | ||
|
|
45e86832c2 | ||
|
|
1bd91b23ca | ||
|
|
ac34380eb8 | ||
|
|
17707852e0 | ||
|
|
8b95218577 | ||
|
|
a79d23c631 | ||
|
|
52c81ad525 | ||
|
|
8ec836737e | ||
|
|
e4a90294ea | ||
|
|
7c8d562f03 | ||
|
|
11c3a65e63 | ||
|
|
8dd5e4dc24 | ||
|
|
9bd9e7a986 | ||
|
|
66e00f8172 | ||
|
|
b95e25e937 | ||
|
|
5722c530a1 | ||
|
|
267c23616d | ||
|
|
19f8cbcf76 | ||
|
|
aee3ee21d1 | ||
|
|
ff82bb5661 | ||
|
|
8a78134b72 | ||
|
|
1dbb29e847 | ||
|
|
2077da8665 | ||
|
|
b2751f75d5 | ||
|
|
1afd221795 | ||
|
|
aeb4df894a | ||
|
|
f91c19e1fd | ||
|
|
bcd277eaaa | ||
|
|
da35afbd8f | ||
|
|
cafc13a7d5 | ||
|
|
2b6bff3c1d | ||
|
|
95f499d2bd | ||
|
|
6659fd1b97 | ||
|
|
45b02d8827 | ||
|
|
59cde0dbb3 | ||
|
|
1aece399f7 | ||
|
|
c3589ded08 | ||
|
|
c7fbd76dae | ||
|
|
6b9c796218 | ||
|
|
5cb49c3307 | ||
|
|
f41bb05c70 | ||
|
|
c68189788c | ||
|
|
e603c83f55 | ||
|
|
edfa85bcd5 | ||
|
|
b86d4c647f | ||
|
|
4884f0d297 | ||
|
|
f1db24e303 | ||
|
|
7f15147286 | ||
|
|
e0a6db7f97 | ||
|
|
0d7d3e5c92 | ||
|
|
8b49402e4c | ||
|
|
347464250e | ||
|
|
aa02801c3d | ||
|
|
a3ee07f693 | ||
|
|
511908a964 | ||
|
|
425576be25 | ||
|
|
92f458dad2 | ||
|
|
043a91d719 | ||
|
|
54e2d7fb38 | ||
|
|
321e97f9fe | ||
|
|
4e0dfd410d | ||
|
|
8506385ef9 | ||
|
|
e74952902e | ||
|
|
4a51f4d2c1 | ||
|
|
2c283bcc08 | ||
|
|
a2e9bcd333 | ||
|
|
33d53121a2 | ||
|
|
e0b201c810 | ||
|
|
a8000f644f | ||
|
|
7d0e909a30 | ||
|
|
b2662eeb1f | ||
|
|
0b274dd67e | ||
|
|
2ddd50edc4 | ||
|
|
0287acb8f0 | ||
|
|
10c94b3665 | ||
|
|
ea48ca377e | ||
|
|
6f5d86ed84 | ||
|
|
c383f391e3 | ||
|
|
8a91a7adbb | ||
|
|
96181d91a6 | ||
|
|
eff5129a5f | ||
|
|
38e5adc462 | ||
|
|
ff4ea1eecc | ||
|
|
dbfd1beed5 | ||
|
|
4b6774463e | ||
|
|
cb14b97a6e | ||
|
|
18bc4b708c | ||
|
|
6d951e6987 | ||
|
|
365660764d | ||
|
|
8b91af8a5b | ||
|
|
b4092f59ae | ||
|
|
7a768144ea | ||
|
|
3839eb5ab0 | ||
|
|
fd02bee0fe | ||
|
|
42222cd2f6 | ||
|
|
e3222f2ac3 | ||
|
|
35f961fecb | ||
|
|
85bfca79ef | ||
|
|
661a4a099d | ||
|
|
72c0534008 | ||
|
|
78579ed2bd | ||
|
|
7bcb4ba1cc | ||
|
|
6b45cf3197 | ||
|
|
73d0b209d7 | ||
|
|
c93752bdbb | ||
|
|
7a4dd5890e | ||
|
|
60ee55fcaa | ||
|
|
1fe9790d0d | ||
|
|
3c0853a675 | ||
|
|
2b941b7e2c | ||
|
|
db772a058c | ||
|
|
0bfbf9c750 | ||
|
|
5c7647f45b | ||
|
|
6c952875e8 | ||
|
|
af7e12aa2f | ||
|
|
bcc506b423 | ||
|
|
3d7c8277d7 | ||
|
|
a8a2dc2347 | ||
|
|
6c74b0326b | ||
|
|
f51af92491 | ||
|
|
77528a1e7d | ||
|
|
ba8b8e8330 | ||
|
|
23f9a32a99 | ||
|
|
0190eb8b28 | ||
|
|
f482fdcfd5 | ||
|
|
ed4766188d | ||
|
|
e682cb1b04 | ||
|
|
36fda30c61 | ||
|
|
fa7cc376d1 | ||
|
|
3fc2ff1ef9 | ||
|
|
1d81eef805 | ||
|
|
8fcfac61b5 | ||
|
|
0d544dacdb | ||
|
|
147b50e719 | ||
|
|
eeb689dd55 | ||
|
|
c2571cfdb6 | ||
|
|
12c812d379 | ||
|
|
bf106db6e2 | ||
|
|
18009349c0 | ||
|
|
89b6055d61 | ||
|
|
d9a8869132 | ||
|
|
9d5c0d350c | ||
|
|
4dedd6e267 | ||
|
|
276213193b | ||
|
|
553bb4b530 | ||
|
|
5083525189 | ||
|
|
e4185259b4 | ||
|
|
5323d76a5b | ||
|
|
608387084c | ||
|
|
9556d1bd42 | ||
|
|
a6bf05815c | ||
|
|
a4deaf07d6 | ||
|
|
4adf01ab04 | ||
|
|
1abcdf96fa | ||
|
|
3456b5f6a7 | ||
|
|
d053778bf2 | ||
|
|
fbad39a120 | ||
|
|
e8d1d369cf | ||
|
|
fbea52416c | ||
|
|
cb9a20fefa | ||
|
|
8db9664700 | ||
|
|
08add653c7 | ||
|
|
eed9676536 | ||
|
|
22480a7648 | ||
|
|
aa2073f9e9 | ||
|
|
e0618f81a5 | ||
|
|
ea90018979 | ||
|
|
5a4074e90a | ||
|
|
0e9bbecbee | ||
|
|
c8a1ccaf4b | ||
|
|
79f4907cb3 | ||
|
|
6a0fffe002 | ||
|
|
6e116a76fd | ||
|
|
f52607f3b5 | ||
|
|
f716122eab | ||
|
|
353c2b0be2 | ||
|
|
58bbbbd395 | ||
|
|
57b072edfc | ||
|
|
f6039246c6 | ||
|
|
fcee13b017 | ||
|
|
ef5197a514 | ||
|
|
7438812db3 | ||
|
|
48af78278d | ||
|
|
3abc2e8328 | ||
|
|
a48043c2aa | ||
|
|
7e4f50a01c | ||
|
|
40d3078bf2 | ||
|
|
662334abfb | ||
|
|
aa5ad47177 | ||
|
|
890c21dda4 | ||
|
|
c7635b2783 | ||
|
|
47cd5f4d01 | ||
|
|
0d98b4b96f | ||
|
|
a20cf70105 | ||
|
|
23c7ab2bc4 | ||
|
|
0680e0c58b | ||
|
|
b3df253880 | ||
|
|
a78b44d0c1 | ||
|
|
d272a1fd22 | ||
|
|
095e4402ac | ||
|
|
60d2def428 | ||
|
|
2f02b3a6e1 | ||
|
|
0886e4e972 | ||
|
|
4f0ddcf632 | ||
|
|
693621a6e3 | ||
|
|
5b201392cc | ||
|
|
a70bcf81c0 | ||
|
|
ed880d5018 | ||
|
|
ea84e82ad5 | ||
|
|
4216d69ccb | ||
|
|
550a40d6a2 | ||
|
|
dcad5003f5 | ||
|
|
bd9c06a99d | ||
|
|
48932ef54d | ||
|
|
261f6dc20d | ||
|
|
4aeefc5a1a | ||
|
|
e96ff90029 | ||
|
|
f6e77b845b | ||
|
|
a0bb02d05a | ||
|
|
354ad7092c | ||
|
|
f9d862d854 | ||
|
|
f41576dd65 | ||
|
|
ffa20aa7d0 | ||
|
|
f7a2cf96b9 | ||
|
|
cfeac79b99 | ||
|
|
821bed0ea6 | ||
|
|
1a20390454 | ||
|
|
9e9111666b | ||
|
|
5065322d31 | ||
|
|
ad4796cdb2 | ||
|
|
43b7ba82da | ||
|
|
3785c79ac9 | ||
|
|
4384e9eb0e | ||
|
|
9364f8da2e | ||
|
|
a4ef359660 | ||
|
|
848c05f247 | ||
|
|
ec556360b6 | ||
|
|
d99b426e3b | ||
|
|
19a78297b4 | ||
|
|
e95eea694c | ||
|
|
4c6aaafe88 | ||
|
|
dc8c099d9e | ||
|
|
259ae674a1 | ||
|
|
731f023c6d | ||
|
|
86b19d4c74 | ||
|
|
17b8c29799 | ||
|
|
29af2849ba | ||
|
|
a7ac5efd70 | ||
|
|
15c7a9dcf8 | ||
|
|
8e55a2a866 | ||
|
|
0f306da63b | ||
|
|
ba9ea5c752 | ||
|
|
53b7d6f89f | ||
|
|
f5fb095df4 | ||
|
|
721919fae9 | ||
|
|
d3e27e87fe | ||
|
|
e1ff92e8c6 | ||
|
|
ac5d744914 | ||
|
|
b94a265fad | ||
|
|
1ba3a92745 | ||
|
|
9814fd705e | ||
|
|
20455f4fc2 | ||
|
|
9f37bf7397 | ||
|
|
892b884745 | ||
|
|
e8dd0a7daf | ||
|
|
26151e39c9 | ||
|
|
453e331014 | ||
|
|
7f72006020 | ||
|
|
3c13df3c2d | ||
|
|
d31af813e2 | ||
|
|
a85dc66a39 | ||
|
|
9492f0ae29 | ||
|
|
51149c75ff | ||
|
|
56bedb821f | ||
|
|
d3bca574aa | ||
|
|
c462bf229f | ||
|
|
8a452c42af | ||
|
|
07f2d74dc3 | ||
|
|
2ce65dc1e0 | ||
|
|
37be06448c | ||
|
|
9c13089a2f | ||
|
|
b642cb2d93 | ||
|
|
9e5d521567 | ||
|
|
6eabc99e01 | ||
|
|
ea917dd811 | ||
|
|
070d8e1731 | ||
|
|
664c60d2bc | ||
|
|
e25814e1ee | ||
|
|
27ea117731 | ||
|
|
7ab156e117 | ||
|
|
f2d415663f | ||
|
|
bdf08a19d1 |
@@ -11,3 +11,4 @@
|
||||
playwright.config.ts
|
||||
jest.config.js
|
||||
test/live-preview/next-app
|
||||
tsconfig.tsbuildinfo
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,6 +9,7 @@ module.exports = {
|
||||
rules: {
|
||||
'payload/no-jsx-import-statements': 'warn',
|
||||
'payload/no-relative-monorepo-imports': 'error',
|
||||
'payload/no-imports-from-exports-dir': 'error',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -30,6 +31,12 @@ module.exports = {
|
||||
'perfectionist/sort-objects': 'off',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
files: ['templates/vercel-postgres/**'],
|
||||
rules: {
|
||||
'no-restricted-exports': 'off',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
files: ['package.json', 'tsconfig.json'],
|
||||
rules: {
|
||||
|
||||
13
.github/CODEOWNERS
vendored
13
.github/CODEOWNERS
vendored
@@ -3,22 +3,19 @@
|
||||
### Package Exports ###
|
||||
/**/exports/ @denolfe @jmikrut
|
||||
|
||||
### Adapters ###
|
||||
### Packages ###
|
||||
/packages/richtext-*/ @AlessioGr
|
||||
|
||||
### Plugins ###
|
||||
/packages/plugin-cloud*/ @denolfe
|
||||
/packages/email-*/ @denolfe
|
||||
/packages/storage-*/ @denolfe
|
||||
/packages/create-payload-app/ @denolfe
|
||||
/packages/eslint-*/ @denolfe
|
||||
|
||||
### Templates ###
|
||||
/templates/ @jacobsfletch @denolfe
|
||||
|
||||
### Misc ###
|
||||
/packages/create-payload-app/ @denolfe
|
||||
/packages/eslint-*/ @denolfe
|
||||
|
||||
### Build Files ###
|
||||
/**/package.json @denolfe
|
||||
|
||||
/tsconfig.json @denolfe
|
||||
/**/tsconfig*.json @denolfe
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
48
.github/actions/setup/action.yml
vendored
Normal file
48
.github/actions/setup/action.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
name: Setup node and pnpm
|
||||
description: Configure the Node.js and pnpm versions
|
||||
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
node-version:
|
||||
description: 'The Node.js version to use'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
default: 18.20.2
|
||||
pnpm-version:
|
||||
description: 'The pnpm version to use'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
default: 8.15.7
|
||||
|
||||
runs:
|
||||
using: composite
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# https://github.com/actions/virtual-environments/issues/1187
|
||||
- name: tune linux network
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: sudo ethtool -K eth0 tx off rx off
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup Node@${{ inputs.node-version }}
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
node-version: ${{ inputs.node-version }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install pnpm
|
||||
uses: pnpm/action-setup@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
version: ${{ inputs.pnpm-version }}
|
||||
run_install: false
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get pnpm store directory
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "STORE_PATH=$(pnpm store path --silent)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup pnpm cache
|
||||
uses: actions/cache@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: ${{ env.STORE_PATH }}
|
||||
key: pnpm-store-${{ hashFiles('**/pnpm-lock.yaml') }}
|
||||
restore-keys: |
|
||||
pnpm-store-
|
||||
pnpm-store-${{ hashFiles('**/pnpm-lock.yaml') }}
|
||||
|
||||
- shell: bash
|
||||
run: pnpm install
|
||||
50
.github/workflows/label-author.yml
vendored
Normal file
50
.github/workflows/label-author.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
name: label-author
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
types: [opened]
|
||||
issues:
|
||||
types: [opened]
|
||||
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
contents: read
|
||||
pull-requests: write
|
||||
issues: write
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
debug-context:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: View context attributes
|
||||
uses: actions/github-script@v7
|
||||
with:
|
||||
script: console.log(context)
|
||||
|
||||
label-created-by:
|
||||
name: Label pr/issue on opening
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Tag with 'created-by'
|
||||
uses: actions/github-script@v7
|
||||
if: github.event.action == 'opened'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
github-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
script: |
|
||||
const type = context.payload.pull_request ? 'pull_request' : 'issue';
|
||||
const association = context.payload[type].author_association;
|
||||
let label = ''
|
||||
if (association === 'MEMBER' || association === 'OWNER') {
|
||||
label = 'created-by: Payload team';
|
||||
} else if (association === 'CONTRIBUTOR') {
|
||||
label = 'created-by: Contributor';
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!label) return;
|
||||
|
||||
github.rest.issues.addLabels({
|
||||
issue_number: context.issue.number,
|
||||
owner: context.repo.owner,
|
||||
repo: context.repo.repo,
|
||||
labels: [label],
|
||||
});
|
||||
console.log('Added created-by: Payload team label');
|
||||
123
.github/workflows/main.yml
vendored
123
.github/workflows/main.yml
vendored
@@ -2,12 +2,18 @@ name: build
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
types: [opened, reopened, synchronize]
|
||||
types:
|
||||
- opened
|
||||
- reopened
|
||||
- synchronize
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches: ['main', 'beta']
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
- beta
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.ref }}
|
||||
# <workflow_name>-<branch_name>-<true || commit_sha if branch is protected>
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.ref }}-${{ github.ref_protected && github.sha || ''}}
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: true
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
@@ -49,6 +55,51 @@ jobs:
|
||||
echo "needs_build: ${{ steps.filter.outputs.needs_build }}"
|
||||
echo "templates: ${{ steps.filter.outputs.templates }}"
|
||||
|
||||
lint:
|
||||
if: >
|
||||
github.event_name == 'pull_request' && !contains(github.event.pull_request.title, 'no-lint') && !contains(github.event.pull_request.title, 'skip-lint')
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 0
|
||||
|
||||
# https://github.com/actions/virtual-environments/issues/1187
|
||||
- name: tune linux network
|
||||
run: sudo ethtool -K eth0 tx off rx off
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup Node@${{ env.NODE_VERSION }}
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
node-version: ${{ env.NODE_VERSION }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install pnpm
|
||||
uses: pnpm/action-setup@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
version: ${{ env.PNPM_VERSION }}
|
||||
run_install: false
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get pnpm store directory
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "STORE_PATH=$(pnpm store path --silent)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup pnpm cache
|
||||
uses: actions/cache@v4
|
||||
timeout-minutes: 720
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: ${{ env.STORE_PATH }}
|
||||
key: pnpm-store-${{ hashFiles('**/pnpm-lock.yaml') }}
|
||||
restore-keys: |
|
||||
pnpm-store-
|
||||
pnpm-store-${{ hashFiles('**/pnpm-lock.yaml') }}
|
||||
|
||||
- run: pnpm install
|
||||
- name: Lint staged
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git diff --name-only --diff-filter=d origin/${GITHUB_BASE_REF}...${GITHUB_SHA}
|
||||
npx lint-staged --diff="origin/${GITHUB_BASE_REF}...${GITHUB_SHA}"
|
||||
|
||||
build:
|
||||
needs: changes
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.changes.outputs.needs_build == 'true' }}
|
||||
@@ -239,7 +290,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
suite:
|
||||
- _community
|
||||
- access-control
|
||||
- admin
|
||||
- admin__e2e__1
|
||||
- admin__e2e__2
|
||||
- auth
|
||||
- field-error-states
|
||||
- fields-relationship
|
||||
@@ -248,9 +300,17 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- fields__collections__Array
|
||||
- fields__collections__Relationship
|
||||
- fields__collections__RichText
|
||||
- fields__collections__Lexical
|
||||
- fields__collections__Lexical__e2e__main
|
||||
- fields__collections__Lexical__e2e__blocks
|
||||
- fields__collections__Date
|
||||
- fields__collections__Number
|
||||
- fields__collections__Point
|
||||
- fields__collections__Tabs
|
||||
- fields__collections__Text
|
||||
- fields__collections__Upload
|
||||
- live-preview
|
||||
- localization
|
||||
- i18n
|
||||
- plugin-cloud-storage
|
||||
- plugin-form-builder
|
||||
- plugin-nested-docs
|
||||
@@ -295,7 +355,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Cache Playwright Browsers for Playwright's Version
|
||||
id: cache-playwright-browsers
|
||||
uses: actions/cache@v3
|
||||
uses: actions/cache@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: ~/.cache/ms-playwright
|
||||
key: playwright-browsers-${{ env.PLAYWRIGHT_VERSION }}
|
||||
@@ -368,13 +428,12 @@ jobs:
|
||||
cd templates/blank-3.0
|
||||
cp .env.example .env
|
||||
ls -la
|
||||
pnpm add ./*.tgz
|
||||
pnpm install --ignore-workspace
|
||||
pnpm add ./*.tgz --ignore-workspace
|
||||
pnpm install --ignore-workspace --no-frozen-lockfile
|
||||
cat package.json
|
||||
pnpm run build
|
||||
|
||||
tests-type-generation:
|
||||
if: false # This should be replaced with gen on a real Payload project
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
needs: build
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -441,3 +500,49 @@ jobs:
|
||||
yarn install
|
||||
yarn build
|
||||
yarn generate:types
|
||||
|
||||
generated-templates:
|
||||
needs: build
|
||||
if: false # Needs to pull in tgz files from build
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# https://github.com/actions/virtual-environments/issues/1187
|
||||
- name: tune linux network
|
||||
run: sudo ethtool -K eth0 tx off rx off
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup Node@${{ env.NODE_VERSION }}
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
node-version: ${{ env.NODE_VERSION }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install pnpm
|
||||
uses: pnpm/action-setup@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
version: ${{ env.PNPM_VERSION }}
|
||||
run_install: false
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Restore build
|
||||
uses: actions/cache@v4
|
||||
timeout-minutes: 10
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: ./*
|
||||
key: ${{ github.sha }}-${{ github.run_number }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build all generated templates
|
||||
run: pnpm tsx ./scripts/build-generated-templates.ts
|
||||
|
||||
all-green:
|
||||
name: All Green
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
needs:
|
||||
- lint
|
||||
- build
|
||||
- tests-unit
|
||||
- tests-int
|
||||
- tests-e2e
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- if: ${{ always() && (contains(needs.*.result, 'failure') || contains(needs.*.result, 'cancelled')) }}
|
||||
run: exit 1
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/pr-title.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/pr-title.yml
vendored
@@ -66,7 +66,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
translations
|
||||
ui
|
||||
templates
|
||||
examples
|
||||
examples(\/(\w|-)+)?
|
||||
deps
|
||||
|
||||
# Disallow uppercase letters at the beginning of the subject
|
||||
|
||||
36
.github/workflows/release-canary.yml
vendored
Normal file
36
.github/workflows/release-canary.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
name: release-canary
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- beta
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
NODE_VERSION: 18.20.2
|
||||
PNPM_VERSION: 8.15.7
|
||||
DO_NOT_TRACK: 1 # Disable Turbopack telemetry
|
||||
NEXT_TELEMETRY_DISABLED: 1 # Disable Next telemetry
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
release:
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
id-token: write
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- name: Setup
|
||||
uses: ./.github/actions/setup
|
||||
with:
|
||||
node-version: ${{ env.NODE_VERSION }}
|
||||
pnpm-version: ${{ env.PNPM_VERSION }}
|
||||
- name: Load npm token
|
||||
run: echo "//registry.npmjs.org/:_authToken=$NPM_TOKEN" >> ~/.npmrc
|
||||
env:
|
||||
NPM_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NPM_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Canary release script
|
||||
# dry run hard-coded to true for testing and no npm token provided
|
||||
run: pnpm tsx ./scripts/publish-canary.ts
|
||||
env:
|
||||
NPM_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NPM_TOKEN }}
|
||||
NPM_CONFIG_PROVENANCE: true
|
||||
5
.gitignore
vendored
5
.gitignore
vendored
@@ -12,6 +12,11 @@ test-results
|
||||
.localstack
|
||||
.turbo
|
||||
|
||||
meta_client.json
|
||||
meta_server.json
|
||||
meta_index.json
|
||||
meta_shared.json
|
||||
|
||||
.turbo
|
||||
|
||||
# Ignore test directory media folder/files
|
||||
|
||||
28
.idea/payload.iml
generated
28
.idea/payload.iml
generated
@@ -47,6 +47,34 @@
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/templates" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/test/.swc" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/versions" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/richtext-slate/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/richtext-slate/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/email-nodemailer/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/email-nodemailer/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/email-resend/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/email-resend/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/live-preview-vue/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/live-preview-vue/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/payload/.swc" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/plugin-form-builder/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/plugin-relationship-object-ids/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/plugin-relationship-object-ids/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/plugin-stripe/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/storage-azure/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/storage-azure/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/storage-gcs/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/storage-gcs/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/storage-s3/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/storage-s3/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/storage-uploadthing/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/storage-uploadthing/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/storage-vercel-blob/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/storage-vercel-blob/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/translations/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/translations/dist" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/ui/.swc" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/ui/.turbo" />
|
||||
<excludeFolder url="file://$MODULE_DIR$/packages/ui/dist" />
|
||||
</content>
|
||||
<orderEntry type="inheritedJdk" />
|
||||
<orderEntry type="sourceFolder" forTests="false" />
|
||||
|
||||
9
.idea/runConfigurations/_template__of_JavaScriptTestRunnerJest.xml
generated
Normal file
9
.idea/runConfigurations/_template__of_JavaScriptTestRunnerJest.xml
generated
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
<component name="ProjectRunConfigurationManager">
|
||||
<configuration default="true" type="JavaScriptTestRunnerJest">
|
||||
<node-interpreter value="project" />
|
||||
<node-options value="--experimental-vm-modules --no-deprecation" />
|
||||
<envs />
|
||||
<scope-kind value="ALL" />
|
||||
<method v="2" />
|
||||
</configuration>
|
||||
</component>
|
||||
@@ -12,3 +12,5 @@
|
||||
tsconfig.json
|
||||
packages/payload/*.js
|
||||
packages/payload/*.d.ts
|
||||
payload-types.ts
|
||||
tsconfig.tsbuildinfo
|
||||
|
||||
9
.swcrc
9
.swcrc
@@ -7,6 +7,15 @@
|
||||
"syntax": "typescript",
|
||||
"tsx": true,
|
||||
"dts": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"transform": {
|
||||
"react": {
|
||||
"runtime": "automatic",
|
||||
"pragmaFrag": "React.Fragment",
|
||||
"throwIfNamespace": true,
|
||||
"development": false,
|
||||
"useBuiltins": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"module": {
|
||||
|
||||
22
.vscode/launch.json
vendored
22
.vscode/launch.json
vendored
@@ -16,6 +16,14 @@
|
||||
"request": "launch",
|
||||
"type": "node-terminal"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"command": "node --no-deprecation test/dev.js storage-uploadthing",
|
||||
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
|
||||
"name": "Uploadthing",
|
||||
"request": "launch",
|
||||
"type": "node-terminal",
|
||||
"envFile": "${workspaceFolder}/test/storage-uploadthing/.env"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"command": "node --no-deprecation test/dev.js live-preview",
|
||||
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
|
||||
@@ -58,6 +66,13 @@
|
||||
"PAYLOAD_PUBLIC_CLOUD_STORAGE_ADAPTER": "s3"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"command": "node --no-deprecation test/dev.js collections-graphql",
|
||||
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
|
||||
"name": "Run Dev GraphQL",
|
||||
"request": "launch",
|
||||
"type": "node-terminal"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"command": "node --no-deprecation test/dev.js fields",
|
||||
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
|
||||
@@ -96,6 +111,13 @@
|
||||
"request": "launch",
|
||||
"type": "node-terminal"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"command": "node --no-deprecation test/dev.js field-error-states",
|
||||
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
|
||||
"name": "Run Dev Field Error States",
|
||||
"request": "launch",
|
||||
"type": "node-terminal"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"command": "pnpm run test:int live-preview",
|
||||
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
|
||||
|
||||
6
.vscode/settings.json
vendored
6
.vscode/settings.json
vendored
@@ -41,5 +41,9 @@
|
||||
"source.fixAll.eslint": "explicit"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"files.insertFinalNewline": true
|
||||
"files.insertFinalNewline": true,
|
||||
"jestrunner.jestCommand": "pnpm exec cross-env NODE_OPTIONS=\"--experimental-vm-modules --no-deprecation\" node 'node_modules/jest/bin/jest.js'",
|
||||
"jestrunner.debugOptions": {
|
||||
"runtimeArgs": ["--experimental-vm-modules", "--no-deprecation"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
/* THIS FILE WAS GENERATED AUTOMATICALLY BY PAYLOAD. */
|
||||
import configPromise from '@payload-config'
|
||||
import { RootLayout } from '@payloadcms/next/layouts'
|
||||
// import '@payloadcms/ui/styles.css' // Uncomment this line if `@payloadcms/ui` in `tsconfig.json` points to `/ui/dist` instead of `/ui/src`
|
||||
/* DO NOT MODIFY IT BECAUSE IT COULD BE REWRITTEN AT ANY TIME. */
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Collection Access Control
|
||||
label: Collections
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
desc: With Collection-level Access Control you can define which users can create, read, update or delete Collections.
|
||||
keywords: collections, access control, permissions, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: collections, access control, permissions, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
You can define Collection-level Access Control within each Collection's `access` property. All Access Control functions accept one `args` argument.
|
||||
@@ -51,10 +51,10 @@ Returns a boolean which allows/denies access to the `create` request.
|
||||
|
||||
**Available argument properties:**
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`data`** | The data passed to create the document with. |
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`data`** | The data passed to create the document with. |
|
||||
|
||||
**Example:**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ Read access functions can return a boolean result or optionally return a [query
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| --------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`id`** | `id` of document requested, if within `findByID` |
|
||||
|
||||
**Example:**
|
||||
@@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ Update access functions can return a boolean result or optionally return a [quer
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`id`** | `id` of document requested to update |
|
||||
| **`data`** | The data passed to update the document with |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -138,7 +138,7 @@ Similarly to the Update function, returns a boolean or a [query constraint](/doc
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| --------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object with additional `user` property, which is the currently logged in user |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object with additional `user` property, which is the currently logged in user |
|
||||
| **`id`** | `id` of document requested to delete |
|
||||
|
||||
**Example:**
|
||||
@@ -173,7 +173,7 @@ If the Collection is [used to access the Payload Admin panel](/docs/admin/overvi
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| --------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
|
||||
### Unlock
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -183,4 +183,4 @@ Determines which users can [unlock](/docs/authentication/operations#unlock) othe
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| --------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Field-level Access Control
|
||||
label: Fields
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
desc: Field-level Access Control is specified within a field's config, and allows you to define which users can create, read or update Fields.
|
||||
keywords: fields, access control, permissions, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: fields, access control, permissions, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Field Access Control is specified with functions inside a field's config. All field-level Controls return a boolean value to allow or deny access for the specified operation. No field-level Access Controls support returning query constraints. All Access Control functions accept one `args` argument.
|
||||
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ Returns a boolean which allows or denies the ability to set a field's value when
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`data`** | The full data passed to create the document. |
|
||||
| **`siblingData`** | Immediately adjacent field data passed to create the document. |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -59,7 +59,7 @@ Returns a boolean which allows or denies the ability to read a field's value. If
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`id`** | `id` of the document being read |
|
||||
| **`doc`** | The full document data. |
|
||||
| **`siblingData`** | Immediately adjacent field data of the document being read. |
|
||||
@@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ If `false` is returned and you attempt to update the field's value, the operatio
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`id`** | `id` of the document being updated |
|
||||
| **`data`** | The full data passed to update the document. |
|
||||
| **`siblingData`** | Immediately adjacent field data passed to update the document with. |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,13 +3,11 @@ title: Globals Access Control
|
||||
label: Globals
|
||||
order: 40
|
||||
desc: Global-level Access Control is specified within each Global's `access` property and allows you to define which users can read or update Globals.
|
||||
keywords: globals, access control, permissions, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: globals, access control, permissions, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
You can define Global-level Access Control within each Global's `access` property. All Access Control functions accept one `args` argument.
|
||||
|
||||
\*\*Available argument properties:
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Controls
|
||||
|
||||
| Function | Allows/Denies Access |
|
||||
@@ -47,7 +45,7 @@ Returns a boolean result or optionally a [query constraint](/docs/queries/overvi
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| --------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
|
||||
### Update
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,5 +55,5 @@ Returns a boolean result or optionally a [query constraint](/docs/queries/overvi
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
|
||||
| **`data`** | The data passed to update the global with. |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Access Control
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: Payload makes it simple to define and manage access control. By declaring roles, you can set permissions and restrict what your users can interact with.
|
||||
keywords: overview, access control, permissions, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: overview, access control, permissions, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Access control within Payload is extremely powerful while remaining easy and intuitive to manage. Declaring who should have access to what documents is no more complex than writing a simple JavaScript function that either returns a `boolean` or a [`query`](/docs/queries/overview) constraint to restrict which documents users can interact with.
|
||||
@@ -19,9 +19,9 @@ Access control within Payload is extremely powerful while remaining easy and int
|
||||
- Restricting a `User` to only be able to see their own `Order`(s), but no others
|
||||
- Allowing `User`s that belong to a certain `Organization` to access only that `Organization`'s `Resource`s
|
||||
|
||||
### Default Settings
|
||||
## Default Settings
|
||||
|
||||
**By default, all Collections and Globals require that a user is logged in to be able to interact in any way.** The default Access Control function evaluates the `user` from the Express `req` and returns `true` if a user is logged in, and `false` if not.
|
||||
**By default, all Collections and Globals require that a user is logged in to be able to interact in any way.** The default Access Control function evaluates the `user` from the `req` and returns `true` if a user is logged in, and `false` if not.
|
||||
|
||||
**Default Access function:**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,13 +37,15 @@ const defaultPayloadAccess = ({ req: { user } }) => {
|
||||
<strong>Note:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
In the Local API, all Access Control functions are skipped by default, allowing your server to do
|
||||
whatever it needs. But, you can opt back in by setting the option <strong>
|
||||
whatever it needs. But, you can opt back in by setting the option
|
||||
<strong>
|
||||
overrideAccess
|
||||
</strong>{' '}
|
||||
</strong>
|
||||
{' '}
|
||||
to <strong>false</strong>.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Access Control Types
|
||||
## Access Control Types
|
||||
|
||||
You can manage access within Payload on three different levels:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -51,7 +53,7 @@ You can manage access within Payload on three different levels:
|
||||
- [Fields](/docs/access-control/fields)
|
||||
- [Globals](/docs/access-control/globals)
|
||||
|
||||
### When Access Control is Executed
|
||||
## When Access Control is Executed
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
<strong>Note:</strong>
|
||||
@@ -60,17 +62,17 @@ You can manage access within Payload on three different levels:
|
||||
your access control is executed.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
#### As you execute operations
|
||||
### As you execute operations
|
||||
|
||||
When you perform Payload operations like `create`, `read`, `update`, and `delete`, your access control functions will be executed before any changes or operations are completed.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Within the Admin UI
|
||||
### Within the Admin UI
|
||||
|
||||
The Payload Admin UI responds dynamically to the access control that you define. For example, if you restrict editing a `ExampleCollection` to only users that feature a `role` of `admin`, the Payload Admin UI will **hide** the `ExampleCollection` from the Admin UI entirely. This is super powerful and allows you to control who can do what with your Admin UI.
|
||||
|
||||
To accomplish this, Payload ships with an `Access` operation, which is executed when a user logs into the Admin UI. Payload will execute each one of your access control functions, across all collections, globals, and fields, at the top level and return a response that contains a reflection of what the currently authenticated user can do with your application.
|
||||
|
||||
### Argument Availability
|
||||
## Argument Availability
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Important:</strong>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,54 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Bundlers
|
||||
label: Bundlers
|
||||
order: 60
|
||||
desc: Bundlers are used to bundle the code that serves Payload's Admin Panel.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload has two official bundlers, the [Webpack Bundler](/docs/admin/webpack) and the [Vite Bundler](/docs/admin/vite). You must install a bundler to use the admin panel.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Install a bundler
|
||||
|
||||
Webpack (recommended):
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
yarn add @payloadcms/bundler-webpack
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Vite (beta):
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
yarn add @payloadcms/bundler-vite
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### Configure the bundler
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { webpackBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-webpack'
|
||||
// import { viteBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-vite'
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
// highlight-start
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
bundler: webpackBundler(), // or viteBundler()
|
||||
},
|
||||
// highlight-end
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### What are bundlers?
|
||||
|
||||
At their core, a bundler's main goal is to take a bunch of files and turn them into a few optimized files that you ship to the browser. The admin UI has a root `index.html` entry point, and from there the bundler traverses the dependency tree, bundling all of the files that are required from that point on.
|
||||
|
||||
Since the bundled file is sent to the browser, it can't include any server-only code. You will need to remove any server-only code from your admin UI before bundling it. You can learn more about [excluding server code](/docs/admin/excluding-server-code) section.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Using environment variables in the admin UI</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
Bundles should not contain sensitive information. By default, Payload excludes env variables from
|
||||
the bundle. If you need to use env variables in your payload config, you need to prefix them with
|
||||
`PAYLOAD_PUBLIC_` to make them available to the client-side code.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
@@ -3,12 +3,16 @@ title: Swap in your own React components
|
||||
label: Custom Components
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
desc: Fully customize your Admin Panel by swapping in your own React components. Add fields, remove views, update routes and change functions to sculpt your perfect Dashboard.
|
||||
keywords: admin, components, custom, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: admin, components, custom, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
While designing the Payload Admin panel, we determined it should be as minimal and straightforward as possible to allow easy customization and control. There are many times where you may want to completely control how a whole view or a field works. You might even want to add in new views entirely. In order for Payload to support this level of customization without introducing versioning / future-proofing issues, Payload provides for a pattern to supply your own React components via your Payload config.
|
||||
The [Payload Admin](./overview) panel is designed to be as minimal and straightforward as possible to allow easy customization and control. In order for Payload to support this level of customization without introducing versioning or future-proofing issues, Payload provides a pattern for you to supply your own React components via your Payload config.
|
||||
|
||||
To swap in your own React component, first, consult the list of available component overrides below. Determine the scope that corresponds to what you are trying to accomplish, and then author your React component accordingly.
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
All Custom Components in the Admin Panel are [React Server Components](https://react.dev/reference/rsc/server-components). This means they are rendered on the server
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
To swap in your own React component, first, consult the list of available components below. Determine the scope that corresponds to what you are trying to accomplish, and then author your React component accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
<strong>Tip:</strong>
|
||||
@@ -17,12 +21,12 @@ To swap in your own React component, first, consult the list of available compon
|
||||
normally accepts.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Base Component Overrides
|
||||
## Base Component Overrides
|
||||
|
||||
You can override a set of admin panel-wide components by providing a component to your base Payload config's `admin.components` property. The following options are available:
|
||||
|
||||
| Path | Description |
|
||||
| --------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
|-----------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **`Nav`** | Contains the sidebar / mobile menu in its entirety. |
|
||||
| **`BeforeNavLinks`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Nav, _before_ the links themselves. |
|
||||
| **`AfterNavLinks`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Nav, _after_ the links. |
|
||||
@@ -33,9 +37,9 @@ You can override a set of admin panel-wide components by providing a component t
|
||||
| **`logout.Button`** | A custom React component. |
|
||||
| **`graphics.Icon`** | Used as a graphic within the `Nav` component. Often represents a condensed version of a full logo. |
|
||||
| **`graphics.Logo`** | The full logo to be used in contexts like the `Login` view. |
|
||||
| **`providers`** | Define your own provider components that will wrap the Payload Admin UI. [More](#custom-providers) |
|
||||
| **`actions`** | Array of custom components to be rendered in the Payload Admin UI header, providing additional interactivity and functionality. |
|
||||
| **`views`** | Override or create new views within the Payload Admin UI. [More](#views) |
|
||||
| **`providers`** | Define your own provider components that will wrap the [Admin Panel](./overview). [More](#custom-providers) |
|
||||
| **`actions`** | Array of custom components to be rendered in the [Admin Panel](./overview) header, providing additional interactivity and functionality. |
|
||||
| **`views`** | Override or create new [Views](./views) within the [Admin Panel](./overview). |
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a full example showing how to swap some of these components for your own.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -73,79 +77,7 @@ export default buildConfig({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Views
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily swap entire views with your own by using the `admin.components.views` property. At the root level, Payload renders the following views by default, all of which can be overridden:
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| --------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Account`** | The Account view is used to show the currently logged in user's Account page. |
|
||||
| **`Dashboard`** | The main landing page of the Admin panel. |
|
||||
|
||||
To swap out any of these views, simply pass in your custom component to the `admin.components.views` property of your Payload config. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Account: MyCustomAccountView,
|
||||
Dashboard: MyCustomDashboardView,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more granular control, pass a configuration object instead. Each view corresponds to its own `<Route />` component in [React Router v5](https://v5.reactrouter.com). Payload exposes all of the properties of React Router:
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Component`** \* | Pass in the component that should be rendered when a user navigates to this route. |
|
||||
| **`path`** \* | React Router `path`. [See the React Router docs](https://v5.reactrouter.com/web/api/Route/path-string-string) for more info. |
|
||||
| **`exact`** | React Router `exact` property. [More](https://v5.reactrouter.com/web/api/Route/exact-bool) |
|
||||
| **`strict`** | React Router `strict` property. [More](https://v5.reactrouter.com/web/api/Route/strict-bool) |
|
||||
| **`sensitive`** | React Router `sensitive` property. [More](https://v5.reactrouter.com/web/api/Route/sensitive-bool) |
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
#### Adding new views
|
||||
|
||||
To add a _new_ view to the Admin Panel, simply add another key to the `views` object with at least a `path` and `Component` property. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
MyCustomView: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomView,
|
||||
path: '/my-custom-view',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Note:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
Routes are cascading. This means that unless explicitly given the `exact` property, they will
|
||||
match on URLs that simply _start_ with the route's path. This is helpful when creating catch-all
|
||||
routes in your application. Alternatively, you could define your nested route _before_ your parent
|
||||
route.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
_For more examples regarding how to customize components, look at the following [examples](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/test/admin/components)._
|
||||
|
||||
For help on how to build your own custom view components, see [building a custom view component](#building-a-custom-view-component).
|
||||
|
||||
### Collections
|
||||
## Collections
|
||||
|
||||
You can override components on a collection-by-collection basis via the `admin.components` property.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -159,25 +91,33 @@ You can override components on a collection-by-collection basis via the `admin.c
|
||||
| **`edit.SaveDraftButton`** | Replace the default `Save Draft` button with a custom component. Drafts must be enabled and autosave must be disabled. |
|
||||
| **`edit.PublishButton`** | Replace the default `Publish` button with a custom component. Drafts must be enabled. |
|
||||
| **`edit.PreviewButton`** | Replace the default `Preview` button with a custom component. |
|
||||
| **`views`** | Override or create new views within the Payload Admin UI. [More](#collection-views) |
|
||||
| **`views`** | Override or create new [Views](./views) within the [Admin Panel](./overview). |
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a full example showing how to swap some of these components for your own:
|
||||
|
||||
`Collection.ts`
|
||||
`CustomSaveButton.tsx`
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import * as React from 'react'
|
||||
import { CustomSaveButtonProps } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
import {
|
||||
CustomSaveButtonProps,
|
||||
CustomSaveDraftButtonProps,
|
||||
CustomPublishButtonProps,
|
||||
CustomPreviewButtonProps,
|
||||
} from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
export const CustomSaveButton: CustomSaveButtonProps = ({ DefaultButton, label, save }) => {
|
||||
return <DefaultButton label={label} save={save} />
|
||||
const CustomSaveButton: CustomSaveButtonProps = ({
|
||||
DefaultButton,
|
||||
label,
|
||||
save
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<DefaultButton
|
||||
label={label}
|
||||
save={save}
|
||||
/>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`CustomSaveDraftButton.tsx`
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { CustomSaveDraftButtonProps } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
export const CustomSaveDraftButton: CustomSaveDraftButtonProps = ({
|
||||
DefaultButton,
|
||||
@@ -185,8 +125,20 @@ export const CustomSaveDraftButton: CustomSaveDraftButtonProps = ({
|
||||
label,
|
||||
saveDraft,
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return <DefaultButton label={label} disabled={disabled} saveDraft={saveDraft} />
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<DefaultButton
|
||||
label={label}
|
||||
disabled={disabled}
|
||||
saveDraft={saveDraft}
|
||||
/>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`CustomPublishButton.tsx`
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { CustomPreviewButtonProps } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
export const CustomPublishButton: CustomPublishButtonProps = ({
|
||||
DefaultButton,
|
||||
@@ -194,8 +146,20 @@ export const CustomPublishButton: CustomPublishButtonProps = ({
|
||||
label,
|
||||
publish,
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return <DefaultButton label={label} disabled={disabled} publish={publish} />
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<DefaultButton
|
||||
label={label}
|
||||
disabled={disabled}
|
||||
publish={publish}
|
||||
/>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`CustomPreviewButton`
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { CustomPreviewButtonProps } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
export const CustomPreviewButton: CustomPreviewButtonProps = ({
|
||||
DefaultButton,
|
||||
@@ -203,8 +167,25 @@ export const CustomPreviewButton: CustomPreviewButtonProps = ({
|
||||
label,
|
||||
preview,
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return <DefaultButton label={label} disabled={disabled} preview={preview} />
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<DefaultButton
|
||||
label={label}
|
||||
disabled={disabled}
|
||||
preview={preview}
|
||||
/>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`collection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import * as React from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
import { CustomSaveButton } from './CustomSaveButton'
|
||||
import { CustomSaveDraftButton } from './CustomSaveDraftButton'
|
||||
import { CustomPublishButton } from './CustomPublishButton'
|
||||
import { CustomPreviewButton } from './CustomPreviewButton'
|
||||
|
||||
export const MyCollection: SanitizedCollectionConfig = {
|
||||
slug: 'my-collection',
|
||||
@@ -221,83 +202,7 @@ export const MyCollection: SanitizedCollectionConfig = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Collection views
|
||||
|
||||
To swap out entire views on collections, you can use the `admin.components.views` property on the collection's config. Payload renders the following views by default, all of which can be overridden:
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Edit`** | The Edit view is used to edit a single document for a given collection. |
|
||||
| **`List`** | The List view is used to show a list of documents for a given collection. |
|
||||
|
||||
To swap out any of these views, simply pass in your custom component to the `admin.components.views` property of your Payload config. This will replace the entire view, including the page breadcrumbs, title, tabs, etc, _as well as all nested routes_.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Collection.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: MyCustomEditView,
|
||||
List: MyCustomListView,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
_For help on how to build your own custom view components, see [building a custom view component](#building-a-custom-view-component)._
|
||||
|
||||
**Customizing Nested Views within 'Edit' in Collections**
|
||||
|
||||
The `Edit` view in collections consists of several nested views, each serving a unique purpose. You can customize these nested views using the `admin.components.views.Edit` property in the collection's configuration. This approach allows you to replace specific nested views while keeping the overall structure of the `Edit` view intact, including the page breadcrumbs, title, tabs, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of how you can customize nested views within the `Edit` view in collections, including the use of the `actions` property:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Collection.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: {
|
||||
Default: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomDefaultTab,
|
||||
actions: [CollectionEditButton], // Custom actions for the default edit view
|
||||
},
|
||||
API: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomAPIView,
|
||||
actions: [CollectionAPIButton], // Custom actions for API view
|
||||
},
|
||||
LivePreview: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomLivePreviewView,
|
||||
actions: [CollectionLivePreviewButton], // Custom actions for Live Preview
|
||||
},
|
||||
Version: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomVersionView,
|
||||
actions: [CollectionVersionButton], // Custom actions for Version view
|
||||
},
|
||||
Versions: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomVersionsView,
|
||||
actions: [CollectionVersionsButton], // Custom actions for Versions view
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
List: {
|
||||
actions: [CollectionListButton],
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Adding New Tabs to 'Edit' View**
|
||||
|
||||
You can also add _new_ tabs to the `Edit` view by adding another key to the `components.views.Edit[key]` object with a `path` and `Component` property. See [Custom Tabs](#custom-tabs) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### Globals
|
||||
## Globals
|
||||
|
||||
As with Collections, you can override components on a global-by-global basis via the `admin.components` property.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -307,368 +212,18 @@ As with Collections, you can override components on a global-by-global basis via
|
||||
| **`elements.SaveDraftButton`** | Replace the default `Save Draft` button with a custom component. Drafts must be enabled and autosave must be disabled. |
|
||||
| **`elements.PublishButton`** | Replace the default `Publish` button with a custom component. Drafts must be enabled. |
|
||||
| **`elements.PreviewButton`** | Replace the default `Preview` button with a custom component. |
|
||||
| **`views`** | Override or create new views within the Payload Admin UI. [More](#global-views) |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Global views
|
||||
|
||||
To swap out views for globals, you can use the `admin.components.views` property on the global's config. Payload renders the following views by default, all of which can be overridden:
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Edit`** | The Edit view is used to edit a single document for a given Global. |
|
||||
|
||||
To swap out any of these views, simply pass in your custom component to the `admin.components.views` property of your Payload config. This will replace the entire view, including the page breadcrumbs, title, and tabs, _as well as all nested views_.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Global.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: MyCustomEditView,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
_For help on how to build your own custom view components, see [building a custom view component](#building-a-custom-view-component)._
|
||||
|
||||
**Customizing Nested Views within 'Edit' in Globals**
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to collections, Globals allow for detailed customization within the `Edit` view. This includes the ability to swap specific nested views while maintaining the overall structure of the `Edit` view. You can use the `admin.components.views.Edit` property in the Globals configuration to achieve this, and this will only replace the nested view, leaving the page breadcrumbs, title, and tabs intact.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how you can customize nested views within the `Edit` view in Globals, including the use of the `actions` property:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Global.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: {
|
||||
Default: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomGlobalDefaultTab,
|
||||
actions: [GlobalEditButton], // Custom actions for the default edit view
|
||||
},
|
||||
API: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomGlobalAPIView,
|
||||
actions: [GlobalAPIButton], // Custom actions for API view
|
||||
},
|
||||
LivePreview: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomGlobalLivePreviewView,
|
||||
actions: [GlobalLivePreviewButton], // Custom actions for Live Preview
|
||||
},
|
||||
Version: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomGlobalVersionView,
|
||||
actions: [GlobalVersionButton], // Custom actions for Version view
|
||||
},
|
||||
Versions: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomGlobalVersionsView,
|
||||
actions: [GlobalVersionsButton], // Custom actions for Versions view
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also add _new_ tabs to the `Edit` view by adding another key to the `components.views.Edit[key]` object with a `path` and `Component` property. See [Custom Tabs](#custom-tabs) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Tabs
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily swap individual collection or global edit views. To do this, pass an _object_ to the `admin.components.views.Edit` property of the config. Payload renders the following views by default, all of which can be overridden:
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Default`** | The Default view is the primary view in which your document is edited. |
|
||||
| **`Versions`** | The Versions view is used to view the version history of a single document. [More details](../versions) |
|
||||
| **`Version`** | The Version view is used to view a single version of a single document for a given collection. [More details](../versions). |
|
||||
| **`API`** | The API view is used to display the REST API JSON response for a given document. |
|
||||
| **`LivePreview`** | The LivePreview view is used to display the Live Preview interface. [More details](../live-preview) |
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Collection.ts or Global.ts
|
||||
export const MyCollection: SanitizedCollectionConfig = {
|
||||
slug: 'my-collection',
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: {
|
||||
// You can also define `components.views.Edit` as a component, this will override _all_ nested views
|
||||
Default: MyCustomDefaultTab,
|
||||
Versions: MyCustomVersionsTab,
|
||||
Version: MyCustomVersionTab,
|
||||
API: MyCustomAPITab,
|
||||
LivePreview: MyCustomLivePreviewTab,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To add a _new_ tab to the `Edit` view, simply add another key to `components.views.Edit[key]` with at least a `path` and `Component` property. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// `Collection.ts` or `Global.ts`
|
||||
export const MyCollection: SanitizedCollectionConfig = {
|
||||
slug: 'my-collection',
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: {
|
||||
MyCustomTab: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomTab,
|
||||
path: '/my-custom-tab',
|
||||
// You an swap the entire tab component out for your own
|
||||
Tab: MyCustomTab,
|
||||
},
|
||||
AnotherCustomView: {
|
||||
Component: AnotherCustomView,
|
||||
path: '/another-custom-view',
|
||||
// Or you can use the default tab component and just pass in your own label and href
|
||||
Tab: {
|
||||
label: 'Another Custom View',
|
||||
href: '/another-custom-view',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Building a custom view component
|
||||
|
||||
Your custom view components will be given all the props that a React Router `<Route />` typically would receive, as well as two props from Payload:
|
||||
|
||||
| Prop | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`user`** | The currently logged in user. Will be `null` if no user is logged in. |
|
||||
| **`canAccessAdmin`** \* | If the currently logged in user is allowed to access the admin panel or not. |
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Note:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
It's up to you to secure your custom views. If your view requires a user to be logged in or to
|
||||
have certain access rights, you should handle that within your view component yourself.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
You can find examples of custom views in the [Payload source code `/test/admin/components/views` folder](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/test/admin/components/views). There, you'll find two custom views:
|
||||
|
||||
1. A custom view that uses the `DefaultTemplate`, which is the built-in Payload template that displays the sidebar and "eyebrow nav"
|
||||
1. A custom view that uses the `MinimalTemplate` - which is just a centered template used for things like logging in or out
|
||||
|
||||
To see how to pass in your custom views to create custom views of your own, take a look at the `admin.components.views` property of the [Payload test admin config](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/test/admin/config.ts).
|
||||
|
||||
### Fields
|
||||
|
||||
All Payload fields support the ability to swap in your own React components. So, for example, instead of rendering a default Text input, you might need to render a color picker that provides the editor with a custom color picker interface to restrict the data entered to colors only.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
<strong>Tip:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
Don't see a built-in field type that you need? Build it! Using a combination of custom validation
|
||||
and custom components, you can override the entirety of how a component functions within the admin
|
||||
panel and effectively create your own field type.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
**Fields support the following custom components:**
|
||||
|
||||
| Component | Description |
|
||||
| ------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Filter`** | Override the text input that is presented in the `List` view when a user is filtering documents by the customized field. |
|
||||
| **`Cell`** | Used in the `List` view's table to represent a table-based preview of the data stored in the field. [More](#cell-component) |
|
||||
| **`Field`** | Swap out the field itself within all `Edit` views. [More](#field-component) |
|
||||
|
||||
As an alternative to replacing the entire Field component, you may want to keep the majority of the default Field component and only swap components within. This allows you to replace the **`Label`** or **`Error`** within a field component or add additional components inside the field with **`beforeInput`** or **`afterInput`**. **`beforeInput`** and **`afterInput`** are allowed in any fields that don't contain other fields, except [UI](/docs/fields/ui) and [Rich Text](/docs/fields/rich-text).
|
||||
|
||||
| Component | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Label`** | Override the default Label in the Field Component. [More](#label-component) |
|
||||
| **`Error`** | Override the default Label in the Field Component. [More](#error-component) |
|
||||
| **`beforeInput`** | An array of elements that will be added before `input`/`textarea` elements. [More](#afterinput-and-beforeinput) |
|
||||
| **`afterInput`** | An array of elements that will be added after `input`/`textarea` elements. [More](#afterinput-and-beforeinput) |
|
||||
|
||||
## Cell Component
|
||||
|
||||
These are the props that will be passed to your custom Cell to use in your own components.
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`field`** | An object that includes the field configuration. |
|
||||
| **`colIndex`** | A unique number for the column in the list. |
|
||||
| **`collection`** | An object with the config of the collection that the field is in. |
|
||||
| **`cellData`** | The data for the field that the cell represents. |
|
||||
| **`rowData`** | An object with all the field values for the row. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
import type { Props } from 'payload/components/views/Cell'
|
||||
import './index.scss'
|
||||
|
||||
const baseClass = 'custom-cell'
|
||||
|
||||
const CustomCell: React.FC<Props> = (props) => {
|
||||
const { field, colIndex, collection, cellData, rowData } = props
|
||||
|
||||
return <span className={baseClass}>{cellData}</span>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Field Component
|
||||
|
||||
When writing your own custom components you can make use of a number of hooks to set data, get reactive changes to other fields, get the id of the document or interact with a context from a custom provider.
|
||||
|
||||
### Sending and receiving values from the form
|
||||
|
||||
When swapping out the `Field` component, you'll be responsible for sending and receiving the field's `value` from the form itself. To do so, import the `useField` hook as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { useField } from 'payload/components/forms'
|
||||
|
||||
const CustomTextField: React.FC<{ path: string }> = ({ path }) => {
|
||||
// highlight-start
|
||||
const { value, setValue } = useField<string>({ path })
|
||||
// highlight-end
|
||||
|
||||
return <input onChange={(e) => setValue(e.target.value)} value={value} />
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
For more information regarding the hooks that are available to you while you build custom
|
||||
components, including the <strong>useField</strong> hook, [click here](/docs/admin/hooks).
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
## Label Component
|
||||
|
||||
These are the props that will be passed to your custom Label.
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| -------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`htmlFor`** | Property used to set `for` attribute for label. |
|
||||
| **`label`** | Label value provided in field, it can be used with i18n. |
|
||||
| **`required`** | A boolean value that represents if the field is required or not. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next'
|
||||
|
||||
import { getTranslation } from 'payload/utilities/getTranslation'
|
||||
|
||||
type Props = {
|
||||
htmlFor?: string
|
||||
label?: Record<string, string> | false | string
|
||||
required?: boolean
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const CustomLabel: React.FC<Props> = (props) => {
|
||||
const { htmlFor, label, required = false } = props
|
||||
|
||||
const { i18n } = useTranslation()
|
||||
|
||||
if (label) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<span>
|
||||
{getTranslation(label, i18n)}
|
||||
{required && <span className="required">*</span>}
|
||||
</span>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return null
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Error Component
|
||||
|
||||
These are the props that will be passed to your custom Error.
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`message`** | The error message. |
|
||||
| **`showError`** | A boolean value that represents if the error should be shown. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
type Props = {
|
||||
message: string
|
||||
showError?: boolean
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const CustomError: React.FC<Props> = (props) => {
|
||||
const { message, showError } = props
|
||||
|
||||
if (showError) {
|
||||
return <p style={{ color: 'red' }}>{message}</p>
|
||||
} else return null
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## afterInput and beforeInput
|
||||
|
||||
With these properties you can add multiple components before and after the input element. For example, you can add an absolutely positioned button to clear the current field value.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
import { Field } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
import './style.scss'
|
||||
|
||||
const ClearButton: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<button
|
||||
onClick={() => {
|
||||
/* ... */
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
X
|
||||
</button>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const titleField: Field = {
|
||||
name: 'title',
|
||||
type: 'text',
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
afterInput: [ClearButton],
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default titleField
|
||||
```
|
||||
| **`views`** | Override or create new [Views](./views) within the [Admin Panel](./overview). |
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom providers
|
||||
|
||||
As your admin customizations gets more complex you may want to share state between fields or other components. You can add custom providers to do add your own context to any Payload app for use in other custom components within the admin panel. Within your config add `admin.components.providers`, these can be used to share context or provide other custom functionality. Read the [React context](https://reactjs.org/docs/context.html) docs to learn more.
|
||||
As your admin customizations gets more complex you may want to share state between fields or other components. You can add custom providers to do add your own context to any Payload app for use in other custom components within the [Admin Panel](./overview). Within your config add `admin.components.providers`, these can be used to share context or provide other custom functionality. See the [React Context](https://reactjs.org/docs/context.html) docs to learn more.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Reminder:</strong> Don't forget to pass the **children** prop through the provider
|
||||
component for the admin UI to show
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Styling Custom Components
|
||||
## Styling Custom Components
|
||||
|
||||
Payload exports its SCSS variables and mixins for reuse in your own custom components. This is helpful in cases where you might want to style a custom input similarly to Payload's built-ini styling, so it blends more thoroughly into the existing admin UI.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -678,23 +233,23 @@ To make use of Payload SCSS variables / mixins to use directly in your own compo
|
||||
@import '~payload/scss';
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting the current language
|
||||
## Getting the current language
|
||||
|
||||
When developing custom components you can support multiple languages to be consistent with Payload's i18n support. The best way to do this is to add your translation resources to the [i18n configuration](https://payloadcms.com/docs/configuration/i18n) and import `useTranslation` from `react-i18next` in your components.
|
||||
When developing custom components you can support multiple languages to be consistent with Payload's i18n support. The best way to do this is to add your translation resources to the [i18n configuration](https://payloadcms.com/docs/configuration/i18n) and import `useTranslation` from `@payloadcms/ui/providers/Translation` in your components.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next'
|
||||
import { useTranslation } from '@payloadcms/ui/providers/Translation'
|
||||
|
||||
const CustomComponent: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
// highlight-start
|
||||
const { t, i18n } = useTranslation('namespace1')
|
||||
const { t, i18n } = useTranslation()
|
||||
// highlight-end
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>{t('key', { variable: 'value' })}</li>
|
||||
<li>{t('namespace1:key', { variable: 'value' })}</li>
|
||||
<li>{t('namespace2:key', { variable: 'value' })}</li>
|
||||
<li>{i18n.language}</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -702,7 +257,7 @@ const CustomComponent: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting the current locale
|
||||
## Getting the current locale
|
||||
|
||||
In any custom component you can get the selected locale with `useLocale` hook. `useLocale` returns the full locale object, consisting of a `label`, `rtl`(right-to-left) property, and then `code`. Here is a simple example:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Customizing CSS & SCSS
|
||||
label: Customizing CSS
|
||||
order: 40
|
||||
order: 60
|
||||
desc: Customize your Payload admin panel further by adding your own CSS or SCSS style sheet to the configuration, powerful theme and design options are waiting for you.
|
||||
keywords: admin, css, scss, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: admin, css, scss, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding your own CSS / SCSS
|
||||
## Adding your own CSS / SCSS
|
||||
|
||||
You can add your own CSS by providing your base Payload config with a path to your own CSS or SCSS. Customize the styling of any part of the Payload dashboard as necessary.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ const config = buildConfig({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Overriding built-in styles
|
||||
## Overriding built-in styles
|
||||
|
||||
To make it as easy as possible for you to override our styles, Payload uses [BEM naming conventions](http://getbem.com/) for all CSS within the Admin UI. If you provide your own CSS, you can override any built-in styles easily.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ You can find the built-in Payload CSS variables within [`./src/admin/scss/app.sc
|
||||
- Fonts
|
||||
- Horizontal gutter
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dark mode
|
||||
### Dark mode
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
If you're overriding colors or theme elevations, make sure to consider how your changes will
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,206 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Excluding server-only code from admin UI
|
||||
label: Excluding server code
|
||||
order: 70
|
||||
desc: Learn how to exclude server-only code from the Payload Admin UI bundle
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Because the Admin Panel browser bundle includes your Payload Config file, files using server-only modules need to be excluded.
|
||||
It's common for your config to rely on server only modules to perform logic in access control functions, hooks, and other contexts.
|
||||
|
||||
Any file that imports a server-only module such as `fs`, `stripe`, `authorizenet`, `nodemailer`, etc. **cannot** be included in the browser bundle.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example Scenario
|
||||
|
||||
Say we have a collection called `Subscriptions` that has a `beforeChange` hook that creates a Stripe subscription whenever a Subscription document is created in Payload.
|
||||
|
||||
**Collection config**:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// collections/Subscriptions/index.ts
|
||||
|
||||
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
import createStripeSubscription from './hooks/createStripeSubscription'
|
||||
|
||||
export const Subscription: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
slug: 'subscriptions',
|
||||
hooks: {
|
||||
beforeChange: [createStripeSubscription],
|
||||
},
|
||||
fields: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'stripeSubscriptionID',
|
||||
type: 'text',
|
||||
required: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Collection hook**:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// collections/Subscriptions/hooks/createStripeSubscription.ts
|
||||
|
||||
// highlight-start
|
||||
import Stripe from 'stripe' // <-- server-only module
|
||||
// highlight-end
|
||||
|
||||
const stripe = new Stripe(process.env.STRIPE_SECRET_KEY)
|
||||
|
||||
export const createStripeSubscription = async ({ data, operation }) => {
|
||||
if (operation === 'create') {
|
||||
const dataWithStripeID = { ...data }
|
||||
|
||||
// use Stripe to create a Stripe subscription
|
||||
const subscription = await stripe.subscriptions.create({
|
||||
// Configure the subscription accordingly
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// Automatically add the Stripe subscription ID
|
||||
// to the data that will be saved to this Subscription doc
|
||||
dataWithStripeID.stripeSubscriptionID = subscription.id
|
||||
|
||||
return dataWithStripeID
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return data
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="error">
|
||||
<strong>Warning:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
The above code is NOT production-ready and should not be referenced to create Stripe
|
||||
subscriptions. Although creating a beforeChange hook is a completely valid spot to do things like
|
||||
create subscriptions, the code above is incomplete and insecure, meant for explanation purposes
|
||||
only.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
**As-is, this collection will prevent your Admin panel from bundling or loading correctly, because Stripe relies on some Node-only packages.**
|
||||
|
||||
#### How to fix this
|
||||
|
||||
You need to make sure that you use `alias`es to tell your bundler to import "safe" files vs. attempting to import any server-side code that you need to get rid of. Depending on your bundler (Webpack, Vite, etc.) the steps involved may be slightly different.
|
||||
|
||||
The basic idea is to create a file that exports an empty object, and then alias import paths of any files that import server-only modules to that empty object file.
|
||||
|
||||
This way when your bundler goes to import a file that contains server-only modules, it will instead import the empty object file, which will not break the browser bundle.
|
||||
|
||||
### Aliasing server-only modules
|
||||
|
||||
To remove files that contain server-only modules from your bundle, you can use an `alias`.
|
||||
|
||||
In the Subscriptions config file above, we are importing the hook like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// collections/Subscriptions/index.ts
|
||||
|
||||
import createStripeSubscription from './hooks/createStripeSubscription'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default the browser bundle will now include all the code from that file and any files down the tree. We know that the file imports `stripe`.
|
||||
|
||||
To fix this, we need to alias the `createStripeSubscription` file to a different file that can safely be included in the browser bundle.
|
||||
|
||||
First, we will create a mock file to replace the server-only file when bundling:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// mocks/modules.js
|
||||
|
||||
export default {}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* NOTE: if you are destructuring an import
|
||||
* the mock file will need to export matching
|
||||
* variables as the destructured object.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* export const namedExport = {}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Aliasing with [Webpack](/docs/admin/webpack) can be done by:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { webpackBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-webpack'
|
||||
|
||||
import { Subscriptions } from './collections/Subscriptions'
|
||||
|
||||
const mockModulePath = path.resolve(__dirname, 'mocks/emptyObject.js')
|
||||
const fullFilePath = path.resolve(
|
||||
__dirname,
|
||||
'collections/Subscriptions/hooks/createStripeSubscription',
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
collections: [Subscriptions],
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
bundler: webpackBundler(),
|
||||
webpack: (config) => {
|
||||
return {
|
||||
...config,
|
||||
resolve: {
|
||||
...config.resolve,
|
||||
// highlight-start
|
||||
alias: {
|
||||
...config.resolve.alias,
|
||||
[fullFilePath]: mockModulePath,
|
||||
},
|
||||
// highlight-end
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Aliasing with [Vite](/docs/admin/vite) can be done by:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { viteBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-vite'
|
||||
|
||||
import { Subscriptions } from './collections/Subscriptions'
|
||||
|
||||
const mockModulePath = path.resolve(__dirname, 'mocks/emptyObject.js')
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
collections: [Subscriptions],
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
bundler: viteBundler(),
|
||||
vite: (incomingViteConfig) => {
|
||||
const existingAliases = incomingViteConfig?.resolve?.alias || {}
|
||||
let aliasArray: { find: string | RegExp; replacement: string }[] = []
|
||||
|
||||
// Pass the existing Vite aliases
|
||||
if (Array.isArray(existingAliases)) {
|
||||
aliasArray = existingAliases
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
aliasArray = Object.values(existingAliases)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// highlight-start
|
||||
// Add your own aliases using the find and replacement keys
|
||||
// remember, vite aliases are exact-match only
|
||||
aliasArray.push({
|
||||
find: '../server-only-module',
|
||||
replacement: path.resolve(__dirname, './path/to/browser-safe-module.js'),
|
||||
})
|
||||
// highlight-end
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
...incomingViteConfig,
|
||||
resolve: {
|
||||
...(incomingViteConfig?.resolve || {}),
|
||||
alias: aliasArray,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
194
docs/admin/fields.mdx
Normal file
194
docs/admin/fields.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,194 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Customizing Fields
|
||||
label: Customizing Fields
|
||||
order: 40
|
||||
desc:
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
All Payload fields support the ability to swap in your own React components. So, for example, instead of rendering a default Text input, you might need to render a color picker that provides the editor with a custom color picker interface to restrict the data entered to colors only.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
<strong>Tip:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
Don't see a built-in field type that you need? Build it! Using a combination of custom validation
|
||||
and custom components, you can override the entirety of how a component functions within the admin
|
||||
panel and effectively create your own field type.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
**Fields support the following custom components:**
|
||||
|
||||
| Component | Description |
|
||||
| ------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Filter`** | Override the text input that is presented in the `List` view when a user is filtering documents by the customized field. |
|
||||
| **`Cell`** | Used in the `List` view's table to represent a table-based preview of the data stored in the field. [More](#cell-component) |
|
||||
| **`Field`** | Swap out the field itself within all `Edit` views. [More](#field-component) |
|
||||
|
||||
As an alternative to replacing the entire Field component, you may want to keep the majority of the default Field component and only swap components within. This allows you to replace the **`Label`** or **`Error`** within a field component or add additional components inside the field with **`beforeInput`** or **`afterInput`**. **`beforeInput`** and **`afterInput`** are allowed in any fields that don't contain other fields, except [UI](/docs/fields/ui) and [Rich Text](/docs/fields/rich-text).
|
||||
|
||||
| Component | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Label`** | Override the default Label in the Field Component. [More](#label-component) |
|
||||
| **`Error`** | Override the default Label in the Field Component. [More](#error-component) |
|
||||
| **`beforeInput`** | An array of elements that will be added before `input`/`textarea` elements. [More](#afterinput-and-beforeinput) |
|
||||
| **`afterInput`** | An array of elements that will be added after `input`/`textarea` elements. [More](#afterinput-and-beforeinput) |
|
||||
|
||||
## Cell Component
|
||||
|
||||
These are the props that will be passed to your custom Cell to use in your own components.
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`field`** | An object that includes the field configuration. |
|
||||
| **`colIndex`** | A unique number for the column in the list. |
|
||||
| **`collection`** | An object with the config of the collection that the field is in. |
|
||||
| **`cellData`** | The data for the field that the cell represents. |
|
||||
| **`rowData`** | An object with all the field values for the row. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
import type { Props } from 'payload/components/views/Cell'
|
||||
import './index.scss'
|
||||
|
||||
const baseClass = 'custom-cell'
|
||||
|
||||
const CustomCell: React.FC<Props> = (props) => {
|
||||
const { field, colIndex, collection, cellData, rowData } = props
|
||||
|
||||
return <span className={baseClass}>{cellData}</span>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Field Component
|
||||
|
||||
When writing your own custom components you can make use of a number of hooks to set data, get reactive changes to other fields, get the id of the document or interact with a context from a custom provider.
|
||||
|
||||
### Sending and receiving values from the form
|
||||
|
||||
When swapping out the `Field` component, you'll be responsible for sending and receiving the field's `value` from the form itself. To do so, import the `useField` hook as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { useField } from 'payload/components/forms'
|
||||
|
||||
const CustomTextField: React.FC<{ path: string }> = ({ path }) => {
|
||||
// highlight-start
|
||||
const { value, setValue } = useField<string>({ path })
|
||||
// highlight-end
|
||||
|
||||
return <input onChange={(e) => setValue(e.target.value)} value={value} />
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
For more information regarding the hooks that are available to you while you build custom
|
||||
components, including the <strong>useField</strong> hook, [click here](/docs/admin/hooks).
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
## Label Component
|
||||
|
||||
These are the props that will be passed to your custom Label.
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| -------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`htmlFor`** | Property used to set `for` attribute for label. |
|
||||
| **`label`** | Label value provided in field, it can be used with i18n. |
|
||||
| **`required`** | A boolean value that represents if the field is required or not. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next'
|
||||
|
||||
import { getTranslation } from 'payload/utilities/getTranslation'
|
||||
|
||||
type Props = {
|
||||
htmlFor?: string
|
||||
label?: Record<string, string> | false | string
|
||||
required?: boolean
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const CustomLabel: React.FC<Props> = (props) => {
|
||||
const { htmlFor, label, required = false } = props
|
||||
|
||||
const { i18n } = useTranslation()
|
||||
|
||||
if (label) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<span>
|
||||
{getTranslation(label, i18n)}
|
||||
{required && <span className="required">*</span>}
|
||||
</span>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return null
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Error Component
|
||||
|
||||
These are the props that will be passed to your custom Error.
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`message`** | The error message. |
|
||||
| **`showError`** | A boolean value that represents if the error should be shown. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
type Props = {
|
||||
message: string
|
||||
showError?: boolean
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const CustomError: React.FC<Props> = (props) => {
|
||||
const { message, showError } = props
|
||||
|
||||
if (showError) {
|
||||
return <p style={{ color: 'red' }}>{message}</p>
|
||||
} else return null
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## afterInput and beforeInput
|
||||
|
||||
With these properties you can add multiple components before and after the input element. For example, you can add an absolutely positioned button to clear the current field value.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
import { Field } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
import './style.scss'
|
||||
|
||||
const ClearButton: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<button
|
||||
onClick={() => {
|
||||
/* ... */
|
||||
}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
X
|
||||
</button>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const titleField: Field = {
|
||||
name: 'title',
|
||||
type: 'text',
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
afterInput: [ClearButton],
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default titleField
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: React Hooks
|
||||
label: React Hooks
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
order: 50
|
||||
desc: Make use of all of the powerful React hooks that Payload provides.
|
||||
keywords: admin, components, custom, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: admin, components, custom, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload provides a variety of powerful hooks that can be used within your own React components. With them, you can interface with Payload itself and build just about any type of complex customization you can think of—directly in familiar React code.
|
||||
|
||||
### useField
|
||||
## useField
|
||||
|
||||
The `useField` hook is used internally within every applicable Payload field component, and it manages sending and receiving a field's state from its parent form.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ const {
|
||||
// The rest of your component goes here
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### useFormFields
|
||||
## useFormFields
|
||||
|
||||
There are times when a custom field component needs to have access to data from other fields, and you have a few options to do so. The `useFormFields` hook is a powerful and highly performant way to retrieve a form's field state, as well as to retrieve the `dispatchFields` method, which can be helpful for setting other fields' form states from anywhere within a form.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ const MyComponent: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### useAllFormFields
|
||||
## useAllFormFields
|
||||
|
||||
**To retrieve more than one field**, you can use the `useAllFormFields` hook. Your component will re-render when _any_ field changes, so use this hook only if you absolutely need to. Unlike the `useFormFields` hook, this hook does not accept a "selector", and it always returns an array with type of `[fields: Fields, dispatch: React.Dispatch<Action>]]`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ const ExampleComponent: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### Updating other fields' values
|
||||
#### Updating other fields' values
|
||||
|
||||
If you are building a custom component, then you should use `setValue` which is returned from the `useField` hook to programmatically set your field's value. But if you're looking to update _another_ field's value, you can use `dispatchFields` returned from `useFormFields`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ You can send the following actions to the `dispatchFields` function.
|
||||
|
||||
To see types for each action supported within the `dispatchFields` hook, check out the Form types [here](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/packages/payload/src/admin/components/forms/Form/types.ts).
|
||||
|
||||
### useForm
|
||||
## useForm
|
||||
|
||||
The `useForm` hook can be used to interact with the form itself, and sends back many methods that can be used to reactively fetch form state without causing rerenders within your components each time a field is changed. This is useful if you have action-based callbacks that your components fire, and need to interact with form state _based on a user action_.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -635,7 +635,7 @@ export const CustomArrayManager = () => {
|
||||
]}
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### useCollapsible
|
||||
## useCollapsible
|
||||
|
||||
The `useCollapsible` hook allows you to control parent collapsibles:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -667,7 +667,7 @@ const CustomComponent: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### useDocumentInfo
|
||||
## useDocumentInfo
|
||||
|
||||
The `useDocumentInfo` hook provides lots of information about the document currently being edited, including the following:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -707,7 +707,7 @@ const LinkFromCategoryToPosts: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### useLocale
|
||||
## useLocale
|
||||
|
||||
In any custom component you can get the selected locale object with the `useLocale` hook. `useLocale`gives you the full locale object, consisting of a `label`, `rtl`(right-to-left) property, and then `code`. Here is a simple example:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -728,7 +728,7 @@ const Greeting: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### useAuth
|
||||
## useAuth
|
||||
|
||||
Useful to retrieve info about the currently logged in user as well as methods for interacting with it. It sends back an object with the following properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -755,7 +755,7 @@ const Greeting: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### useConfig
|
||||
## useConfig
|
||||
|
||||
Used to easily fetch the full Payload config.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -771,7 +771,7 @@ const MyComponent: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### useEditDepth
|
||||
## useEditDepth
|
||||
|
||||
Sends back how many editing levels "deep" the current component is. Edit depth is relevant while adding new documents / editing documents in modal windows and other cases.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -787,11 +787,11 @@ const MyComponent: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### usePreferences
|
||||
## usePreferences
|
||||
|
||||
Returns methods to set and get user preferences. More info can be found [here](https://payloadcms.com/docs/admin/preferences).
|
||||
|
||||
### useTheme
|
||||
## useTheme
|
||||
|
||||
Returns the currently selected theme (`light`, `dark` or `auto`), a set function to update it and a boolean `autoMode`, used to determine if the theme value should be set automatically based on the user's device preferences.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -819,7 +819,7 @@ const MyComponent: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### useTableColumns
|
||||
## useTableColumns
|
||||
|
||||
Returns methods to manipulate table columns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -843,7 +843,7 @@ const MyComponent: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### useDocumentEvents
|
||||
## useDocumentEvents
|
||||
|
||||
The `useDocumentEvents` hook provides a way of subscribing to cross-document events, such as updates made to nested documents within a drawer. This hook will report document events that are outside the scope of the document currently being edited. This hook provides the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,16 +3,15 @@ title: The Admin Panel
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: Manage your data and customize the Admin Panel by swapping in your own React components. Create, modify or remove views, fields, styles and much more.
|
||||
keywords: admin, components, custom, customize, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: admin, components, custom, customize, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload dynamically generates a beautiful, fully functional React admin panel to manage your data. It's extremely powerful and can be customized / extended upon easily by swapping in your own React components. You can add additional views, modify how built-in views look / work, swap out Payload branding for your client's, build your own field types and much more.
|
||||
Payload dynamically generates a beautiful, fully functional Admin Panel to manage your users and data. The Payload Admin Panel is highly performant, even with 100+ fields, and is written fully in TypeScript. It is built with [React](https://react.dev) using the [Next.js App Router](https://nextjs.org/docs/app) and fully supports [React Server Components](https://react.dev/reference/rsc/server-components) which enables the use of the [Local API](/docs/local-api/overview) on the front-end.
|
||||
|
||||
The Payload Admin panel can be bundled with our officially supported [Vite](/docs/admin/vite) and [webpack](/docs/admin/webpack) bundlers or you can integrate another bundler following our adapter pattern approach.
|
||||
When bundled, it is code-split, highly performant (even with 100+ fields), and written fully in TypeScript.
|
||||
You can endlessly customize and extend the Admin UI by swapping your own in [Custom Components](./components) for everything from field labels to entire views. You can also modify built-in views, build your own fields, [swap out Payload branding for your own](https://payloadcms.com/blog/white-label-admin-ui), and so much more.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
The Admin panel is meant to be simple enough to give you a starting point but not bring too much
|
||||
The Admin Panel is meant to be simple enough to give you a starting point but not bring too much
|
||||
complexity, so that you can easily customize it to suit the needs of your application and your
|
||||
editors.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
@@ -20,44 +19,36 @@ When bundled, it is code-split, highly performant (even with 100+ fields), and w
|
||||
<LightDarkImage
|
||||
srcLight="https://payloadcms.com/images/docs/admin.jpg"
|
||||
srcDark="https://payloadcms.com/images/docs/admin-dark.jpg"
|
||||
alt="Admin panel with collapsible sidebar"
|
||||
caption="Redesigned admin panel with a collapsible sidebar that's open by default, providing greater extensibility and enhanced horizontal real estate."
|
||||
alt="Admin Panel with collapsible sidebar"
|
||||
caption="Redesigned Admin Panel with a collapsible sidebar that's open by default, providing greater extensibility and enhanced horizontal real estate."
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
## Admin Options
|
||||
|
||||
All options for the Admin panel are defined in your base Payload config file.
|
||||
All high-level options for the Admin Panel are defined in your Payload config under the `admin` key:
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `bundler` | The bundler that you would like to use to bundle the admin panel. Officially supported bundlers: [Webpack](/docs/admin/webpack) and [Vite](/docs/admin/vite). |
|
||||
| `user` | The `slug` of a Collection that you want be used to log in to the Admin dashboard. [More](/docs/admin/overview#the-admin-user-collection) |
|
||||
| `buildPath` | Specify an absolute path for where to store the built Admin panel bundle used in production. Defaults to `path.resolve(process.cwd(), 'build')`. |
|
||||
| `meta` | Base meta data to use for the Admin panel. Included properties are `titleSuffix`, `ogImage`, and `favicon`. |
|
||||
| `disable` | If set to `true`, the entire Admin panel will be disabled. |
|
||||
| `indexHTML` | Optionally replace the entirety of the `index.html` file used by the Admin panel. Reference the [base index.html file](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/packages/payload/src/admin/index.html) to ensure your replacement has the appropriate HTML elements. |
|
||||
| `css` | Absolute path to a stylesheet that you can use to override / customize the Admin panel styling. [More](/docs/admin/customizing-css). |
|
||||
| `scss` | Absolute path to a Sass variables / mixins stylesheet meant to override Payload styles to make for an easy re-skinning of the Admin panel. [More](/docs/admin/customizing-css#overriding-scss-variables). |
|
||||
| `dateFormat` | Global date format that will be used for all dates in the Admin panel. Any valid [date-fns](https://date-fns.org/) format pattern can be used. |
|
||||
| `user` | The `slug` of a Collection that you want to be used to log in to the Admin Panel. [More](/docs/admin/overview#the-admin-user-collection) |
|
||||
| `buildPath` | Specify an absolute path for where to store the built Admin bundle used in production. Defaults to `path.resolve(process.cwd(), 'build')`. |
|
||||
| `meta` | Base meta data to use for the Admin Panel. Included properties are `titleSuffix`, `icons`, and `openGraph`. Can be overridden on a per collection or per global basis. |
|
||||
| `disable` | If set to `true`, the entire Admin Panel will be disabled. |
|
||||
| `dateFormat` | Global date format that will be used for all dates in the Admin Panel. Any valid [date-fns](https://date-fns.org/) format pattern can be used. |
|
||||
| `avatar` | Set account profile picture. Options: `gravatar`, `default` or a custom React component. |
|
||||
| `autoLogin` | Used to automate admin log-in for dev and demonstration convenience. [More](/docs/authentication/config). |
|
||||
| `livePreview` | Enable real-time editing for instant visual feedback of your front-end application. [More](/docs/live-preview/overview). |
|
||||
| `components` | Component overrides that affect the entirety of the Admin panel. [More](/docs/admin/components) |
|
||||
| `webpack` | Customize the Webpack config that's used to generate the Admin panel. [More](/docs/admin/webpack) |
|
||||
| `vite` | Customize the Vite config that's used to generate the Admin panel. [More](/docs/admin/vite) |
|
||||
| `logoutRoute` | The route for the `logout` page. |
|
||||
| `inactivityRoute` | The route for the `logout` inactivity page. |
|
||||
| `components` | Component overrides that affect the entirety of the Admin Panel. [More](/docs/admin/components) |
|
||||
| `routes` | Replace built-in Admin Panel routes with your own custom routes. [More](#custom-admin-panel-routes) |
|
||||
|
||||
### The Admin User Collection
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Important:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
The Payload Admin panel can only be used by one Collection that supports
|
||||
[Authentication](/docs/authentication/overview).
|
||||
The Admin Panel can only be used by a single auth-enabled Collection. To enable authentication for a Collection, simply set `auth: true` in the Collection's configuration. See [Authentication](/docs/authentication/overview) for more information.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
To specify which Collection to use to log in to the Admin panel, pass the `admin` options a `user` key equal to the slug of the Collection that you'd like to use.
|
||||
To specify which Collection to allow to login to the Admin Panel, pass the `admin.user` key equal to the slug of any auth-enabled Collection. See [Authentication](/docs/authentication/overview) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
`payload.config.js`:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,21 +62,67 @@ const config = buildConfig({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, if you have not specified a Collection, Payload will automatically provide you with a `User` Collection which will be used to access the Admin panel. You can customize or override the fields and settings of the default `User` Collection by passing your own collection using `users` as its `slug` to Payload. When this is done, Payload will use your provided `User` Collection instead of its default version.
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
By default, if you have not specified a Collection, Payload will automatically provide a `User` Collection with access the Admin Panel. You can customize or override the fields and settings of the default `User` Collection by adding your own Collection with `slug: 'users'`. Doing this will force Payload to use your provided `User` Collection instead of its default version.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: you can use whatever Collection you'd like to access the Admin panel as long as the Collection supports Authentication. It doesn't need to be called `users`!**
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Note:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
You can use whatever Collection you'd like to access the Admin Panel as long as the Collection supports [Authentication](/docs/authentication/overview). It doesn't need to be called `users`. For example, you could use a Collection called `admins` or `editors` instead.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you may wish to have two Collections that both support `Authentication`:
|
||||
For example, you may wish to have two Collections that both support Authentication:
|
||||
|
||||
- `admins` - meant to have a higher level of permissions to manage your data and access the Admin panel
|
||||
- `customers` - meant for end users of your app that should not be allowed to log into the Admin panel
|
||||
- `admins` - meant to have a higher level of permissions to manage your data and access the Admin Panel
|
||||
- `customers` - meant for end users of your app that should not be allowed to log into the Admin Panel
|
||||
|
||||
This is totally possible. For the above scenario, by specifying `admin: { user: 'admins' }`, your Payload Admin panel will use `admins`. Any users logged in as `customers` will not be able to log in via the Admin panel.
|
||||
|
||||
### Light and dark modes
|
||||
|
||||
Users in the admin panel have access to choosing between light mode and dark mode for their editing experience. The setting is managed while logged into the admin UI within the user account page and will be stored with the browser. By default, the operating system preference is detected and used.
|
||||
This is totally possible. For the above scenario, by specifying `admin: { user: 'admins' }`, your Admin Panel will use `admins`. Any users logged in as `customers` will not be able to log in via the Admin Panel.
|
||||
|
||||
### Restricting user access
|
||||
|
||||
If you would like to restrict which users from a single Collection can access the Admin panel, you can use the `admin` access control function. [Click here](/docs/access-control/overview#admin) to learn more.
|
||||
It is also possible to allow _multiple admin user types_ into the Admin Panel with limited permissions. To do this, add a `roles` or similar field to your auth-enabled Collection and use the `access.admin` property to limit access. See [Access Control](/docs/access-control/overview) for full details. For a working example, check out the [Auth Example](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/auth/payload).
|
||||
|
||||
### I18n
|
||||
|
||||
The Payload Admin Panel is translated in over 30 languages and counting. Languages are automatically detected based on the user's browser and all text displays in that language. If no language was detected, or if the user's language is not yet supported, English will be chosen. Users can easily specify their language by selecting one from their account page. See [I18n](../configuration/i18n) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
<strong>Note:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
If there is a language that Payload does not yet support, we accept code
|
||||
[contributions](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md).
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Light and dark modes
|
||||
|
||||
Users in the Admin Panel have access to choosing between light mode and dark mode for their editing experience. The setting is managed while logged into the admin UI within the user account page and will be stored with the browser. By default, the operating system preference is detected and used.
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom admin panel routes
|
||||
|
||||
You can configure custom routes in the Admin Panel for the following routes:
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Default route |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ----------------------- |
|
||||
| `account` | `/account` |
|
||||
| `createFirstUser` | `/create-first-user` |
|
||||
| `forgot` | `/forgot` |
|
||||
| `inactivity` | `/logout-inactivity` |
|
||||
| `login` | `/login` |
|
||||
| `logout` | `/logout` |
|
||||
| `reset` | `/reset` |
|
||||
| `unauthorized` | `/unauthorized` |
|
||||
|
||||
`payload.config.js`:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
|
||||
const config = buildConfig({
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
routes: {
|
||||
admin: '/custom-admin-route'
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Managing User Preferences
|
||||
label: Preferences
|
||||
order: 50
|
||||
desc: Store the preferences of your users as they interact with the Admin panel.
|
||||
keywords: admin, preferences, custom, customize, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: admin, preferences, custom, customize, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
As your users interact with your Admin panel, you might want to store their preferences in a persistent manner, so that when they revisit the Admin panel, they can pick right back up where they left off.
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ Out of the box, Payload handles the persistence of your users' preferences in a
|
||||
that is reading or setting a preference via all provided authentication methods.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Use cases
|
||||
## Use cases
|
||||
|
||||
This API is used significantly for internal operations of the Admin panel, as mentioned above. But, if you're building your own React components for use in the Admin panel, you can allow users to set their own preferences in correspondence to their usage of your components. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ This API is used significantly for internal operations of the Admin panel, as me
|
||||
- You might want to store `recentlyAccessed` documents to give admin editors an easy shortcut back to their recently accessed documents on the `Dashboard` or similar
|
||||
- Many other use cases exist. Invent your own! Give your editors an intelligent and persistent editing experience.
|
||||
|
||||
### Database
|
||||
## Database
|
||||
|
||||
Payload automatically creates an internally used `payload-preferences` collection that stores user preferences. Each document in the `payload-preferences` collection contains the following shape:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,15 +44,15 @@ Payload automatically creates an internally used `payload-preferences` collectio
|
||||
| `createdAt` | A timestamp of when the preference was created. |
|
||||
| `updatedAt` | A timestamp set to the last time the preference was updated. |
|
||||
|
||||
### APIs
|
||||
## APIs
|
||||
|
||||
Preferences are available to both [GraphQL](/docs/graphql/overview#preferences) and [REST](/docs/rest-api/overview#) APIs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding or reading Preferences in your own components
|
||||
## Adding or reading Preferences in your own components
|
||||
|
||||
The Payload admin panel offers a `usePreferences` hook. The hook is only meant for use within the admin panel itself. It provides you with two methods:
|
||||
|
||||
##### `getPreference`
|
||||
#### `getPreference`
|
||||
|
||||
This async method provides an easy way to retrieve a user's preferences by `key`. It will return a promise containing the resulting preference value.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ This async method provides an easy way to retrieve a user's preferences by `key`
|
||||
|
||||
- `key`: the `key` of your preference to retrieve.
|
||||
|
||||
##### `setPreference`
|
||||
#### `setPreference`
|
||||
|
||||
Also async, this method provides you with an easy way to set a user preference. It returns `void`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
315
docs/admin/views.mdx
Normal file
315
docs/admin/views.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,315 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Customizing Views
|
||||
label: Customizing Views
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
desc:
|
||||
keywords:
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Root
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily swap entire views with your own by using the `admin.components.views` property. At the root level, Payload renders the following views by default, all of which can be overridden:
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| --------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Account`** | The Account view is used to show the currently logged in user's Account page. |
|
||||
| **`Dashboard`** | The main landing page of the [Admin Panel](./overview). |
|
||||
|
||||
To swap out any of these views, simply pass in your custom component to the `admin.components.views` property of your Payload config. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Account: MyCustomAccountView,
|
||||
Dashboard: MyCustomDashboardView,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more granular control, pass a configuration object instead. Payload exposes the following properties for each view:
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| **`Component`** \* | Pass in the component that should be rendered when a user navigates to this route. |
|
||||
| **`path`** \* | Any valid URL path or array of paths that [`path-to-regexp`](https://www.npmjs.com/package/path-to-regex) understands. |
|
||||
| **`exact`** | Boolean. When true, will only match if the path matches the `usePathname()` exactly. |
|
||||
| **`strict`** | When true, a path that has a trailing slash will only match a location.pathname with a trailing slash. This has no effect when there are additional URL segments in the location.pathname. |
|
||||
| **`sensitive`** | When true, will match if the path is case sensitive. |
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
#### Adding new root views
|
||||
|
||||
To add a _new_ view to the [Admin Panel](./overview), simply add another key to the `views` object with at least a `path` and `Component` property. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
MyCustomView: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomView,
|
||||
path: '/my-custom-view',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Note:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
Routes are cascading. This means that unless explicitly given the `exact` property, they will
|
||||
match on URLs that simply _start_ with the route's path. This is helpful when creating catch-all
|
||||
routes in your application. Alternatively, you could define your nested route _before_ your parent
|
||||
route.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
For help on how to build your own custom view components, see [Building Custom View Components](#building-custom-view-components). For more examples regarding how to customize components, [look at the following examples](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/test/admin/components)._
|
||||
|
||||
### Collections
|
||||
|
||||
To swap out entire views on collections, you can use the `admin.components.views` property on the collection's config. Payload renders the following views by default, all of which can be overridden:
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Edit`** | The Edit view is used to edit a single document for a given collection. |
|
||||
| **`List`** | The List view is used to show a list of documents for a given collection. |
|
||||
|
||||
To swap out any of these views, simply pass in your custom component to the `admin.components.views` property of your Payload config. This will replace the entire view, including the page breadcrumbs, title, tabs, etc, _as well as all nested routes_.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Collection.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: MyCustomEditView,
|
||||
List: MyCustomListView,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For help on how to build your own custom view components, see [Building Custom View Components](#building-custom-view-components).
|
||||
|
||||
**Customizing Nested Views within 'Edit' in Collections**
|
||||
|
||||
The `Edit` view in collections consists of several nested views, each serving a unique purpose. You can customize these nested views using the `admin.components.views.Edit` property in the collection's configuration. This approach allows you to replace specific nested views while keeping the overall structure of the `Edit` view intact, including the page breadcrumbs, title, tabs, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of how you can customize nested views within the `Edit` view in collections, including the use of the `actions` property:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Collection.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: {
|
||||
Default: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomDefaultTab,
|
||||
actions: [CollectionEditButton], // Custom actions for the default edit view
|
||||
},
|
||||
API: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomAPIView,
|
||||
actions: [CollectionAPIButton], // Custom actions for API view
|
||||
},
|
||||
LivePreview: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomLivePreviewView,
|
||||
actions: [CollectionLivePreviewButton], // Custom actions for Live Preview
|
||||
},
|
||||
Version: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomVersionView,
|
||||
actions: [CollectionVersionButton], // Custom actions for Version view
|
||||
},
|
||||
Versions: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomVersionsView,
|
||||
actions: [CollectionVersionsButton], // Custom actions for Versions view
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
List: {
|
||||
actions: [CollectionListButton],
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Adding New Tabs to 'Edit' View**
|
||||
|
||||
You can also add _new_ tabs to the `Edit` view by adding another key to the `components.views.Edit[key]` object with a `path` and `Component` property. See [Custom Tabs](#custom-tabs) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### Globals
|
||||
|
||||
To swap out views for globals, you can use the `admin.components.views` property on the global's config. Payload renders the following views by default, all of which can be overridden:
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Edit`** | The Edit view is used to edit a single document for a given Global. |
|
||||
|
||||
To swap out any of these views, simply pass in your custom component to the `admin.components.views` property of your Payload config. This will replace the entire view, including the page breadcrumbs, title, and tabs, _as well as all nested views_.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Global.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: MyCustomEditView,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For help on how to build your own custom view components, see [Building Custom View Components](#building-custom-view-components).
|
||||
|
||||
**Customizing Nested Views within 'Edit' in Globals**
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to collections, Globals allow for detailed customization within the `Edit` view. This includes the ability to swap specific nested views while maintaining the overall structure of the `Edit` view. You can use the `admin.components.views.Edit` property in the Globals configuration to achieve this, and this will only replace the nested view, leaving the page breadcrumbs, title, and tabs intact.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how you can customize nested views within the `Edit` view in Globals, including the use of the `actions` property:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Global.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: {
|
||||
Default: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomGlobalDefaultTab,
|
||||
actions: [GlobalEditButton], // Custom actions for the default edit view
|
||||
},
|
||||
API: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomGlobalAPIView,
|
||||
actions: [GlobalAPIButton], // Custom actions for API view
|
||||
},
|
||||
LivePreview: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomGlobalLivePreviewView,
|
||||
actions: [GlobalLivePreviewButton], // Custom actions for Live Preview
|
||||
},
|
||||
Version: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomGlobalVersionView,
|
||||
actions: [GlobalVersionButton], // Custom actions for Version view
|
||||
},
|
||||
Versions: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomGlobalVersionsView,
|
||||
actions: [GlobalVersionsButton], // Custom actions for Versions view
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also add _new_ tabs to the `Edit` view by adding another key to the `components.views.Edit[key]` object with a `path` and `Component` property. See [Custom Tabs](#custom-tabs) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Tabs
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily swap individual collection or global edit views. To do this, pass an _object_ to the `admin.components.views.Edit` property of the config. Payload renders the following views by default, all of which can be overridden:
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`Default`** | The Default view is the primary view in which your document is edited. |
|
||||
| **`Versions`** | The Versions view is used to view the version history of a single document. [More details](../versions) |
|
||||
| **`Version`** | The Version view is used to view a single version of a single document for a given collection. [More details](../versions). |
|
||||
| **`API`** | The API view is used to display the REST API JSON response for a given document. |
|
||||
| **`LivePreview`** | The LivePreview view is used to display the Live Preview interface. [More details](../live-preview) |
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Collection.ts or Global.ts
|
||||
export const MyCollection: SanitizedCollectionConfig = {
|
||||
slug: 'my-collection',
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: {
|
||||
// You can also define `components.views.Edit` as a component, this will override _all_ nested views
|
||||
Default: MyCustomDefaultTab,
|
||||
Versions: MyCustomVersionsTab,
|
||||
Version: MyCustomVersionTab,
|
||||
API: MyCustomAPITab,
|
||||
LivePreview: MyCustomLivePreviewTab,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To add a _new_ tab to the `Edit` view, simply add another key to `components.views.Edit[key]` with at least a `path` and `Component` property. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// `Collection.ts` or `Global.ts`
|
||||
export const MyCollection: SanitizedCollectionConfig = {
|
||||
slug: 'my-collection',
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: {
|
||||
MyCustomTab: {
|
||||
Component: MyCustomTab,
|
||||
path: '/my-custom-tab',
|
||||
// You an swap the entire tab component out for your own
|
||||
Tab: MyCustomTab,
|
||||
},
|
||||
AnotherCustomView: {
|
||||
Component: AnotherCustomView,
|
||||
path: '/another-custom-view',
|
||||
// Or you can use the default tab component and just pass in your own label and href
|
||||
Tab: {
|
||||
label: 'Another Custom View',
|
||||
href: '/another-custom-view',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Building Custom View Components
|
||||
|
||||
Your custom view components will be provided with the following props:
|
||||
|
||||
| Prop | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`user`** | The currently logged in user. Will be `null` if no user is logged in. |
|
||||
| **`canAccessAdmin`** \* | If the currently logged in user is allowed to access the [Admin Panel](./overview) or not. |
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Note:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
It's up to you to secure your custom views. If your view requires a user to be logged in or to
|
||||
have certain access rights, you should handle that within your view component yourself.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Examples
|
||||
|
||||
You can find examples of custom views in the [Payload source code `/test/admin/components/views` folder](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/test/admin/components/views). There, you'll find two custom views:
|
||||
|
||||
1. A custom view that uses the `DefaultTemplate`, which is the built-in Payload template that displays the sidebar and "eyebrow nav"
|
||||
1. A custom view that uses the `MinimalTemplate` - which is just a centered template used for things like logging in or out
|
||||
|
||||
To see how to pass in your custom views to create custom views of your own, take a look at the `admin.components.views` property of the [Payload test admin config](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/test/admin/config.ts).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Vite
|
||||
label: Vite
|
||||
order: 90
|
||||
desc: NEEDS TO BE WRITTEN
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
The Vite bundler is currently in beta. If you would like to help us test this package, we'd love
|
||||
to hear from you if you find any [bugs or issues](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/issues/)!
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
Payload has a Vite bundler that you can install and bundle the Admin Panel with. This is an alternative to the [Webpack](/docs/admin/webpack) bundler and might give some performance boosts to your development workflow.
|
||||
|
||||
To use Vite as your bundler, first you need to install the package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yarn add @payloadcms/bundler-vite
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you will need to add the [bundler](/docs/admin/bundlers) to your Payload config:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from '@payloadcms/config'
|
||||
import { viteBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-vite'
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
collections: [],
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
bundler: viteBundler(),
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Vite works fundamentally differently than Webpack. In development mode, it will first pre-bundle any of your dependencies that are CommonJS-only, and then it'll leverage ESM directly in your browser for a better HMR experience.
|
||||
|
||||
It then uses Rollup to create production builds of your admin UI. With Vite, you should see a decent performance boost—especially after your first cold start. However, that first cold start might take a few more seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
In most cases, Vite should work out of the box. But existing Payload plugins may need to make
|
||||
compatibility changes to support Vite.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
This is because Vite aliases work fundamentally differently than Webpack aliases, and Payload relies on aliasing server-only code out of the Payload config to ensure that the bundled admin JS works within your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the main differences between how Vite aliases work and how Webpack aliases work.
|
||||
|
||||
**Vite aliases do not work with absolute paths.**
|
||||
|
||||
In Vite, alias keys must <strong>exactly match</strong> a import paths. If you have 2 files that import the same server-only module, but have different import paths, you would need to add 2 aliases to support both import paths.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// File A
|
||||
import serverOnlyModule from '../server-only-module'
|
||||
|
||||
// File B
|
||||
import serverOnlyModule from '../../server-only-module'
|
||||
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
// You would need to add 2 aliases to support both import paths
|
||||
export const buildConfig({
|
||||
collections: [],
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
bundler: viteBundler(),
|
||||
vite: (incomingViteConfig) => {
|
||||
const existingAliases = incomingViteConfig?.resolve?.alias || {};
|
||||
let aliasArray: { find: string | RegExp; replacement: string; }[] = [];
|
||||
|
||||
// Pass the existing Vite aliases
|
||||
if (Array.isArray(existingAliases)) {
|
||||
aliasArray = existingAliases;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
aliasArray = Object.values(existingAliases);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add your own aliases using the find and replacement keys
|
||||
aliasArray.push({
|
||||
find: '../server-only-module',
|
||||
replacement: path.resolve(__dirname, './path/to/browser-safe-module.js')
|
||||
find: '../../server-only-module',
|
||||
replacement: path.resolve(__dirname, './path/to/browser-safe-module.js')
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
...incomingViteConfig,
|
||||
resolve: {
|
||||
...(incomingViteConfig?.resolve || {}),
|
||||
alias: aliasArray,
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Vite aliases do not get applied to pre-bundled dependencies.**
|
||||
|
||||
This especially affects plugins, as plugins will be pre-bundled by Vite using `esbuild`. To get around this and support Vite, plugin authors need to configure an alias to their plugin at the top level, so that the alias will work accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example. Say your plugin is called `payload-plugin-cool`. It's imported as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { myCoolPlugin } from 'payload-plugin-cool'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That plugin should create an alias to support Vite as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// aliases go here
|
||||
find: 'payload-plugin-cool',
|
||||
replacement: path.resolve(__dirname, './my-admin-plugin.js')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will effectively alias the entire plugin and work with Vite. If the plugin requires admin-specific code, then the `./my-admin-plugin.js` alias target file should reflect any changes necessary to the admin UI that the main server-side plugin performs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Extending the Vite config
|
||||
|
||||
The Payload config supports a new property for plugins to be able to extend the Vite config specifically. That property exists on the main Payload config under `admin.vite`. You can check out the [Vite docs](https://vitejs.dev/config/shared-options.html) for more information on what you can do with the Vite config.
|
||||
|
||||
It's a function that takes a Vite config, and returns an updated Vite config. Here's an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
export const buildConfig({
|
||||
collections: [],
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
bundler: viteBundler(),
|
||||
vite: (incomingViteConfig) => {
|
||||
const existingAliases = incomingViteConfig?.resolve?.alias || {};
|
||||
let aliasArray: { find: string | RegExp; replacement: string; }[] = [];
|
||||
|
||||
// Pass the existing Vite aliases
|
||||
if (Array.isArray(existingAliases)) {
|
||||
aliasArray = existingAliases;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
aliasArray = Object.values(existingAliases);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add your own aliases using the find and replacement keys
|
||||
aliasArray.push({
|
||||
find: '../server-only-module',
|
||||
replacement: path.resolve(__dirname, './path/to/browser-safe-module.js')
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
...incomingViteConfig,
|
||||
resolve: {
|
||||
...(incomingViteConfig?.resolve || {}),
|
||||
alias: aliasArray,
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Learn more about [aliasing server-only modules](https://payloadcms.com/docs/admin/excluding-server-code#aliasing-server-only-modules).
|
||||
|
||||
Even though there is a new property for Vite configs specifically, we have implemented some "compatibility" between Webpack and Vite out-of-the-box.
|
||||
|
||||
If your config specifies Webpack aliases, we attempt to leverage them automatically within the Vite config. They are merged into the Vite alias configuration seamlessly and may work out-of-the-box.
|
||||
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Webpack
|
||||
label: Webpack
|
||||
order: 80
|
||||
desc: The Payload admin panel uses Webpack 5 and supports many common functionalities such as SCSS and Typescript out of the box to give you more freedom.
|
||||
keywords: admin, webpack, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload has a Webpack (v5) bundler that you can build the Admin panel with. For now, we recommended using it because it is stable. If you are feeling a bit more adventurous you can give the [Vite](/docs/admin/vite) bundler a shot.
|
||||
|
||||
Out of the box, the Webpack bundler supports common functionalities such as SCSS and Typescript, but there are many cases where you may need to add support for additional functionalities.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installation
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yarn add @payloadcms/bundler-webpack
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Import the bundler
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { webpackBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-webpack'
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
// highlight-start
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
bundler: webpackBundler(),
|
||||
},
|
||||
// highlight-end
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Extending Webpack
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to extend the Webpack config, you can do so by passing a function to the `admin.webpack` property on your Payload config.
|
||||
The function will receive the Webpack config as an argument and should return the modified config.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { webpackBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-webpack'
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
bundler: webpackBundler()
|
||||
// highlight-start
|
||||
webpack: (config) => {
|
||||
// full control of the Webpack config
|
||||
|
||||
return config
|
||||
},
|
||||
// highlight-end
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
<strong>Tip:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
If changes to your Webpack aliases are not surfacing, they might be
|
||||
[cached](https://webpack.js.org/configuration/cache/) in `node_modules/.cache/webpack`. Try
|
||||
deleting that folder and restarting your server.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Authentication Config
|
||||
label: Config
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
desc: Enable and customize options in the Authentication config for features including Forgot Password, Login Attempts, API key usage and more.
|
||||
keywords: authentication, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: authentication, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload's Authentication is extremely powerful and gives you everything you need when you go to build a new app or site in a secure and responsible manner.
|
||||
@@ -13,12 +13,12 @@ To enable Authentication on a collection, define an `auth` property and set it t
|
||||
## Options
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| -------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
|----------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **`useAPIKey`** | Payload Authentication provides for API keys to be set on each user within an Authentication-enabled Collection. [More](/docs/authentication/config#api-keys) |
|
||||
| **`tokenExpiration`** | How long (in seconds) to keep the user logged in. JWTs and HTTP-only cookies will both expire at the same time. |
|
||||
| **`maxLoginAttempts`** | Only allow a user to attempt logging in X amount of times. Automatically locks out a user from authenticating if this limit is passed. Set to `0` to disable. |
|
||||
| **`lockTime`** | Set the time (in milliseconds) that a user should be locked out if they fail authentication more times than `maxLoginAttempts` allows for. |
|
||||
| **`depth`** | How many levels deep a `user` document should be populated when creating the JWT and binding the `user` to the express `req`. Defaults to `0` and should only be modified if absolutely necessary, as this will affect performance. |
|
||||
| **`depth`** | How many levels deep a `user` document should be populated when creating the JWT and binding the `user` to the `req`. Defaults to `0` and should only be modified if absolutely necessary, as this will affect performance. |
|
||||
| **`cookies`** | Set cookie options, including `secure`, `sameSite`, and `domain`. For advanced users. |
|
||||
| **`forgotPassword`** | Customize the way that the `forgotPassword` operation functions. [More](/docs/authentication/config#forgot-password) |
|
||||
| **`verify`** | Set to `true` or pass an object with verification options to require users to verify by email before they are allowed to log into your app. [More](/docs/authentication/config#email-verification) |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,12 +3,12 @@ title: Authentication Operations
|
||||
label: Operations
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
desc: Enabling Authentication automatically makes key operations available such as Login, Logout, Verify, Unlock, Reset Password and more.
|
||||
keywords: authentication, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: authentication, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Enabling Authentication on a Collection automatically exposes additional auth-based operations in the Local, REST, and GraphQL APIs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Access
|
||||
## Access
|
||||
|
||||
The Access operation returns what a logged in user can and can't do with the collections and globals that are registered via your config. This data can be immensely helpful if your app needs to show and hide certain features based on access control, as the Payload Admin panel does.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ query {
|
||||
|
||||
Document access can also be queried on a collection/global basis. Access on a global can queried like `http://localhost:3000/api/global-slug/access`, Collection document access can be queried like `http://localhost:3000/api/collection-slug/access/:id`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Me
|
||||
## Me
|
||||
|
||||
Returns either a logged in user with token or null when there is no logged in user.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -105,9 +105,9 @@ query {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Login
|
||||
## Login
|
||||
|
||||
Accepts an `email` and `password`. On success, it will return the logged in user as well as a token that can be used to authenticate. In the GraphQL and REST APIs, this operation also automatically sets an HTTP-only cookie including the user's token. If you pass an Express `res` to the Local API operation, Payload will set a cookie there as well.
|
||||
Accepts an `email` and `password`. On success, it will return the logged in user as well as a token that can be used to authenticate. In the GraphQL and REST APIs, this operation also automatically sets an HTTP-only cookie including the user's token. If you pass a `res` to the Local API operation, Payload will set a cookie there as well.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example REST API login**:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -166,7 +166,7 @@ const result = await payload.login({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Logout
|
||||
## Logout
|
||||
|
||||
As Payload sets HTTP-only cookies, logging out cannot be done by just removing a cookie in JavaScript, as HTTP-only cookies are inaccessible by JS within the browser. So, Payload exposes a `logout` operation to delete the token in a safe way.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -189,7 +189,7 @@ mutation {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Refresh
|
||||
## Refresh
|
||||
|
||||
Allows for "refreshing" JWTs. If your user has a token that is about to expire, but the user is still active and using the app, you might want to use the `refresh` operation to receive a new token by sending the operation the token that is about to expire.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -244,7 +244,7 @@ mutation {
|
||||
`token` arg.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Verify by Email
|
||||
## Verify by Email
|
||||
|
||||
If your collection supports email verification, the Verify operation will be exposed which accepts a verification token and sets the user's `_verified` property to `true`, thereby allowing the user to authenticate with the Payload API.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -276,7 +276,7 @@ const result = await payload.verifyEmail({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Unlock
|
||||
## Unlock
|
||||
|
||||
If a user locks themselves out and you wish to deliberately unlock them, you can utilize the Unlock operation. The Admin panel features an Unlock control automatically for all collections that feature max login attempts, but you can programmatically unlock users as well by using the Unlock operation.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -309,7 +309,7 @@ const result = await payload.unlock({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Forgot Password
|
||||
## Forgot Password
|
||||
|
||||
Payload comes with built-in forgot password functionality. Submitting an email address to the Forgot Password operation will generate an email and send it to the respective email address with a link to reset their password.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -361,7 +361,7 @@ const token = await payload.forgotPassword({
|
||||
use the token to "reset" their password.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Reset Password
|
||||
## Reset Password
|
||||
|
||||
After a user has "forgotten" their password and a token is generated, that token can be used to send to the reset password operation along with a new password which will allow the user to reset their password securely.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Authentication Overview
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: Payload provides highly secure user Authentication out of the box, and you can fully customize, override, or remove the default Authentication support.
|
||||
keywords: authentication, config, configuration, overview, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: authentication, config, configuration, overview, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<YouTube
|
||||
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ _Admin panel screenshot depicting an Admins Collection with Auth enabled_
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Payload provides you with a `User` collection that supports Authentication, which is used to access the Admin panel. But, you can add support to one or many Collections of your own. For more information on how to customize, override, or remove the default `User` collection, [click here](/docs/admin/overview#the-admin-user-collection).
|
||||
|
||||
### Enabling Auth on a collection
|
||||
## Enabling Auth on a collection
|
||||
|
||||
Every Payload Collection can opt-in to supporting Authentication by specifying the `auth` property on the Collection's config to either `true` or to an object containing `auth` options.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,33 +71,33 @@ export const Admins: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
|
||||
Once enabled, each document that is created within the Collection can be thought of as a `user` - who can make use of commonly required authentication functions such as logging in / out, resetting their password, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
### Logging in / out, resetting password, etc.
|
||||
## Logging in / out, resetting password, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
[Click here](/docs/authentication/operations) for a list of all automatically-enabled Auth operations, including `login`, `logout`, `refresh`, and others.
|
||||
|
||||
### Token-based auth
|
||||
## Token-based auth
|
||||
|
||||
Successfully logging in returns a `JWT` (JSON web token) which is how a user will identify themselves to Payload. By providing this JWT via either an HTTP-only cookie or an `Authorization: JWT` or `Authorization: Bearer` header, Payload will automatically identify the user and add its user JWT data to the Express `req`, which is available throughout Payload including within access control, hooks, and more.
|
||||
Successfully logging in returns a `JWT` (JSON web token) which is how a user will identify themselves to Payload. By providing this JWT via either an HTTP-only cookie or an `Authorization: JWT` or `Authorization: Bearer` header, Payload will automatically identify the user and add its user JWT data to the `req`, which is available throughout Payload including within access control, hooks, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify what data gets encoded to the JWT token by setting `saveToJWT` to true in your auth collection fields. If you wish to use a different key other than the field `name`, you can provide it to `saveToJWT` as a string. It is also possible to use `saveToJWT` on fields that are nested in inside groups and tabs. If a group has a `saveToJWT` set it will include the object with all sub-fields in the token. You can set `saveToJWT: false` for any fields you wish to omit. If a field inside a group has `saveToJWT` set, but the group does not, the field will be included at the top level of the token.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
<strong>Tip:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
You can access the logged-in user from access control functions and hooks via the Express{' '}
|
||||
You can access the logged-in user from access control functions and hooks via the{' '}
|
||||
<strong>req</strong>. The logged-in user is automatically added as the <strong>user</strong>{' '}
|
||||
property.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### HTTP-only cookies
|
||||
## HTTP-only cookies
|
||||
|
||||
Payload `login`, `logout`, and `refresh` operations make use of HTTP-only cookies for authentication purposes. HTTP-only cookies are a highly secure method of storing identifiable data on a user's device so that Payload can automatically recognize a returning user until their cookie expires. They are totally protected from common XSS attacks and cannot be read at all via JavaScript in the browser.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Automatic browser inclusion
|
||||
#### Automatic browser inclusion
|
||||
|
||||
Modern browsers automatically include `http-only` cookies when making requests directly to URLs—meaning that if you are running your API on http://example.com, and you have logged in and visit http://example.com/test-page, your browser will automatically include the Payload authentication cookie for you.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Using Fetch or other HTTP APIs
|
||||
#### Using Fetch or other HTTP APIs
|
||||
|
||||
However, if you use `fetch` or similar APIs to retrieve Payload resources from its REST or GraphQL API, you need to specify to include credentials (cookies).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -121,7 +121,7 @@ For more about how to automatically include cookies in requests from your app to
|
||||
will still show HTTP-only cookies, even when JavaScript running on the page can't.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### CSRF Protection
|
||||
## CSRF Protection
|
||||
|
||||
CSRF (cross-site request forgery) attacks are common and dangerous. By using an HTTP-only cookie, Payload removes many XSS vulnerabilities, however, CSRF attacks can still be possible.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -159,7 +159,7 @@ const config = buildConfig({
|
||||
export default config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Identifying users via the Authorization Header
|
||||
## Identifying users via the Authorization Header
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to authenticating via an HTTP-only cookie, you can also identify users via the `Authorization` header on an HTTP request.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Using the Payload Auth Middleware
|
||||
label: Using the Middleware
|
||||
order: 40
|
||||
desc: Make full use of Payload's built-in authentication with your own custom Express endpoints by adding Payload's authentication middleware.
|
||||
keywords: authentication, middleware, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Because Payload uses your existing Express server, you are free to add whatever logic you need to your app through endpoints of your own. However, Payload does not add its middleware to your Express app itself—instead, it scopes all of its middleware to Payload-specific routers.
|
||||
|
||||
This approach has a ton of benefits - it's great for isolation of concerns and limiting scope, but it also means that your additional routes won't have access to Payload's user authentication.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
You can make full use of Payload's built-in authentication within your own custom Express
|
||||
endpoints by adding Payload's authentication middleware.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
Payload must be initialized before the `payload.authenticate` middleware can be used. This is done
|
||||
by calling `payload.init()` prior to adding the middleware.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
Example in `server.js`:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import express from 'express'
|
||||
import payload from 'payload'
|
||||
|
||||
const app = express()
|
||||
|
||||
const start = async () => {
|
||||
await payload.init({
|
||||
secret: 'PAYLOAD_SECRET_KEY',
|
||||
express: app,
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
const router = express.Router()
|
||||
|
||||
// Note: Payload must be initialized before the `payload.authenticate` middleware can be used
|
||||
router.use(payload.authenticate) // highlight-line
|
||||
|
||||
router.get('/', (req, res) => {
|
||||
if (req.user) {
|
||||
return res.send(`Authenticated successfully as ${req.user.email}.`)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return res.send('Not authenticated')
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
app.use('/some-route-here', router)
|
||||
|
||||
app.listen(3000)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
start()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ desc: Quickly configure and deploy your Payload Cloud project in a few simple st
|
||||
keywords: configuration, config, settings, project, cloud, payload cloud, deploy, deployment
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Select your plan
|
||||
## Select your plan
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have created a project, you will need to select your plan. This will determine the resources that are allocated to your project and the features that are available to you.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ Once you have created a project, you will need to select your plan. This will de
|
||||
anytime.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Project Details
|
||||
## Project Details
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ---------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ Once you have created a project, you will need to select your plan. This will de
|
||||
| **Project Slug** | Choose a unique slug to identify your project. This needs to be unique for your team and you can change it any time. |
|
||||
| **Team** | Select the team you want to create the project under. If this is your first project, a personal team will be created for you automatically. You can modify your team settings and invite new members at any time from the Team Settings page. |
|
||||
|
||||
### Build Settings
|
||||
## Build Settings
|
||||
|
||||
If you are deploying a new project from a template, the following settings will be automatically configured for you. If you are using your own repository, you need to make sure your build settings are accurate for your project to deploy correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -39,17 +39,17 @@ If you are deploying a new project from a template, the following settings will
|
||||
| **Branch to Deploy** | Select the branch of your repository that you want to deploy from. This is the branch that will be used to build your project when you commit new changes. |
|
||||
| **Default Domain** | Set a default domain for your project. This must be unique and you will not able to change it. You can always add a custom domain later in your project settings. |
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment Variables
|
||||
## Environment Variables
|
||||
|
||||
Any of the features in Payload Cloud that require environment variables will automatically be provided to your application. If your app requires any custom environment variables, you can set them here.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
Note: For security reasons, any variables you wish to provide to the Admin panel must be prefixed
|
||||
with `PAYLOAD_PUBLIC_`. Learn more
|
||||
[here](https://payloadcms.com/docs/admin/webpack#admin-environment-vars).
|
||||
[here](https://payloadcms.com/docs/admin/environment-vars).
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Payment
|
||||
## Payment
|
||||
|
||||
Payment methods can be set per project and can be updated any time. You can use team’s default payment method, or add a new one. Modify your payment methods in your Project settings / Team settings.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ desc: Manage your Payload Cloud projects.
|
||||
keywords: cloud, payload cloud, projects, project, overview, database, file storage, build settings, environment variables, custom domains, email, developing locally
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Overview
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
The overview tab shows your most recent deployment, along with build and deployment logs. From
|
||||
@@ -18,19 +18,19 @@ keywords: cloud, payload cloud, projects, project, overview, database, file stor
|
||||
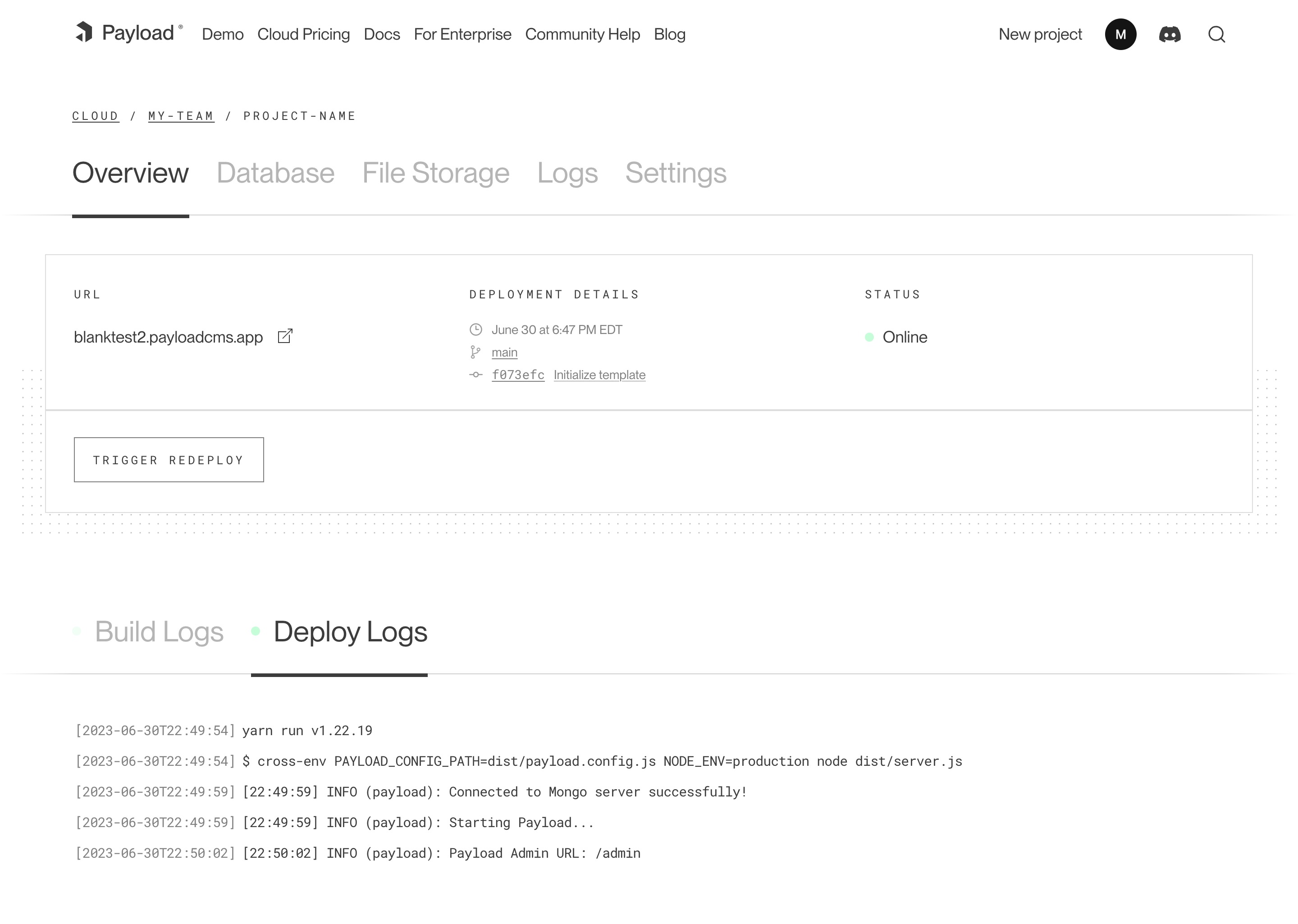
|
||||
_A screenshot of the Overview page for a Cloud project._
|
||||
|
||||
### Database
|
||||
## Database
|
||||
|
||||
Your Payload Cloud project comes with a MongoDB serverless Atlas DB instance or a Dedicated Atlas cluster, depending on your plan. To interact with your cloud database, you will be provided with a MongoDB connection string. This can be found under the **Database** tab of your project.
|
||||
|
||||
`mongodb+srv://your_connection_string`
|
||||
|
||||
### File Storage
|
||||
## File Storage
|
||||
|
||||
Payload Cloud gives you S3 file storage backed by Cloudflare as a CDN, and this plugin extends Payload so that all of your media will be stored in S3 rather than locally.
|
||||
|
||||
AWS Cognito is used for authentication to your S3 bucket. The [Payload Cloud Plugin](https://github.com/payloadcms/plugin-cloud) will automatically pick up these values. These values are only if you'd like to access your files directly, outside of Payload Cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Accessing Files Outside of Payload Cloud
|
||||
### Accessing Files Outside of Payload Cloud
|
||||
|
||||
If you'd like to access your files outside of Payload Cloud, you'll need to retrieve some values from your project's settings and put them into your environment variables. In Payload Cloud, navigate to the File Storage tab and copy the values using the copy button. Put these values in your .env file. Also copy the Cognito Password value separately and put into your .env file as well.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -50,21 +50,21 @@ PAYLOAD_CLOUD_COGNITO_PASSWORD=
|
||||
|
||||
The plugin will pick up these values and use them to access your files.
|
||||
|
||||
### Build Settings
|
||||
## Build Settings
|
||||
|
||||
You can update settings from your Project’s Settings tab. Changes to your build settings will trigger a redeployment of your project.
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment Variables
|
||||
## Environment Variables
|
||||
|
||||
From the Environment Variables page of the Settings tab, you can add, update and delete variables for use in your project. Like build settings, these changes will trigger a redeployment of your project.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
Note: For security reasons, any variables you wish to provide to the Admin panel must be prefixed
|
||||
with `PAYLOAD_PUBLIC_`. Learn more
|
||||
[here](https://payloadcms.com/docs/admin/webpack#admin-environment-vars).
|
||||
[here](https://payloadcms.com/docs/admin/environment-vars).
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Domains
|
||||
## Custom Domains
|
||||
|
||||
With Payload Cloud, you can add custom domain names to your project. To do so, first go to the Domains page of the Settings tab of your project. Here you can see your default domain. To add a new domain, type in the domain name you wish to use.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -84,19 +84,19 @@ export default buildConfig({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Email
|
||||
## Email
|
||||
|
||||
Powered by [Resend](https://resend.com), Payload Cloud comes with integrated email support out of the box. No configuration is needed, and you can use `payload.sendEmail()` to send email right from your Payload app. To learn more about sending email with Payload, checkout the [Email Configuration](https://payloadcms.com/docs/email/overview) overview.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are on the Pro or Enterprise plan, you can add your own custom Email domain name. From the Email page of your project’s Settings, add the domain you wish to use for email delivery. This will generate a set of DNS records. Add these records to your DNS provider and click verify to check that your records are resolving properly. Once verified, your emails will now be sent from your custom domain name.
|
||||
|
||||
### Developing Locally
|
||||
## Developing Locally
|
||||
|
||||
To make changes to your project, you will need to clone the repository defined in your project settings to your local machine. In order to run your project locally, you will need configure your local environment first. Refer to your repository’s `README.md` file to see the steps needed for your specific template.
|
||||
|
||||
From there, you are ready to make updates to your project. When you are ready to make your changes live, commit your changes to the branch you specified in your Project settings, and your application will automatically trigger a redeploy and build from your latest commit.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloud Plugin
|
||||
## Cloud Plugin
|
||||
|
||||
Projects generated from a template will come pre-configured with the official Cloud Plugin, but if you are using your own repository you will need to add this into your project. To do so, add the plugin to your Payload config:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -117,7 +117,7 @@ export default buildConfig({
|
||||
over Payload Cloud's email service.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
##### **Optional configuration**
|
||||
#### **Optional configuration**
|
||||
|
||||
If you wish to opt-out of any Payload cloud features, the plugin also accepts options to do so.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,22 +14,22 @@ keywords: team, teams, billing, subscription, payment, plan, plans, cloud, paylo
|
||||
|
||||
_A screenshot of the Team Settings page._
|
||||
|
||||
### Members
|
||||
## Members
|
||||
|
||||
Each team has members that can interact with your projects. You can invite multiple people to your team and each individual can belong to more than one team. You can assign them either `owner` or `user` permissions. Owners are able to make admin-only changes, such as deleting projects, and editing billing information.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding Members
|
||||
## Adding Members
|
||||
|
||||
To add a new member to your team, visit your Team’s Settings page, and click “Invite Teammate”. You can then add their email address, and assign their role. Press “Save” to send the invitations, which will send an email to the invited team member where they can create a new account.
|
||||
|
||||
### Billing
|
||||
## Billing
|
||||
|
||||
Users can update billing settings and subscriptions for any teams where they are designated as an `owner`. To make updates to the team’s payment methods, visit the Billing page under the Team Settings tab. You can add new cards, delete cards, and set a payment method as a default. The default payment method will be used in the event that another payment method fails.
|
||||
|
||||
### Subscriptions
|
||||
## Subscriptions
|
||||
|
||||
From the Subscriptions page, a team owner can see all current plans for their team. From here, you can see the price of each plan, if there is an active trial, and when you will be billed next.
|
||||
|
||||
### Invoices
|
||||
## Invoices
|
||||
|
||||
The Invoices page will you show you the invoices for your account, as well as the status on their payment.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Collection Configs
|
||||
label: Collections
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
desc: Structure your Collections for your needs by defining fields, adding slugs and labels, establishing access control, tying in hooks, setting timestamps and more.
|
||||
keywords: collections, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: collections, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload Collections are defined through configs of their own, and you can define as many as your application needs. Each
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ It's often best practice to write your Collections in separate files and then im
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
#### Simple collection example
|
||||
### Simple collection example
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
@@ -58,13 +58,13 @@ export const Orders: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### More collection config examples
|
||||
### More collection config examples
|
||||
|
||||
You can find an assortment
|
||||
of [example collection configs](https://github.com/payloadcms/public-demo/tree/master/src/payload/collections) in the Public
|
||||
Demo source code on GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin options
|
||||
## Admin options
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize the way that the Admin panel behaves on a collection-by-collection basis by defining the `admin`
|
||||
property on a collection's config.
|
||||
@@ -80,13 +80,14 @@ property on a collection's config.
|
||||
| `hideAPIURL` | Hides the "API URL" meta field while editing documents within this collection. |
|
||||
| `enableRichTextLink` | The [Rich Text](/docs/fields/rich-text) field features a `Link` element which allows for users to automatically reference related documents within their rich text. Set to `true` by default. |
|
||||
| `enableRichTextRelationship` | The [Rich Text](/docs/fields/rich-text) field features a `Relationship` element which allows for users to automatically reference related documents within their rich text. Set to `true` by default. |
|
||||
| `meta` | Metadata overrides to apply to the [Admin panel](../admin/overview). Included properties are `description` and `openGraph`. |
|
||||
| `preview` | Function to generate preview URLS within the Admin panel that can point to your app. [More](#preview). |
|
||||
| `livePreview` | Enable real-time editing for instant visual feedback of your front-end application. [More](/docs/live-preview/overview). |
|
||||
| `components` | Swap in your own React components to be used within this collection. [More](/docs/admin/components#collections) |
|
||||
| `listSearchableFields` | Specify which fields should be searched in the List search view. [More](#list-searchable-fields) |
|
||||
| **`pagination`** | Set pagination-specific options for this collection. [More](#pagination) |
|
||||
|
||||
### Preview
|
||||
## Preview
|
||||
|
||||
Collection `admin` options can accept a `preview` function that will be used to generate a link pointing to the frontend
|
||||
of your app to preview data.
|
||||
@@ -125,7 +126,7 @@ export const Posts: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Pagination
|
||||
## Pagination
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few options that you can specify options for pagination on a collection-by-collection basis:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -134,23 +135,23 @@ Here are a few options that you can specify options for pagination on a collecti
|
||||
| `defaultLimit` | Integer that specifies the default per-page limit that should be used. Defaults to 10. |
|
||||
| `limits` | Provide an array of integers to use as per-page options for admins to choose from in the List view. |
|
||||
|
||||
### Access control
|
||||
## Access control
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify extremely granular access control (what users can do with documents in a collection) on a collection by
|
||||
collection basis. To learn more, go to the [Access Control](/docs/access-control/overview) docs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Hooks
|
||||
## Hooks
|
||||
|
||||
Hooks are a powerful way to extend collection functionality and execute your own logic, and can be defined on a
|
||||
collection by collection basis. To learn more, go to the [Hooks](/docs/hooks/overview) documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Field types
|
||||
## Field types
|
||||
|
||||
Collections support all field types that Payload has to offer—including simple fields like text and checkboxes all the
|
||||
way to more complicated layout-building field groups like Blocks. [Click here](/docs/fields/overview) to learn more
|
||||
about field types.
|
||||
|
||||
### List Searchable Fields
|
||||
## List Searchable Fields
|
||||
|
||||
In the List view, there is a "search" box that allows you to quickly find a document with a search. By default, it
|
||||
searches on the ID field. If you have `admin.useAsTitle` defined, the list search will use that field. However, you can
|
||||
@@ -168,7 +169,7 @@ those three fields plus the ID field.
|
||||
so your admin queries can remain performant.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
You can import collection types as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Express
|
||||
label: Express
|
||||
order: 60
|
||||
desc: Payload utilizes Express middleware packages, you can customize how they work by passing in configuration options.
|
||||
keywords: config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload utilizes a few Express-specific middleware packages within its own routers. You can customize how they work by passing in configuration options to the main Payload config's `express` property.
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Middleware
|
||||
|
||||
Payload allows you to pass in custom Express middleware to be used on all of the routes it opens. This is useful for adding logging or any other custom functionality to your endpoints.
|
||||
|
||||
There are 2 exposed properties. Each property is an array of middleware functions.
|
||||
|
||||
- `preMiddleware` - runs before any of the Payload middleware
|
||||
- `postMiddleware` - runs after all of the Payload middleware
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
express: {
|
||||
preMiddleware: [
|
||||
(req, res, next) => {
|
||||
// do something
|
||||
next()
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
postMiddleware: [
|
||||
(req, res, next) => {
|
||||
// do something
|
||||
next()
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Example logging middleware function
|
||||
const requestLoggerMiddleware = (req, res, next) => {
|
||||
req.payload.logger.info(`request: ${req.method} ${req.url}`)
|
||||
next()
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### JSON
|
||||
|
||||
`express.json()` is used to parse JSON body content into JavaScript objects accessible on the Express `req`. Payload allows you to customize all of the `json` method's options. Common examples of customization use-cases are increasing the max allowed JSON body size which defaults to `2MB`.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example payload.config.js for how to increase the max JSON size allowed to be sent to Payload endpoints:**
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
{
|
||||
express: {
|
||||
json: {
|
||||
limit: '4mb',
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can find a list of all available options that are able to be passed to `express.json()` [here](https://expressjs.com/en/api.html).
|
||||
|
||||
### Compression
|
||||
|
||||
Payload uses the `compression` package to optimize transfer size for all of the routes it opens, and you can pass customization options through the Payload config.
|
||||
|
||||
To customize compression options, pass an object to the Payload config's `express` property.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example payload.config.js:**
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
{
|
||||
express: {
|
||||
compression: {
|
||||
// settings go here
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Typically, the default options for this package are suitable. However, for a list of all available customization options, [click here](http://expressjs.com/en/resources/middleware/compression.html).
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Global Configs
|
||||
label: Globals
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
desc: Set up your Global config for your needs by defining fields, adding slugs and labels, establishing access control, tying in hooks and more.
|
||||
keywords: globals, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: globals, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Global configs are in many ways similar to [Collections](/docs/configuration/collections). The big difference is that Collections will potentially contain _many_ documents, while a Global is a "one-off". Globals are perfect for things like header nav, site-wide banner alerts, app-wide localized strings, and other "global" data that your site or app might rely on.
|
||||
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ As with Collection configs, it's often best practice to write your Globals in se
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
#### Simple Global example
|
||||
### Simple Global example
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { GlobalConfig } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
@@ -58,11 +58,11 @@ const Nav: GlobalConfig = {
|
||||
export default Nav
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Global config example
|
||||
### Global config example
|
||||
|
||||
You can find a few [example Global configs](https://github.com/payloadcms/public-demo/tree/master/src/payload/globals) in the Public Demo source code on GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin options
|
||||
## Admin options
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize the way that the Admin panel behaves on a Global-by-Global basis by defining the `admin` property on a Global's config.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -74,8 +74,9 @@ You can customize the way that the Admin panel behaves on a Global-by-Global bas
|
||||
| `preview` | Function to generate a preview URL within the Admin panel for this global that can point to your app. [More](#preview). |
|
||||
| `livePreview` | Enable real-time editing for instant visual feedback of your front-end application. [More](/docs/live-preview/overview). |
|
||||
| `hideAPIURL` | Hides the "API URL" meta field while editing documents within this collection. |
|
||||
| `meta` | Metadata overrides to apply to the [Admin panel](../admin/overview). Included properties are `description` and `openGraph`. |
|
||||
|
||||
### Preview
|
||||
## Preview
|
||||
|
||||
Global `admin` options can accept a `preview` function that will be used to generate a link pointing to the frontend of your app to preview data.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -112,19 +113,19 @@ export const MyGlobal: GlobalConfig = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Access control
|
||||
## Access control
|
||||
|
||||
As with Collections, you can specify extremely granular access control (what users can do with this Global) on a Global-by-Global basis. However, Globals only have `update` and `read` access control due to their nature of only having one document. To learn more, go to the [Access Control](/docs/access-control/overview) docs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Hooks
|
||||
## Hooks
|
||||
|
||||
Globals also fully support a smaller subset of Hooks. To learn more, go to the [Hooks](/docs/hooks/overview) documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Field types
|
||||
## Field types
|
||||
|
||||
Globals support all field types that Payload has to offer—including simple fields like text and checkboxes all the way to more complicated layout-building field groups like Blocks. [Click here](/docs/fields/overview) to learn more about field types.
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
You can import global types as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,12 +3,43 @@ title: I18n
|
||||
label: I18n
|
||||
order: 40
|
||||
desc: Manage and customize internationalization support in your CMS editor experience
|
||||
keywords: internationalization, i18n, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: internationalization, i18n, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Not only does Payload support managing localized content, it also has internationalization support so that admin users can work in their preferred language. Payload's i18n support is built on top of [i18next](https://www.i18next.com). It comes included by default and can be extended in your config.
|
||||
Not only does Payload support managing localized content, it also has internationalization support so that users in the [Admin Panel](../admin/overview) can work in their preferred language. Payload's i18n comes by default without any additional setup, and you can extend the default settings to customize the language settings to your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
While Payload's built-in features come translated, you may want to also translate parts of your project's configuration too. This is possible in places like collections and globals labels and groups, field labels, descriptions and input placeholder text. The admin UI will display all the correct translations you provide based on the user's language.
|
||||
### Configuration Options
|
||||
|
||||
In your Payload config, you can add translations and customize the settings in `i18n`. Payload will use your custom options and merge it with the default, allowing you to override the settings Payload provides.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example Payload config extending i18n:**
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
//...
|
||||
i18n: {
|
||||
fallbackLng: 'en', // default
|
||||
debug: false, // default
|
||||
resources: {
|
||||
en: {
|
||||
custom: {
|
||||
// namespace can be anything you want
|
||||
key1: 'Translation with {{variable}}', // translation
|
||||
},
|
||||
// override existing translation keys
|
||||
general: {
|
||||
dashboard: 'Home',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
//...
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
While Payload's built-in features come translated, you may want to also translate parts of your project's configuration too. This is possible in places like Collections and Globals labels and groups, field labels, descriptions and input placeholder text. The admin UI will display all the correct translations you provide based on the user's language.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of a simple collection supporting both English and Spanish editors:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -56,9 +87,9 @@ export const Articles: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin UI
|
||||
## Admin UI
|
||||
|
||||
The Payload admin panel reads the language settings of a user's browser and display all text in that language, or will fall back to English if the user's language is not yet supported.
|
||||
The [Admin Panel](../admin/overview) reads the language settings of a user's browser and display all text in that language, or will fall back to English if the user's language is not yet supported.
|
||||
After a user logs in, they can change their language selection in the `/account` view.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -68,15 +99,13 @@ After a user logs in, they can change their language selection in the `/account`
|
||||
[contributions](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md).
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Node Express
|
||||
## Node
|
||||
|
||||
Payload's backend uses express middleware to set the language on incoming requests before they are handled. This allows backend validation to return error messages in the user's own language or system generated emails to be sent using the correct translation. You can make HTTP requests with the `accept-language` header and Payload will use that language.
|
||||
Payload's backend sets the language on incoming requests before they are handled. This allows backend validation to return error messages in the user's own language or system generated emails to be sent using the correct translation. You can make HTTP requests with the `accept-language` header and Payload will use that language.
|
||||
|
||||
Anywhere in your Payload app that you have access to the `req` object, you can access i18next's extensive internationalization features assigned to `req.i18n`. To access text translations you can use `req.t('namespace:key')`.
|
||||
Anywhere in your Payload app that you have access to the `req` object, you can access payload's extensive internationalization features assigned to `req.i18n`. To access text translations you can use `req.t('namespace:key')`.
|
||||
|
||||
Read the i18next [API documentation](https://www.i18next.com/overview/api) to learn more.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration Options
|
||||
## Configuration Options
|
||||
|
||||
In your Payload config, you can add translations and customize the settings in `i18n`. Payload will use your custom options and merge it with the default, allowing you to override the settings Payload provides.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -88,9 +117,8 @@ import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
//...
|
||||
i18n: {
|
||||
fallbackLng: 'en', // default
|
||||
debug: false, // default
|
||||
resources: {
|
||||
fallbackLanguage: 'en', // default
|
||||
translations: {
|
||||
en: {
|
||||
custom: {
|
||||
// namespace can be anything you want
|
||||
@@ -107,4 +135,63 @@ export default buildConfig({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See the i18next [configuration options](https://www.i18next.com/overview/configuration-options) to learn more.
|
||||
## Types for custom translations
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use custom translations in your project, you need to provide the types for the translations. Here is an example of how you can define the types for the custom translations in a custom react component:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
'use client'
|
||||
import type { NestedKeysStripped } from '@payloadcms/translations'
|
||||
import type React from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
import { useTranslation } from '@payloadcms/ui/providers/Translation'
|
||||
|
||||
const customTranslations = {
|
||||
en: {
|
||||
general: {
|
||||
test: 'Custom Translation',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type CustomTranslationObject = typeof customTranslations.en
|
||||
type CustomTranslationKeys = NestedKeysStripped<CustomTranslationObject>
|
||||
|
||||
export const MyComponent: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
const { i18n, t } = useTranslation<CustomTranslationObject, CustomTranslationKeys>() // These generics merge your custom translations with the default client translations
|
||||
|
||||
return t('general:test')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, payload exposes the `t` function in various places, for example in labels. Here is how you would type those:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import type {
|
||||
DefaultTranslationKeys,
|
||||
NestedKeysStripped,
|
||||
TFunction,
|
||||
} from '@payloadcms/translations'
|
||||
import type { Field } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
const customTranslations = {
|
||||
en: {
|
||||
general: {
|
||||
test: 'Custom Translation',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type CustomTranslationObject = typeof customTranslations.en
|
||||
type CustomTranslationKeys = NestedKeysStripped<CustomTranslationObject>
|
||||
|
||||
const field: Field = {
|
||||
name: 'myField',
|
||||
type: 'text',
|
||||
label: (
|
||||
{ t }: { t: TFunction<CustomTranslationKeys | DefaultTranslationKeys> }, // The generic passed to TFunction does not automatically merge the custom translations with the default translations. We need to merge them ourselves here
|
||||
) => t('fields:addLabel'),
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,13 +3,13 @@ title: Localization
|
||||
label: Localization
|
||||
order: 50
|
||||
desc: Add and maintain as many locales as you need by adding Localization to your Payload config, set options for default locale, fallbacks, fields and more.
|
||||
keywords: localization, internationalization, i18n, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: localization, internationalization, i18n, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload features deep field-based localization support. Maintaining as many locales as you need is easy. All
|
||||
localization support is opt-in by default. To do so, follow the two steps below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Enabling in the Payload config
|
||||
## Enabling in the Payload config
|
||||
|
||||
Add the `localization` property to your Payload config to enable localization project-wide. You'll need to provide a
|
||||
list of all locales that you'd like to support as well as set a few other options.
|
||||
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ right-to-left), and `fallbackLocale` property. The locale codes do not need to b
|
||||
to define how to represent your locales. Common patterns are to use two-letter ISO 639 language codes or four-letter
|
||||
language and country codes (ISO 3166‑1) such as `en-US`, `en-UK`, `es-MX`, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
### Locale Properties:
|
||||
## Locale Object Properties
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| -------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
@@ -125,7 +125,7 @@ Boolean enabling "fallback" locale functionality. If a document is requested in
|
||||
localized value corresponding to the requested locale, then if this property is enabled, the document will automatically
|
||||
fall back to the fallback locale value. If this property is not enabled, the value will not be populated.
|
||||
|
||||
### Field by field localization
|
||||
## Field by field localization
|
||||
|
||||
Payload localization works on a **field** level—not a document level. In addition to configuring the base Payload config
|
||||
to support localization, you need to specify each field that you would like to localize.
|
||||
@@ -166,12 +166,12 @@ and `block`s.
|
||||
strategy.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Retrieving localized docs
|
||||
## Retrieving localized docs
|
||||
|
||||
When retrieving documents, you can specify which locale you'd like to receive as well as which fallback locale should be
|
||||
used.
|
||||
|
||||
##### REST API
|
||||
#### REST API
|
||||
|
||||
REST API locale functionality relies on URL query parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -190,7 +190,7 @@ valid locale as provided to your base Payload config, or `'null'`, `'false'`, or
|
||||
fetch('https://localhost:3000/api/pages?locale=es&fallback-locale=none');
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### GraphQL API
|
||||
#### GraphQL API
|
||||
|
||||
In the GraphQL API, you can specify `locale` and `fallbackLocale` args to all relevant queries and mutations.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -218,7 +218,7 @@ query {
|
||||
arguments in nested related document queries.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
##### Local API
|
||||
#### Local API
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify `locale` as well as `fallbackLocale` within the Local API as well as properties on the `options`
|
||||
argument. The `locale` property will accept any valid locale, and the `fallbackLocale` property will accept any valid
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: The Payload Config
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: The Payload config is central to everything that Payload does, from adding custom React components, to modifying collections, controlling localization and much more.
|
||||
keywords: overview, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: overview, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload is a _config-based_, code-first CMS and application framework. The Payload config is central to everything that Payload does. It scaffolds the data that Payload stores as well as maintains custom React components, hook logic, custom validations, and much more.
|
||||
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Payload is a _config-based_, code-first CMS and application framework. The Paylo
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Important:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
This file is included in the Payload admin bundle, so make sure you do not embed any sensitive
|
||||
The serializable portions of this config are included in the Payload Admin bundle, so make sure you do not embed any sensitive
|
||||
information.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ Payload is a _config-based_, code-first CMS and application framework. The Paylo
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| --------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `admin` \* | Base Payload admin configuration. Specify bundler\*, custom components, control metadata, set the Admin user collection, and [more](/docs/admin/overview#admin-options). Required. |
|
||||
| `admin` \* | Base Payload admin configuration. Specify, custom components, control metadata, set the Admin user collection, and [more](/docs/admin/overview#admin-options). Required. |
|
||||
| `editor` \* | Rich Text Editor which will be used by richText fields. Required. |
|
||||
| `db` \* | Database Adapter which will be used by Payload. Read more [here](/docs/database/overview). Required. |
|
||||
| `serverURL` | A string used to define the absolute URL of your app including the protocol, for example `https://example.com`. No paths allowed, only protocol, domain and (optionally) port |
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +38,6 @@ Payload is a _config-based_, code-first CMS and application framework. The Paylo
|
||||
| `upload` | Base Payload upload configuration. [More](/docs/upload/overview#payload-wide-upload-options). |
|
||||
| `routes` | Control the routing structure that Payload binds itself to. Specify `admin`, `api`, `graphQL`, and `graphQLPlayground`. |
|
||||
| `email` | Base email settings to allow Payload to generate email such as Forgot Password requests and other requirements. [More](/docs/email/overview#configuration) |
|
||||
| `express` | Express-specific middleware options such as compression and JSON parsing. [More](/docs/configuration/express) |
|
||||
| `debug` | Enable to expose more detailed error information. |
|
||||
| `telemetry` | Disable Payload telemetry by passing `false`. [More](/docs/configuration/overview#telemetry) |
|
||||
| `rateLimit` | Control IP-based rate limiting for all Payload resources. Used to prevent DDoS attacks and [more](/docs/production/preventing-abuse#rate-limiting-requests). |
|
||||
@@ -49,23 +48,17 @@ Payload is a _config-based_, code-first CMS and application framework. The Paylo
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
#### Simple example
|
||||
### Simple example
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { mongooseAdapter } from '@payloadcms/db-mongodb'
|
||||
import { postgresAdapter } from '@payloadcms/db-postgres' // beta
|
||||
|
||||
import { viteBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-vite'
|
||||
import { webpackBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-webpack'
|
||||
|
||||
import { lexicalEditor } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical' // beta
|
||||
import { slateEditor } from '@payloadcms/richtext-slate'
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
bundler: webpackBundler(), // or viteBundler()
|
||||
},
|
||||
db: mongooseAdapter({}) // or postgresAdapter({}),
|
||||
editor: lexicalEditor({}) // or slateEditor({})
|
||||
collections: [
|
||||
@@ -106,11 +99,11 @@ export default buildConfig({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Full example config
|
||||
### Full example config
|
||||
|
||||
You can see a full [example config](https://github.com/payloadcms/public-demo/blob/master/src/payload/payload.config.ts) in the Public Demo source code on GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using environment variables in your config
|
||||
## Using environment variables in your config
|
||||
|
||||
We suggest using the `dotenv` package to handle environment variables alongside of Payload. All that's necessary to do is to require the package as high up in your application as possible (for example, at the top of your `server.js` file), and ensure that it can find an `.env` file that you create.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -139,10 +132,10 @@ project-name
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
If you use an environment variable to configure any properties that are required for the Admin
|
||||
panel to function (ex. serverURL or any routes), you need to make sure that your Admin panel code
|
||||
can access it. [Click here](/docs/admin/webpack#admin-environment-vars) for more info.
|
||||
can access it. [Click here](/docs/admin/environment-vars) for more info.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Customizing & Automating Config Location Detection
|
||||
## Customizing & Automating Config Location Detection
|
||||
|
||||
Payload is designed to automatically locate your configuration file. By default, it will first look in the root of your current working directory for a file named `payload.config.js` or `payload.config.ts` if you're using TypeScript.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -152,7 +145,7 @@ In production mode, Payload will first attempt to find the config file in the ou
|
||||
|
||||
Please ensure your `tsconfig.json` is properly configured if you want Payload to accurately auto-detect your configuration file location. If `tsconfig.json` does not exist or doesn't specify `rootDir` or `outDir`, Payload will default to the current working directory.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Overriding the Config Location
|
||||
### Overriding the Config Location
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the above automated detection, you can specify your own location for the Payload config file. This is done by using the environment variable `PAYLOAD_CONFIG_PATH`. The path you provide via this environment variable can either be absolute or relative to your current working directory. This can be useful in situations where your Payload config is not in a standard location, or you wish to switch between multiple configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -168,11 +161,11 @@ In addition to the above automated detection, you can specify your own location
|
||||
|
||||
When `PAYLOAD_CONFIG_PATH` is set, Payload will use this path to load the configuration, bypassing all automated detection.
|
||||
|
||||
### Developing within the Config
|
||||
## Developing within the Config
|
||||
|
||||
Payload comes with `isomorphic-fetch` installed which means that even in Node, you can use the `fetch` API just as you would within the browser. No need to import `axios` or similar, unless you want to!
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
You can import config types as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -190,7 +183,7 @@ import { SanitizedConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
// Generally, this is only used internally by Payload.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Telemetry
|
||||
## Telemetry
|
||||
|
||||
Payload collects **completely anonymous** telemetry data about general usage. This data is super important to us and helps us accurately understand how we're growing and what we can do to build the software into everything that it can possibly be. The telemetry that we collect also help us demonstrate our growth in an accurate manner, which helps us as we seek investment to build and scale our team. If we can accurately demonstrate our growth, we can more effectively continue to support Payload as free and open-source software. To opt out of telemetry, you can pass `telemetry: false` within your Payload config.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
title: Migrations
|
||||
label: Migrations
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
keywords: database, migrations, ddl, sql, mongodb, postgres, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, typescript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: database, migrations, ddl, sql, mongodb, postgres, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, typescript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
desc: Payload features first-party database migrations all done in TypeScript.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ Ensure you have an npm script called "payload" in your `package.json` file.
|
||||
because Payload should not be globally installed on your system.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Migration file contents
|
||||
## Migration file contents
|
||||
|
||||
Payload stores all created migrations in a folder that you can specify. By default, migrations are stored
|
||||
in `./src/migrations`.
|
||||
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ export async function down({ payload, req }: MigrateDownArgs): Promise<void> {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Migrations Directory
|
||||
## Migrations Directory
|
||||
|
||||
Each DB adapter has an optional property `migrationDir` where you can override where you want your migrations to be
|
||||
stored/read. If this is not specified, Payload will check the default and possibly make a best effort to find your
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: MongoDB
|
||||
label: MongoDB
|
||||
order: 40
|
||||
desc: Payload has supported MongoDB natively since we started. The flexible nature of MongoDB lends itself well to Payload's powerful fields.
|
||||
keywords: MongoDB, documentation, typescript, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: MongoDB, documentation, typescript, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To use Payload with MongoDB, install the package `@payloadcms/db-mongodb`. It will come with everything you need to
|
||||
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ export default buildConfig({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Options
|
||||
## Options
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| -------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --- |
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ export default buildConfig({
|
||||
| `migrationDir` | Customize the directory that migrations are stored. |
|
||||
| `transactionOptions` | An object with configuration properties used in [transactions](https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/transactions/) or `false` which will disable the use of transactions. | |
|
||||
|
||||
### Access to Mongoose models
|
||||
## Access to Mongoose models
|
||||
|
||||
After Payload is initialized, this adapter exposes all of your Mongoose models and they are available for you to work
|
||||
with directly.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
title: Database
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
keywords: database, mongodb, postgres, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, typescript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: database, mongodb, postgres, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, typescript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
desc: With Payload, you bring your own database and own your data. You have full control.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ To use a specific database adapter, you need to install it and configure it acco
|
||||
|
||||
There are several factors to consider when choosing which database technology and hosting option is right for your project and workload. Payload can theoretically support any database, but it's up to you to decide which database to use.
|
||||
|
||||
#### When to use MongoDB
|
||||
### When to use MongoDB
|
||||
|
||||
If your project has a lot of dynamic fields, and you are comfortable with allowing Payload to enforce data integrity across your documents, MongoDB is a great choice. With it, your Payload documents are stored as _one_ document in your database—no matter if you have localization enabled, how many block or array fields you have, etc. This means that the shape of your data in your database will very closely reflect your field schema, and there is minimal complexity involved in storing or retrieving your data.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ You should prefer MongoDB if:
|
||||
- Most (or everything) in your project is localized
|
||||
- You leverage a lot of array fields, block fields, or `hasMany` select fields and similar
|
||||
|
||||
#### When to use a relational DB
|
||||
### When to use a relational DB
|
||||
|
||||
Many projects might call for more rigid database architecture where the shape of your data is strongly enforced at the database level. For example, if you know the shape of your data and it's relatively "flat", and you don't anticipate it to change often, your workload might suit relational databases like Postgres very well.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ You should prefer a relational DB like Postgres if:
|
||||
- You require enforced data consistency at the database level
|
||||
- You have a lot of relationships between collections and require relationships to be enforced
|
||||
|
||||
#### Differences in Payload features
|
||||
### Differences in Payload features
|
||||
|
||||
It's important to note that almost everything Payload does is available in all of our officially supported database adapters, including localization, arrays, blocks, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Postgres
|
||||
label: Postgres
|
||||
order: 50
|
||||
desc: Payload supports Postgres through an officially supported Drizzle database adapter.
|
||||
keywords: Postgres, documentation, typescript, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: Postgres, documentation, typescript, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To use Payload with Postgres, install the package `@payloadcms/db-postgres`. It leverages Drizzle ORM and `node-postgres` to interact with a Postgres database that you provide.
|
||||
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ export default buildConfig({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Options
|
||||
## Options
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
|-----------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ export default buildConfig({
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Access to Drizzle
|
||||
## Access to Drizzle
|
||||
|
||||
After Payload is initialized, this adapter will expose the full power of Drizzle to you for use if you need it.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ You can access Drizzle as follows:
|
||||
payload.db.drizzle
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Tables, relations, and enums
|
||||
## Tables, relations, and enums
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to exposing Drizzle directly, all of the tables, Drizzle relations, and enum configs are exposed for you via the `payload.db` property as well.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ In addition to exposing Drizzle directly, all of the tables, Drizzle relations,
|
||||
- Enums - `payload.db.enums`
|
||||
- Relations - `payload.db.relations`
|
||||
|
||||
### Prototyping in development mode
|
||||
## Prototyping in development mode
|
||||
|
||||
Drizzle exposes two ways to work locally in development mode.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ You will be warned if any changes that you make will entail data loss while in d
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can disable `push` and rely solely on migrations to keep your local database in sync with your Payload config.
|
||||
|
||||
### Migration workflows
|
||||
## Migration workflows
|
||||
|
||||
Migrations are extremely powerful thanks to the seamless way that Payload and Drizzle work together. Let's take the following scenario:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
title: Transactions
|
||||
label: Transactions
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
keywords: database, transactions, sql, mongodb, postgres, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, typescript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: database, transactions, sql, mongodb, postgres, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, typescript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
desc: Database transactions are fully supported within Payload.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ const afterChange: CollectionAfterChangeHook = async ({ req }) => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Async Hooks with Transactions
|
||||
## Async Hooks with Transactions
|
||||
|
||||
Since Payload hooks can be async and be written to not await the result, it is possible to have an incorrect success response returned on a request that is rolled back. If you have a hook where you do not `await` the result, then you should **not** pass the `req.transactionID`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -59,7 +59,7 @@ const afterChange: CollectionAfterChangeHook = async ({ req }) => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Direct Transaction Access
|
||||
## Direct Transaction Access
|
||||
|
||||
When writing your own scripts or custom endpoints, you may wish to have direct control over transactions. This is useful for interacting with your database outside of Payload's local API.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,166 +2,165 @@
|
||||
title: Email Functionality
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: Payload uses NodeMailer to allow you to send emails smoothly from your app. Set up email functions such as password resets, order confirmations and more.
|
||||
keywords: email, overview, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
desc: Payload uses an adapter pattern to enable email functionality. Set up email functions such as password resets, order confirmations and more.
|
||||
keywords: email, overview, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Introduction
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
Payload comes ready to send your application's email. Whether you simply need built-in password reset
|
||||
email to work or you want customers to get an order confirmation email, you're almost there. Payload makes use of
|
||||
[NodeMailer](https://nodemailer.com) for email and won't get in your way for those already familiar.
|
||||
Payload has a few email adapters that can be imported to enable email functionality. The [@payloadcms/email-nodemailer](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@payloadcms/email-nodemailer) package will be the package most will want to install. This package provides an easy way to use [Nodemailer](https://nodemailer.com) for email and won't get in your way for those already familiar.
|
||||
|
||||
For email to send from your Payload server, some configuration is required. The settings you provide will be set
|
||||
in the `email` property object of your payload init call. Payload will make use of the transport that you have configured for it for things like reset password or verifying new user accounts and email send methods are available to you as well on your payload instance.
|
||||
The email adapter should be passed into the `email` property of the Payload config. This will allow Payload to send emails for things like password resets, new user verification, and any other email sending needs you may have.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration
|
||||
## Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
**Three ways to set it up**
|
||||
### Default Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Default**: When email is not needed, a mock email handler will be created and used when nothing is provided. This is ideal for development environments and can be changed later when ready to [go to production](/docs/production/deployment).
|
||||
1. **Recommended**: Set the `transportOptions` and Payload will do the set up for you.
|
||||
1. **Advanced**: The `transport` object can be assigned a nodemailer transport object set up in your server scripts and given for Payload to use.
|
||||
When email is not needed or desired, Payload will log a warning on startup notifying that email is not configured. A warning message will also be logged on any attempt to send an email.
|
||||
|
||||
The following options are configurable in the `email` property object as part of the options object when calling payload.init().
|
||||
### Email Adapter
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`fromName`** \* | The name part of the From field that will be seen on the delivered email |
|
||||
| **`fromAddress`** \* | The email address part of the From field that will be used when delivering email |
|
||||
| **`transport`** | The NodeMailer transport object for when you want to do it yourself, not needed when transportOptions is set |
|
||||
| **`transportOptions`** | An object that configures the transporter that Payload will create. For all the available options see the [NodeMailer documentation](https://nodemailer.com) or see the examples below |
|
||||
| **`logMockCredentials`** | If set to true and no transport/transportOptions, ethereal credentials will be logged to console on startup |
|
||||
An email adapter will require at least the following fields:
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| --------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`defaultFromName`** \* | The name part of the From field that will be seen on the delivered email |
|
||||
| **`defaultFromAddress`** \* | The email address part of the From field that will be used when delivering email |
|
||||
|
||||
### Use SMTP
|
||||
|
||||
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) options can be passed in using the `transportOptions` object on the `email` options. See the [NodeMailer SMTP documentation](https://nodemailer.com/smtp/) for more information, including details on when `secure` should and should not be set to `true`.
|
||||
### Official Email Adapters
|
||||
|
||||
| Name | Package | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Nodemailer | [@payloadcms/email-nodemailer](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@payloadcms/email-nodemailer) | Use any [Nodemailer transport](https://nodemailer.com/transports), including SMTP, Resend, SendGrid, and more. This was provided by default in Payload 2.x. This is the easiest migration path. |
|
||||
| Resend | [@payloadcms/email-resend](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@payloadcms/email-resend) | Resend email via their REST API. This is preferred for serverless platforms such as Vercel because it is much more lightweight than the nodemailer adapter. |
|
||||
|
||||
## Nodemailer Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ---------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`transport`** | The Nodemailer transport object for when you want to do it yourself, not needed when transportOptions is set |
|
||||
| **`transportOptions`** | An object that configures the transporter that Payload will create. For all the available options see the [Nodemailer documentation](https://nodemailer.com) or see the examples below |
|
||||
|
||||
## Use SMTP
|
||||
|
||||
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) options can be passed in using the `transportOptions` object on the `email` options. See the [Nodemailer SMTP documentation](https://nodemailer.com/smtp/) for more information, including details on when `secure` should and should not be set to `true`.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example email options using SMTP:**
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
payload.init({
|
||||
email: {
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { nodemailerAdapter } from '@payloadcms/email-nodemailer'
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
email: nodemailerAdapter({
|
||||
defaultFromAddress: 'info@payloadcms.com',
|
||||
defaultFromName: 'Payload',
|
||||
// Nodemailer transportOptions
|
||||
transportOptions: {
|
||||
host: process.env.SMTP_HOST,
|
||||
port: 587,
|
||||
auth: {
|
||||
user: process.env.SMTP_USER,
|
||||
pass: process.env.SMTP_PASS,
|
||||
},
|
||||
port: Number(process.env.SMTP_HOST),
|
||||
secure: Number(process.env.SMTP_PORT) === 465, // true for port 465, false (the default) for 587 and others
|
||||
requireTLS: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
fromName: 'hello',
|
||||
fromAddress: 'hello@example.com',
|
||||
},
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
}),
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
It is best practice to avoid saving credentials or API keys directly in your code, use
|
||||
[environment variables](/docs/configuration/overview#using-environment-variables-in-your-config).
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Use an email service
|
||||
|
||||
Many third party mail providers are available and offer benefits beyond basic SMTP. As an example, your payload init could look like this if you wanted to use SendGrid.com, though the same approach would work for any other [NodeMailer transports](https://nodemailer.com/transports/) shown here or provided by another third party.
|
||||
**Example email options using nodemailer.createTransport:**
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import payload from 'payload'
|
||||
import nodemailerSendgrid from 'nodemailer-sendgrid'
|
||||
|
||||
const sendGridAPIKey = process.env.SENDGRID_API_KEY
|
||||
|
||||
payload.init({
|
||||
...(sendGridAPIKey
|
||||
? {
|
||||
email: {
|
||||
transportOptions: nodemailerSendgrid({
|
||||
apiKey: sendGridAPIKey,
|
||||
}),
|
||||
fromName: 'Admin',
|
||||
fromAddress: 'admin@example.com',
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
: {}),
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Use a custom NodeMailer transport
|
||||
|
||||
To take full control of the mail transport you may wish to use `nodemailer.createTransport()` on your server and provide it to Payload init.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import payload from 'payload'
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { nodemailerAdapter } from '@payloadcms/email-nodemailer'
|
||||
import nodemailer from 'nodemailer'
|
||||
|
||||
const payload = require('payload')
|
||||
const nodemailer = require('nodemailer')
|
||||
|
||||
const transport = await nodemailer.createTransport({
|
||||
host: process.env.SMTP_HOST,
|
||||
port: 587,
|
||||
auth: {
|
||||
user: process.env.SMTP_USER,
|
||||
pass: process.env.SMTP_PASS,
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
payload.init({
|
||||
email: {
|
||||
fromName: 'Admin',
|
||||
fromAddress: 'admin@example.com',
|
||||
transport,
|
||||
},
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
email: nodemailerAdapter({
|
||||
defaultFromAddress: 'info@payloadcms.com',
|
||||
defaultFromName: 'Payload',
|
||||
// Any Nodemailer transport can be used
|
||||
transport: nodemailer.createTransport({
|
||||
host: process.env.SMTP_HOST,
|
||||
port: 587,
|
||||
auth: {
|
||||
user: process.env.SMTP_USER,
|
||||
pass: process.env.SMTP_PASS,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}),
|
||||
}),
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Sending Mail
|
||||
**Custom Transport:**
|
||||
|
||||
With a working transport you can call it anywhere you have access to payload by calling `payload.sendEmail(message)`. The `message` will contain the `to`, `subject` and `email` or `text` for the email being sent. To see all available message configuration options see [NodeMailer](https://nodemailer.com/message).
|
||||
You also have the ability to bring your own nodemailer transport. This is an example of using the SendGrid nodemailer transport.
|
||||
|
||||
### Mock transport
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Payload uses a mock implementation that only sends mail to the [ethereal](https://ethereal.email) capture service that will never reach a user's inbox. While in development you may wish to make use of the captured messages which is why the payload output during server output helpfully logs this out on the server console.
|
||||
|
||||
To see ethereal credentials, add `logMockCredentials: true` to the email options. This will cause them to be logged to console on startup.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
payload.init({
|
||||
email: {
|
||||
fromName: 'Admin',
|
||||
fromAddress: 'admin@example.com',
|
||||
logMockCredentials: true, // Optional
|
||||
},
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { nodemailerAdapter } from '@payloadcms/email-nodemailer'
|
||||
import nodemailerSendgrid from 'nodemailer-sendgrid'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
email: nodemailerAdapter({
|
||||
defaultFromAddress: 'info@payloadcms.com',
|
||||
defaultFromName: 'Payload',
|
||||
transportOptions: nodemailerSendgrid({
|
||||
apiKey: process.env.SENDGRID_API_KEY,
|
||||
}),
|
||||
}),
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Console output when starting payload with a mock email instance and logMockCredentials: true**
|
||||
During development, if you pass nothing to `nodemailerAdapter`, it will use the [ethereal.email](https://ethereal.email) service.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[06:37:21] INFO (payload): Starting Payload...
|
||||
[06:37:22] INFO (payload): Payload Demo Initialized
|
||||
[06:37:22] INFO (payload): listening on 3000...
|
||||
[06:37:22] INFO (payload): Connected to MongoDB server successfully!
|
||||
[06:37:23] INFO (payload): E-mail configured with mock configuration
|
||||
[06:37:23] INFO (payload): Log into mock email provider at https://ethereal.email
|
||||
[06:37:23] INFO (payload): Mock email account username: hhav5jw7doo4euev@ethereal.email
|
||||
[06:37:23] INFO (payload): Mock email account password: VNdGcvDZeyEhtuPBqf
|
||||
This will log the ethereal.email details to console on startup.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { nodemailerAdapter } from '@payloadcms/email-nodemailer'
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
email: nodemailerAdapter(),
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The mock email handler is used when payload is started with neither `transport` or `transportOptions` to know how to deliver email.
|
||||
## Resend Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
The randomly generated email account username and password will be different each time the Payload
|
||||
server starts.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
The Resend adapter requires an API key to be passed in the options. This can be found in the Resend dashboard. This is the preferred package if you are deploying on Vercel because this is much more lightweight than the Nodemailer adapter.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using multiple mail providers
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------ | ----------------------------------- |
|
||||
| apiKey | The API key for the Resend service. |
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { resendAdapter } from '@payloadcms/email-resend'
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
email: resendAdapter({
|
||||
defaultFromAddress: 'dev@payloadcms.com',
|
||||
defaultFromName: 'Payload CMS',
|
||||
apiKey: process.env.RESEND_API_KEY || '',
|
||||
}),
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Sending Mail
|
||||
|
||||
With a working transport you can call it anywhere you have access to payload by calling `payload.sendEmail(message)`. The `message` will contain the `to`, `subject` and `html` or `text` for the email being sent. Other options are also available and can be seen in the sendEmail args. Support for these will depend on the adapter being used.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Example of sending an email
|
||||
const email = await payload.sendEmail({
|
||||
to: 'test@example.com',
|
||||
subject: 'This is a test email',
|
||||
text: 'This is my message body',
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Using multiple mail providers
|
||||
|
||||
Payload supports the use of a single transporter of email, but there is nothing stopping you from having more. Consider a use case where sending bulk email is handled differently than transactional email and could be done using a [hook](/docs/hooks/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
40
docs/examples/overview.mdx
Normal file
40
docs/examples/overview.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Examples
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc:
|
||||
keywords: example, examples, starter, boilerplate, template, templates
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload provides a vast array of examples to help you get started with your project no matter what you are working on. These examples are designed to be easy to get up and running, and to be easy to understand. They showcase nothing more than the specific features being demonstrated so you can easily decipher what is going on.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples are changing every day, so be sure to check back often to see what new examples have been added. If you have a specific example you would like to see, please feel free to start a new [Discussion](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/discussions) or open a new [PR](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/pulls) to add it yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Auth](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/auth)
|
||||
- [Custom Server](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/custom-server)
|
||||
- [Draft Preview](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/draft-preview)
|
||||
- [Email](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/email)
|
||||
- [Form Builder](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/form-builder)
|
||||
- [Hierarchy](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/hierarchy)
|
||||
- [Live Preview](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/live-preview)
|
||||
- [Multi-tenant](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/multi-tenant)
|
||||
- [Nested Docs](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/nested-docs)
|
||||
- [Redirects](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/redirects)
|
||||
- [Tailwind / Shadcn-ui](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/tailwind-shadcn-ui)
|
||||
- [Tests](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/testing)
|
||||
- [Virtual Fields](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/virtual-fields)
|
||||
- [White-label Admin UI](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/whitelabel)
|
||||
|
||||
When necessary, some examples include a front-end. Examples that require a front-end share this folder structure:
|
||||
|
||||
```plaintext
|
||||
example/
|
||||
├── payload/
|
||||
├── next-app/
|
||||
├── next-pages/
|
||||
├── react-router/
|
||||
├── vue/
|
||||
├── svelte/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...where `payload` is your Payload project, and the other directories are dedicated to their respective front-end framework. We are adding new examples every day, so if your framework of choice is not yet supported in any particular example, please feel free to start a new [Discussion](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/discussions) or open a new [PR](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/pulls) to add it yourself.
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Array Field
|
||||
label: Array
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
desc: Array fields are intended for sets of repeating fields, that you define. Learn how to use array fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: array, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: array, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ keywords: array, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Managemen
|
||||
- Navigational structures where editors can specify nav items containing pages ([relationship field](/docs/fields/relationship)), an "open in new tab" [checkbox field](/docs/fields/checkbox)
|
||||
- Event agenda "timeslots" where you need to specify start & end time ([date field](/docs/fields/date)), label ([text field](/docs/fields/text)), and Learn More page [relationship](/docs/fields/relationship)
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ keywords: array, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Managemen
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin Config
|
||||
## Admin Config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), you can adjust the following properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,8 +57,9 @@ In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-conf
|
||||
| ------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`initCollapsed`** | Set the initial collapsed state |
|
||||
| **`components.RowLabel`** | Function or React component to be rendered as the label on the array row. Receives `({ data, index, path })` as args |
|
||||
| **`isSortable`** | Disable order sorting by setting this value to `false` |
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Blocks Field
|
||||
label: Blocks
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
desc: The Blocks field type is a great layout build and can be used to construct any flexible content model. Learn how to use Block fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: blocks, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: blocks, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ keywords: blocks, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Manageme
|
||||
- A form builder tool where available block configs might be `Text`, `Select`, or `Checkbox`.
|
||||
- Virtual event agenda "timeslots" where a timeslot could either be a `Break`, a `Presentation`, or a `BreakoutSession`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Field config
|
||||
## Field config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -49,15 +49,16 @@ keywords: blocks, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Manageme
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin Config
|
||||
## Admin Config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), you can adjust the following properties:
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------- | ------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`initCollapsed`** | Set the initial collapsed state |
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------- | ---------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`initCollapsed`** | Set the initial collapsed state |
|
||||
| **`isSortable`** | Disable order sorting by setting this value to `false` |
|
||||
|
||||
### Block configs
|
||||
## Block configs
|
||||
|
||||
Blocks are defined as separate configs of their own.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -83,7 +84,7 @@ Blocks are defined as separate configs of their own.
|
||||
| **`dbName`** | Custom table name for this block type when using SQL database adapter ([Postgres](/docs/database/postgres)). Auto-generated from slug if not defined.
|
||||
| **`custom`** | Extension point for adding custom data (e.g. for plugins) |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Auto-generated data per block
|
||||
### Auto-generated data per block
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the field data that you define on each block, Payload will store two additional properties on each block:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -95,7 +96,7 @@ The `blockType` is saved as the slug of the block that has been selected.
|
||||
|
||||
The Admin panel provides each block with a `blockName` field which optionally allows editors to label their blocks for better editability and readability.
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.js`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -138,7 +139,7 @@ export const ExampleCollection: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
As you build your own Block configs, you might want to store them in separate files but retain typing accordingly. To do so, you can import and use Payload's `Block` type:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Checkbox Field
|
||||
label: Checkbox
|
||||
order: 40
|
||||
desc: Checkbox field types allow the developer to save a boolean value in the database. Learn how to use Checkbox fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: checkbox, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: checkbox, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>The Checkbox field type saves a boolean in the database.</Banner>
|
||||
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ keywords: checkbox, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Manage
|
||||
caption="Admin panel screenshot of Checkbox field with Text field below"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ keywords: checkbox, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Manage
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ label: Code
|
||||
order: 50
|
||||
desc: The Code field type will store any string in the Database. Learn how to use Code fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
|
||||
keywords: code, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: code, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ keywords: code, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management
|
||||
|
||||
This field uses the `monaco-react` editor syntax highlighting.
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ This field uses the `monaco-react` editor syntax highlighting.
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin Config
|
||||
## Admin Config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), you can adjust the following properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-conf
|
||||
| **`language`** | This property can be set to any language listed [here](https://github.com/microsoft/monaco-editor/tree/main/src/basic-languages). |
|
||||
| **`editorOptions`** | Options that can be passed to the monaco editor, [view the full list](https://microsoft.github.io/monaco-editor/typedoc/interfaces/editor.IDiffEditorConstructionOptions.html). |
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Collapsible Field
|
||||
label: Collapsible
|
||||
order: 60
|
||||
desc: With the Collapsible field, you can place fields within a collapsible layout component that can be collapsed / expanded.
|
||||
keywords: row, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: row, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ keywords: row, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management
|
||||
caption="Admin panel screenshot of a Collapsible field"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| --------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ keywords: row, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin Config
|
||||
## Admin Config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), you can adjust the following properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-conf
|
||||
| ------------------- | ------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`initCollapsed`** | Set the initial collapsed state |
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Date Field
|
||||
label: Date
|
||||
order: 70
|
||||
desc: The Date field type stores a Date in the database. Learn how to use and customize the Date field, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: date, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: date, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ keywords: date, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management
|
||||
|
||||
This field uses [`react-datepicker`](https://www.npmjs.com/package/react-datepicker) for the Admin panel component.
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ This field uses [`react-datepicker`](https://www.npmjs.com/package/react-datepic
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin Config
|
||||
## Admin Config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), you can customize the following fields that will adjust how the component displays in the admin panel via the `date` property.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-conf
|
||||
|
||||
_\* This property is passed directly to [react-datepicker](https://github.com/Hacker0x01/react-datepicker/blob/master/docs/datepicker.md). ._
|
||||
|
||||
#### Display Format and Picker Appearance
|
||||
### Display Format and Picker Appearance
|
||||
|
||||
These properties only affect how the date is displayed in the UI. The full date is always stored in the format `YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.SSSZ` (e.g. `1999-01-01T8:00:00.000+05:00`).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ These properties only affect how the date is displayed in the UI. The full date
|
||||
|
||||
When only `pickerAppearance` is set, an equivalent format will be rendered in the date field cell. To overwrite this format, set `displayFormat`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Email Field
|
||||
label: Email
|
||||
order: 80
|
||||
desc: The Email field enforces that the value provided is a valid email address. Learn how to use Email fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: email, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: email, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>The Email field enforces that the value provided is a valid email address.</Banner>
|
||||
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ keywords: email, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Managemen
|
||||
caption="Admin panel screenshot of an Email field"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ keywords: email, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Managemen
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin config
|
||||
## Admin config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), this field type allows for the following `admin` properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ Set this property to define a placeholder string for the field.
|
||||
|
||||
Set this property to a string that will be used for browser autocomplete.
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Group Field
|
||||
label: Group
|
||||
order: 90
|
||||
desc: The Group field allows other fields to be nested under a common property. Learn how to use Group fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: group, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: group, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ keywords: group, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Managemen
|
||||
caption="Admin panel screenshot of a Group field"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ keywords: group, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Managemen
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin config
|
||||
## Admin config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), the Group allows for the following admin property:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-conf
|
||||
|
||||
Set this property to `true` to hide this field's gutter within the admin panel. The field gutter is rendered as a vertical line and padding, but often if this field is nested within a Group, Block, or Array, you may want to hide the gutter.
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ label: JSON
|
||||
order: 50
|
||||
desc: The JSON field type will store any string in the Database. Learn how to use JSON fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
|
||||
keywords: json, jsonSchema, schema, validation, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: json, jsonSchema, schema, validation, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ keywords: json, jsonSchema, schema, validation, fields, config, configuration, d
|
||||
|
||||
This field uses the `monaco-react` editor syntax highlighting.
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ This field uses the `monaco-react` editor syntax highlighting.
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin Config
|
||||
## Admin Config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), you can adjust the following properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-conf
|
||||
| ------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`editorOptions`** | Options that can be passed to the monaco editor, [view the full list](https://microsoft.github.io/monaco-editor/typedoc/variables/editor.EditorOptions.html). |
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -69,14 +69,14 @@ export const ExampleCollection: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### JSON Schema Validation
|
||||
## JSON Schema Validation
|
||||
|
||||
Payload JSON fields fully support the [JSON schema](https://json-schema.org/) standard. By providing a schema in your field config, the editor will be guided in the admin UI, getting typeahead for properties and their formats automatically. When the document is saved, the default validation will prevent saving any invalid data in the field according to the schema in your config.
|
||||
|
||||
If you only provide a URL to a schema, Payload will fetch the desired schema if it is publicly available. If not, it is recommended to add the schema directly to your config or import it from another file so that it can be implemented consistently in your project.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Local JSON Schema
|
||||
### Local JSON Schema
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ export const ExampleCollection: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
// Attempting to create {"foo": "not-bar"} will throw an error
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Remote JSON Schema
|
||||
### Remote JSON Schema
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Number Field
|
||||
label: Number
|
||||
order: 100
|
||||
desc: Number fields store and validate numeric data. Learn how to use and format Number fields, see examples and Number field options.
|
||||
keywords: number, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: number, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ keywords: number, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Manageme
|
||||
caption="Admin panel screenshot of a Number field"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
|--------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ keywords: number, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Manageme
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin config
|
||||
## Admin config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), this field type allows for the following `admin` properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ Set this property to define a placeholder string for the field.
|
||||
|
||||
Set this property to a string that will be used for browser autocomplete.
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Fields Overview
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: Fields are the building blocks of Payload, find out how to add or remove a field, change field type, add hooks, define access control and validation.
|
||||
keywords: overview, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: overview, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ export const Page: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Field types
|
||||
## Field types
|
||||
|
||||
- [Array](/docs/fields/array) - for repeating content, supports nested fields
|
||||
- [Blocks](/docs/fields/blocks) - block-based fields, allowing powerful layout creation
|
||||
@@ -60,19 +60,19 @@ export const Page: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
- [Upload](/docs/fields/upload) - allows local file and image upload
|
||||
- [UI](/docs/fields/ui) - inject your own custom components and do whatever you need
|
||||
|
||||
### Field-level hooks
|
||||
## Field-level hooks
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most powerful parts about Payload is its ability for you to define field-level hooks that can control the logic of your fields to a fine-grained level. for more information about how to define field hooks, [click here](/docs/hooks/overview#field-hooks).
|
||||
|
||||
### Field-level access control
|
||||
## Field-level access control
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to being able to define access control on a document-level, you can define extremely granular permissions on a field by field level. For more information about field-level access control, [click here](/docs/access-control/overview#fields).
|
||||
|
||||
### Field names
|
||||
## Field names
|
||||
|
||||
Some fields use their `name` property as a unique identifier to store and retrieve from the database. `__v`, `salt`, and `hash` are all reserved field names which are sanitized from Payload's config and cannot be used.
|
||||
|
||||
### Validation
|
||||
## Validation
|
||||
|
||||
Field validation is enforced automatically based on the field type and other properties such as `required` or `min` and `max` value constraints on certain field types. This default behavior can be replaced by providing your own validate function for any field. It will be used on both the frontend and the backend, so it should not rely on any Node-specific packages. The validation function can be either synchronous or asynchronous and expects to return either `true` or a string error message to display in both API responses and within the Admin panel.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ There are two arguments available to custom validation functions.
|
||||
| `user` | An object containing the currently authenticated user |
|
||||
| `payload` | If the `validate` function is being executed on the server, Payload will be exposed for easily running local operations. |
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
@@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ const field: Field = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Customizable ID
|
||||
## Customizable ID
|
||||
|
||||
Collections ID fields are generated automatically by default. An explicit `id` field can be declared in the `fields` array to override this behavior.
|
||||
Users are then required to provide a custom ID value when creating a record through the Admin UI or API.
|
||||
@@ -159,29 +159,31 @@ Example:
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin config
|
||||
## Admin config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to each field's base configuration, you can define specific traits and properties for fields that only have effect on how they are rendered in the Admin panel. The following properties are available for all fields within the `admin` property:
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `condition` | You can programmatically show / hide fields based on what other fields are doing. [Click here](#conditional-logic) for more info. |
|
||||
| `components` | All field components can be completely and easily swapped out for custom components that you define. [Click here](#custom-components) for more info. |
|
||||
| `description` | Helper text to display with the field to provide more information for the editor user. [Click here](#description) for more info. |
|
||||
| `position` | Specify if the field should be rendered in the sidebar by defining `position: 'sidebar'`. |
|
||||
| `width` | Restrict the width of a field. you can pass any string-based value here, be it pixels, percentages, etc. This property is especially useful when fields are nested within a `Row` type where they can be organized horizontally. |
|
||||
| `style` | Attach raw CSS style properties to the root DOM element of a field. |
|
||||
| `className` | Attach a CSS class name to the root DOM element of a field. |
|
||||
| `readOnly` | Setting a field to `readOnly` has no effect on the API whatsoever but disables the admin component's editability to prevent editors from modifying the field's value. |
|
||||
| `disabled` | If a field is `disabled`, it is completely omitted from the Admin panel. |
|
||||
| `disableBulkEdit` | Set `disableBulkEdit` to `true` to prevent fields from appearing in the select options when making edits for multiple documents. |
|
||||
| `hidden` | Setting a field's `hidden` property on its `admin` config will transform it into a `hidden` input type. Its value will still submit with the Admin panel's requests, but the field itself will not be visible to editors. |
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `condition` | You can programmatically show / hide fields based on what other fields are doing. [Click here](#conditional-logic) for more info. |
|
||||
| `components` | All field components can be completely and easily swapped out for custom components that you define. [Click here](#custom-components) for more info. |
|
||||
| `description` | Helper text to display with the field to provide more information for the editor user. [Click here](#description) for more info. |
|
||||
| `position` | Specify if the field should be rendered in the sidebar by defining `position: 'sidebar'`. |
|
||||
| `width` | Restrict the width of a field. you can pass any string-based value here, be it pixels, percentages, etc. This property is especially useful when fields are nested within a `Row` type where they can be organized horizontally. |
|
||||
| `style` | Attach raw CSS style properties to the root DOM element of a field. |
|
||||
| `className` | Attach a CSS class name to the root DOM element of a field. |
|
||||
| `readOnly` | Setting a field to `readOnly` has no effect on the API whatsoever but disables the admin component's editability to prevent editors from modifying the field's value. |
|
||||
| `disabled` | If a field is `disabled`, it is completely omitted from the Admin panel. |
|
||||
| `disableBulkEdit` | Set `disableBulkEdit` to `true` to prevent fields from appearing in the select options when making edits for multiple documents. |
|
||||
| `disableListColumn` | Set `disableListColumn` to `true` to prevent fields from appearing in the list view column selector. |
|
||||
| `disableListFilter` | Set `disableListFilter` to `true` to prevent fields from appearing in the list view filter options. |
|
||||
| `hidden` | Setting a field's `hidden` property on its `admin` config will transform it into a `hidden` input type. Its value will still submit with the Admin panel's requests, but the field itself will not be visible to editors. |
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom components
|
||||
## Custom components
|
||||
|
||||
All Payload fields support the ability to swap in your own React components with ease. For more information, including examples, [click here](/docs/admin/components#fields).
|
||||
|
||||
### Conditional logic
|
||||
## Conditional logic
|
||||
|
||||
You can show and hide fields based on what other fields are doing by utilizing conditional logic on a field by field basis. The `condition` property on a field's admin config accepts a function which takes three arguments:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -220,7 +222,7 @@ The `condition` function should return a boolean that will control if the field
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Default values
|
||||
## Default values
|
||||
|
||||
Fields can be prefilled with starting values using the `defaultValue` property. This is used in the admin UI and also on the backend as API requests will be populated with missing or undefined field values. You can assign the defaultValue directly in the field configuration or supply a function for dynamic behavior. Values assigned during a create request on the server are added before validation occurs.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -250,7 +252,7 @@ const field = {
|
||||
You can use async defaultValue functions to fill fields with data from API requests.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Description
|
||||
## Description
|
||||
|
||||
A description can be configured in three ways.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -312,7 +314,7 @@ This example will display the number of characters allowed as the user types.
|
||||
|
||||
This component will count the number of characters entered, as well as display the path of the field.
|
||||
|
||||
### TypeScript
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
You can import the internal Payload `Field` type as well as other common field types as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ label: Point
|
||||
order: 110
|
||||
desc: The Point field type stores coordinates in the database. Learn how to use Point field for geolocation and geometry.
|
||||
|
||||
keywords: point, geolocation, geospatial, geojson, 2dsphere, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: point, geolocation, geospatial, geojson, 2dsphere, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ keywords: point, geolocation, geospatial, geojson, 2dsphere, config, configurati
|
||||
|
||||
The data structure in the database matches the GeoJSON structure to represent point. The Payload APIs simplifies the object data to only the [longitude, latitude] location.
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ _\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
<strong>Note:</strong> The Point field type is currently only supported in MongoDB.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -69,6 +69,6 @@ export const ExampleCollection: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Querying
|
||||
## Querying
|
||||
|
||||
In order to do query based on the distance to another point, you can use the `near` operator. When querying using the near operator, the returned documents will be sorted by nearest first.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Radio Group Field
|
||||
label: Radio Group
|
||||
order: 120
|
||||
desc: The Radio field type allows for the selection of one value from a predefined set of possible values. Learn how to use Radio fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: radio, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: radio, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ keywords: radio, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Managemen
|
||||
caption="Admin panel screenshot of a Radio field"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ _\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
being used as a GraphQL enum.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin config
|
||||
## Admin config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), the Radio Group field type allows for the specification of the following `admin` properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-conf
|
||||
|
||||
The `layout` property allows for the radio group to be styled as a horizonally or vertically distributed list. The default value is `horizontal`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Relationship Field
|
||||
label: Relationship
|
||||
order: 130
|
||||
desc: The Relationship field provides the ability to relate documents together. Learn how to use Relationship fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: relationship, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: relationship, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -24,30 +24,30 @@ keywords: relationship, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Ma
|
||||
- To allow for an `Order` to feature a `placedBy` relationship to either an `Organization` or `User` collection
|
||||
- To assign `Category` documents to `Post` documents
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`name`** \* | To be used as the property name when stored and retrieved from the database. [More](/docs/fields/overview#field-names) |
|
||||
| **`relationTo`** \* | Provide one or many collection `slug`s to be able to assign relationships to. |
|
||||
| **`filterOptions`** | A query to filter which options appear in the UI and validate against. [More](#filtering-relationship-options). |
|
||||
| **`hasMany`** | Boolean when, if set to `true`, allows this field to have many relations instead of only one. |
|
||||
| **`minRows`** | A number for the fewest allowed items during validation when a value is present. Used with `hasMany`. |
|
||||
| **`maxRows`** | A number for the most allowed items during validation when a value is present. Used with `hasMany`. |
|
||||
| **`maxDepth`** | Sets a number limit on iterations of related documents to populate when queried. [Depth](/docs/getting-started/concepts#depth) |
|
||||
| **`label`** | Text used as a field label in the Admin panel or an object with keys for each language. |
|
||||
| **`unique`** | Enforce that each entry in the Collection has a unique value for this field. |
|
||||
| **`validate`** | Provide a custom validation function that will be executed on both the Admin panel and the backend. [More](/docs/fields/overview#validation) |
|
||||
| **`index`** | Build an [index](/docs/database/overview) for this field to produce faster queries. Set this field to `true` if your users will perform queries on this field's data often. |
|
||||
| **`saveToJWT`** | If this field is top-level and nested in a config supporting [Authentication](/docs/authentication/config), include its data in the user JWT. |
|
||||
| **`hooks`** | Provide field-based hooks to control logic for this field. [More](/docs/fields/overview#field-level-hooks) |
|
||||
| **`access`** | Provide field-based access control to denote what users can see and do with this field's data. [More](/docs/fields/overview#field-level-access-control) |
|
||||
| **`hidden`** | Restrict this field's visibility from all APIs entirely. Will still be saved to the database, but will not appear in any API or the Admin panel. |
|
||||
| **`defaultValue`** | Provide data to be used for this field's default value. [More](/docs/fields/overview#default-values) |
|
||||
| **`localized`** | Enable localization for this field. Requires [localization to be enabled](/docs/configuration/localization) in the Base config. |
|
||||
| **`required`** | Require this field to have a value. |
|
||||
| **`admin`** | Admin-specific configuration. See the [default field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config) for more details. |
|
||||
| **`custom`** | Extension point for adding custom data (e.g. for plugins) |
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
|---------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **`name`** \* | To be used as the property name when stored and retrieved from the database. [More](/docs/fields/overview#field-names) |
|
||||
| **`relationTo`** \* | Provide one or many collection `slug`s to be able to assign relationships to. |
|
||||
| **`filterOptions`** | A query to filter which options appear in the UI and validate against. [More](#filtering-relationship-options). |
|
||||
| **`hasMany`** | Boolean when, if set to `true`, allows this field to have many relations instead of only one. |
|
||||
| **`minRows`** | A number for the fewest allowed items during validation when a value is present. Used with `hasMany`. |
|
||||
| **`maxRows`** | A number for the most allowed items during validation when a value is present. Used with `hasMany`. |
|
||||
| **`maxDepth`** | Sets a maximum population depth for this field, regardless of the remaining depth when this field is reached. [Max Depth](/docs/getting-started/concepts#field-level-max-depth) |
|
||||
| **`label`** | Text used as a field label in the Admin panel or an object with keys for each language. |
|
||||
| **`unique`** | Enforce that each entry in the Collection has a unique value for this field. |
|
||||
| **`validate`** | Provide a custom validation function that will be executed on both the Admin panel and the backend. [More](/docs/fields/overview#validation) |
|
||||
| **`index`** | Build an [index](/docs/database/overview) for this field to produce faster queries. Set this field to `true` if your users will perform queries on this field's data often. |
|
||||
| **`saveToJWT`** | If this field is top-level and nested in a config supporting [Authentication](/docs/authentication/config), include its data in the user JWT. |
|
||||
| **`hooks`** | Provide field-based hooks to control logic for this field. [More](/docs/fields/overview#field-level-hooks) |
|
||||
| **`access`** | Provide field-based access control to denote what users can see and do with this field's data. [More](/docs/fields/overview#field-level-access-control) |
|
||||
| **`hidden`** | Restrict this field's visibility from all APIs entirely. Will still be saved to the database, but will not appear in any API or the Admin panel. |
|
||||
| **`defaultValue`** | Provide data to be used for this field's default value. [More](/docs/fields/overview#default-values) |
|
||||
| **`localized`** | Enable localization for this field. Requires [localization to be enabled](/docs/configuration/localization) in the Base config. |
|
||||
| **`required`** | Require this field to have a value. |
|
||||
| **`admin`** | Admin-specific configuration. See the [default field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config) for more details. |
|
||||
| **`custom`** | Extension point for adding custom data (e.g. for plugins) |
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ _\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
related documents that are returned by the API.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin config
|
||||
## Admin config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), the Relationship field type also
|
||||
allows for the following admin-specific properties:
|
||||
@@ -122,7 +122,7 @@ In this configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
Note: If `sortOptions` is not defined, the default sorting behavior of the Relationship field dropdown will be used.
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering relationship options
|
||||
## Filtering relationship options
|
||||
|
||||
Options can be dynamically limited by supplying a [query constraint](/docs/queries/overview), which will be used both
|
||||
for validating input and filtering available relationships in the UI.
|
||||
@@ -139,7 +139,7 @@ called with an argument object with the following properties:
|
||||
| `id` | The `id` of the current document being edited. `id` is `undefined` during the `create` operation |
|
||||
| `user` | An object containing the currently authenticated user |
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
@@ -181,13 +181,13 @@ You can learn more about writing queries [here](/docs/queries/overview).
|
||||
<strong>payload/fields/validations</strong> in your validate function.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### How the data is saved
|
||||
## How the data is saved
|
||||
|
||||
Given the variety of options possible within the `relationship` field type, the shape of the data needed for creating
|
||||
and updating these fields can vary. The following sections will describe the variety of data shapes that can arise from
|
||||
this field.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Has One
|
||||
### Has One
|
||||
|
||||
The most simple pattern of a relationship is to use `hasMany: false` with a `relationTo` that allows for only one type
|
||||
of collection.
|
||||
@@ -221,7 +221,7 @@ When querying documents in this collection via REST API, you could query as foll
|
||||
|
||||
`?where[owner][equals]=6031ac9e1289176380734024`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Has One - Polymorphic
|
||||
### Has One - Polymorphic
|
||||
|
||||
Also known as **dynamic references**, in this configuration, the `relationTo` field is an array of Collection slugs that
|
||||
tells Payload which Collections are valid to reference.
|
||||
@@ -263,7 +263,7 @@ You can also query for documents where a field has a relationship to a specific
|
||||
|
||||
This query would return only documents that have an owner relationship to organizations.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Has Many
|
||||
### Has Many
|
||||
|
||||
The `hasMany` tells Payload that there may be more than one collection saved to the field.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -295,7 +295,7 @@ When querying documents, the format does not change for arrays:
|
||||
|
||||
`?where[owners][equals]=6031ac9e1289176380734024`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Has Many - Polymorphic
|
||||
### Has Many - Polymorphic
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -336,7 +336,7 @@ Querying is done in the same way as the earlier Polymorphic example:
|
||||
|
||||
`?where[owners.value][equals]=6031ac9e1289176380734024`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Querying and Filtering Polymorphic Relationships
|
||||
### Querying and Filtering Polymorphic Relationships
|
||||
|
||||
Polymorphic and non-polymorphic relationships must be queried differently because of how the related data is stored and
|
||||
may be inconsistent across different collections. Because of this, filtering polymorphic relationship fields from the
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Rich Text Field
|
||||
label: Rich Text
|
||||
order: 140
|
||||
desc: The Rich Text field allows dynamic content to be written through the Admin Panel. Learn how to use Rich Text fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: rich text, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: rich text, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -30,12 +30,13 @@ Right now, Payload is officially supporting two rich text editors:
|
||||
Consistent with Payload's goal of making you learn as little of Payload as possible, customizing
|
||||
and using the Rich Text Editor does not involve learning how to develop for a <em>Payload</em>{' '}
|
||||
rich text editor.
|
||||
</strong>{' '}
|
||||
</strong>
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, you can invest your time and effort into learning the underlying open-source tools that
|
||||
will allow you to apply your learnings elsewhere as well.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -55,7 +56,7 @@ Right now, Payload is officially supporting two rich text editors:
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin config
|
||||
## Admin config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), the Rich Text editor allows for the following admin properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,6 +72,6 @@ Set this property to `true` to hide this field's gutter within the admin panel.
|
||||
|
||||
Override the default text direction of the Admin panel for this field. Set to `true` to force right-to-left text direction.
|
||||
|
||||
### Editor-specific options
|
||||
## Editor-specific options
|
||||
|
||||
For a ton more editor-specific options, including how to build custom rich text elements directly into your editor, take a look at either the [Slate docs](/docs/rich-text/slate) or the [Lexical docs](/docs/rich-text/lexical) depending on which editor you're using.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Row Field
|
||||
label: Row
|
||||
order: 150
|
||||
desc: With the Row field you can arrange fields next to each other in the Admin Panel to help you customize your Dashboard.
|
||||
keywords: row, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: row, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ keywords: row, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management
|
||||
caption="Admin panel screenshot of a Row field"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| --------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ keywords: row, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Select Field
|
||||
label: Select
|
||||
order: 160
|
||||
desc: The Select field provides a dropdown-style interface for choosing options from a predefined list. Learn how to use Select fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: select, multi-select, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: select, multi-select, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ keywords: select, multi-select, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Co
|
||||
caption="Admin panel screenshot of a Select field"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ _\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
being used as a GraphQL enum.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin config
|
||||
## Admin config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), the Select field type also allows for the following admin-specific properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ Set to `true` if you'd like this field to be clearable within the Admin UI.
|
||||
|
||||
Set to `true` if you'd like this field to be sortable within the Admin UI using drag and drop. (Only works when `hasMany` is set to `true`)
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ export const ExampleCollection: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Customization
|
||||
## Customization
|
||||
|
||||
The Select field UI component can be customized by providing a custom React component to the `components` object in the Base config.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Tabs Field
|
||||
label: Tabs
|
||||
order: 170
|
||||
desc: The Tabs field is a great way to organize complex editing experiences into specific tab-based areas.
|
||||
keywords: tabs, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: tabs, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ keywords: tabs, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management
|
||||
caption="Tabs field type used to separate Hero fields from Page Layout"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ keywords: tabs, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management
|
||||
| **`admin`** | Admin-specific configuration. See the [default field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config) for more details. |
|
||||
| **`custom`** | Extension point for adding custom data (e.g. for plugins) |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tab-specific Config
|
||||
### Tab-specific Config
|
||||
|
||||
Each tab must have either a `name` or `label` and the required `fields` array. You can also optionally pass a `description` to render within each individual tab.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ Each tab must have either a `name` or `label` and the required `fields` array. Y
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Text Field
|
||||
label: Text
|
||||
order: 180
|
||||
desc: Text field types simply save a string to the database and provide the Admin panel with a text input. Learn how to use Text fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: text, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: text, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ keywords: text, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management
|
||||
caption="Admin panel screenshot of a Text field and read-only Text field"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ keywords: text, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin config
|
||||
## Admin config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), the Text field type allows for the following `admin` properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ Set this property to a string that will be used for browser autocomplete.
|
||||
|
||||
Override the default text direction of the Admin panel for this field. Set to `true` to force right-to-left text direction.
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Textarea Field
|
||||
label: Textarea
|
||||
order: 190
|
||||
desc: Textarea field types save a string to the database, similar to the Text field type but equipped for longer text. Learn how to use Textarea fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: textarea, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: textarea, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ keywords: textarea, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Manage
|
||||
caption="Admin panel screenshot of a Textarea field and read-only Textarea field"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ keywords: textarea, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Manage
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin config
|
||||
## Admin config
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the default [field admin config](/docs/fields/overview#admin-config), the Textarea field type allows for the following `admin` properties:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ Set this property to a string that will be used for browser autocomplete.
|
||||
|
||||
Override the default text direction of the Admin panel for this field. Set to `true` to force right-to-left text direction.
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: UI Field
|
||||
label: UI
|
||||
order: 200
|
||||
desc: UI fields are purely presentational and allow developers to customize the admin panel to a very fine degree, including adding actions and other functions.
|
||||
keywords: custom field, react component, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: custom field, react component, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ With this field, you can also inject custom `Cell` components that appear as add
|
||||
- Add a "view page" button into a Pages List view to give editors a shortcut to view a page on the frontend of the site
|
||||
- Build a "clear cache" button or similar mechanism to manually clear caches of specific documents
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -31,11 +31,12 @@ With this field, you can also inject custom `Cell` components that appear as add
|
||||
| **`label`** | Human-readable label for this UI field. |
|
||||
| **`admin.components.Field`** \* | React component to be rendered for this field within the Edit view. [More](/docs/admin/components/#field-component) |
|
||||
| **`admin.components.Cell`** | React component to be rendered as a Cell within collection List views. [More](/docs/admin/components/#field-component) |
|
||||
| **`admin.disableListColumn`** | Set `disableListColumn` to `true` to prevent the UI field from appearing in the list view column selector. |
|
||||
| **`custom`** | Extension point for adding custom data (e.g. for plugins) |
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Upload Field
|
||||
label: Upload
|
||||
order: 210
|
||||
desc: Upload fields will allow a file to be uploaded, only from a collection supporting Uploads. Learn how to use Upload fields, see examples and options.
|
||||
keywords: upload, images media, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: upload, images media, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner>
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ keywords: upload, images media, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Co
|
||||
- To allow for a `Product` to deliver a downloadable asset like PDF or MP3
|
||||
- To give a layout building block the ability to feature a background image
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description |
|
||||
| -------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
@@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ keywords: upload, images media, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Co
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`collections/ExampleCollection.ts`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ export const ExampleCollection: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Filtering upload options
|
||||
## Filtering upload options
|
||||
|
||||
Options can be dynamically limited by supplying a [query constraint](/docs/queries/overview), which will be used both
|
||||
for validating input and filtering available uploads in the UI.
|
||||
@@ -93,7 +93,7 @@ called with an argument object with the following properties:
|
||||
| `id` | The `id` of the current document being edited. `id` is `undefined` during the `create` operation |
|
||||
| `user` | An object containing the currently authenticated user |
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
const uploadField = {
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,18 +3,18 @@ title: Payload Concepts
|
||||
label: Concepts
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
desc: Payload is based around a small and intuitive set of concepts. Key concepts include collections, globals, fields and more.
|
||||
keywords: documentation, getting started, guide, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: documentation, getting started, guide, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload is based around a small and intuitive set of concepts. Before starting to work with Payload, it's a good idea to familiarize yourself with the following:
|
||||
|
||||
### Config
|
||||
## Config
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">The Payload config is where you configure everything that Payload does.</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the Payload config lives in the root folder of your code and is named `payload.config.js` (`payload.config.ts` if you're using TypeScript), but you can customize its name and where you store it. You can write full functions and even full React components right into your config.
|
||||
|
||||
### Collections
|
||||
## Collections
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
A Collection represents a type of content that Payload will store and can contain many documents.
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ Collections define the shape of your data as well as all functionalities attache
|
||||
|
||||
They can represent anything you can store in a database - for example - pages, posts, users, people, orders, categories, events, customers, transactions, and anything else your app needs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Globals
|
||||
## Globals
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
A Global is a "one-off" piece of content that is perfect for storing navigational structures,
|
||||
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ They can represent anything you can store in a database - for example - pages, p
|
||||
|
||||
Globals are in many ways similar to Collections, but there is only ever **one** instance of a Global, whereas Collections can contain many documents.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fields
|
||||
## Fields
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
Fields are the building blocks of Payload. Collections and Globals both use Fields to define the
|
||||
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ Globals are in many ways similar to Collections, but there is only ever **one**
|
||||
|
||||
Payload comes with [many different field types](../fields/overview) that give you a ton of flexibility while designing your API. Each Field type has its own potential properties that allow you to customize how they work.
|
||||
|
||||
### Hooks
|
||||
## Hooks
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
Hooks are where you can "tie in" to existing Payload actions to perform your own additional logic
|
||||
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ Hooks are an extremely powerful concept and are central to extending and customi
|
||||
|
||||
There are many more potential reasons to use Hooks. For more, visit the [Hooks documentation](/docs/hooks/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
### Access Control
|
||||
## Access Control
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
Access Control refers to Payload's system of defining who can do what to your API.
|
||||
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ Access Control is extremely powerful but easy and intuitive to manage. You can e
|
||||
|
||||
For more, visit the [Access Control documentation](/docs/access-control/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
### Depth
|
||||
## Depth
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
"Depth" gives you control over how many levels down related documents should be automatically
|
||||
@@ -156,6 +156,28 @@ To populate `user.author.department` in it's entirety you could specify `?depth=
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Field-level max depth
|
||||
|
||||
Fields like relationships or uploads can have a `maxDepth` property that limits the depth of the population for that field. Here are some examples:
|
||||
|
||||
Depth: 10
|
||||
Current depth when field is accessed: 1
|
||||
`maxDepth`: undefined
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the field would be populated to 9 levels of population.
|
||||
|
||||
Depth: 10
|
||||
Current depth when field is accessed: 0
|
||||
`maxDepth`: 2
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the field would be populated to 2 levels of population, despite there being a remaining depth of 8.
|
||||
|
||||
Depth: 10
|
||||
Current depth when field is accessed: 2
|
||||
`maxDepth`: 1
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the field would not be populated, as the current depth (2) has exceeded the `maxDepth` for this field (1).
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Note:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,10 +3,10 @@ title: Installation
|
||||
label: Installation
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
desc: To quickly get started with Payload, simply run npx create-payload-app or install from scratch.
|
||||
keywords: documentation, getting started, guide, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: documentation, getting started, guide, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
#### Software Requirements
|
||||
## Software Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
Payload requires the following software:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ Then just follow the prompts! You'll get set up with a new folder and a function
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding to an existing app
|
||||
|
||||
Adding Payload to either a new or existing TypeScript + Express app is super straightforward. To add to an existing app, just run `npm install --save --legacy-peer-deps payload`.
|
||||
Adding Payload to either a new or existing TypeScript + Next.js app is super straightforward. To add to an existing app, just run `npm install --save --legacy-peer-deps payload`.
|
||||
|
||||
From there, the first step is writing a baseline config. Create a new `payload.config.ts` in your project's `/src` directory (or whatever your root TS dir is). The simplest config contains the following:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ Write the above code into your newly created config file. This baseline config w
|
||||
|
||||
Although this is just the bare minimum config, there are _many_ more options that you can control here. To reference the full config and all of its options, [click here](/docs/configuration/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
### Server
|
||||
## Server
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you've got a baseline Payload config, it's time to initialize Payload. It requires an Express server that you provide, so if you're not familiar with how to set up a baseline Express server, please read up on exactly what Express is and why to use it. Express' own [Documentation](https://expressjs.com/en/starter/hello-world.html) is a good place to start. Otherwise, follow along below for how to build your own Express server to use with Payload.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -100,54 +100,54 @@ PAYLOAD_SECRET=your-payload-secret
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a list of all properties available to pass through `payload.init`:
|
||||
|
||||
##### secret
|
||||
#### secret
|
||||
|
||||
**Required**. This is a secure string that will be used to authenticate with Payload. It can be random but should be at least 14 characters and be very difficult to guess.
|
||||
|
||||
Payload uses this secret key to generate secure user tokens (JWT). Behind the scenes, we do not use your secret key to encrypt directly - instead, we first take the secret key and create an encrypted string using the SHA-256 hash function. Then, we reduce the encrypted string to its first 32 characters. This final value is what Payload uses for encryption.
|
||||
|
||||
##### config
|
||||
#### config
|
||||
|
||||
Allows you to pass your config directly to the onInit function. The config passed here should match the payload.config file.
|
||||
|
||||
##### disableOnInit
|
||||
#### disableOnInit
|
||||
|
||||
A boolean that disables running your `onInit` function when Payload starts up.
|
||||
|
||||
##### disableDBConnect
|
||||
#### disableDBConnect
|
||||
|
||||
A boolean that disables the database connection when Payload starts up.
|
||||
|
||||
##### email
|
||||
#### email
|
||||
|
||||
An object used to configure SMTP. [Read more](/docs/email/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
##### express
|
||||
#### express
|
||||
|
||||
This is your Express app as shown above. Payload will tie into your existing `app` and scope all of its functionalities to sub-routers. By default, Payload will add an `/admin` router and an `/api` router, but you can customize these paths.
|
||||
|
||||
##### local
|
||||
#### local
|
||||
|
||||
A boolean that when set to `true` tells Payload to start in local-only mode which will bypass setting up API routes. When set to `true`, `express` is not required. This is useful when running scripts that need to use Payload's [local-api](/docs/local-api/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
##### loggerDestination
|
||||
#### loggerDestination
|
||||
|
||||
Specify destination stream for the built-in Pino logger that Payload uses for internal logging. See [Pino Docs](https://getpino.io/#/docs/api?id=pino-destination) for more info on what is available.
|
||||
|
||||
##### loggerOptions
|
||||
#### loggerOptions
|
||||
|
||||
Specify options for the built-in Pino logger that Payload uses for internal logging. See [Pino Docs](https://getpino.io/#/docs/api?id=options) for more info on what is available.
|
||||
|
||||
##### onInit
|
||||
#### onInit
|
||||
|
||||
A function that is called immediately following startup that receives the Payload instance as it's only argument.
|
||||
|
||||
### Test it out
|
||||
## Test it out
|
||||
|
||||
After you've gotten this far, it's time to boot up Payload. Start your project in your application's folder to get going.
|
||||
|
||||
After it starts, you can go to `http://localhost:3000/admin` to create your first Payload user!
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker
|
||||
## Docker
|
||||
|
||||
Looking to deploy Payload with Docker? New projects with `create-payload-app` come with a Dockerfile and docker-compose.yml file ready to go. Examples of these files can be seen in our [Deployment docs](/docs/production/deployment#docker).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: What is Payload?
|
||||
label: What is Payload?
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: Payload is a next-gen headless Content Management System (CMS) and application framework.
|
||||
keywords: documentation, getting started, guide, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: documentation, getting started, guide, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<YouTube
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ In this way, the CMS can ensure that its content editing experience is highly po
|
||||
|
||||
At this point this concept is [widely](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Headless_content_management_system) [discussed](https://css-tricks.com/what-is-a-headless-cms/) online, and for good reason. The web has become more complicated and with complexity comes the demand for developers to better structure their code. The rise of interface libraries like React and Vue are now the de-facto standard for building modern applications and traditional content management systems are often not designed to make use of them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Payload?
|
||||
## Why Payload?
|
||||
|
||||
The team behind Payload has been building websites and apps with existing content management systems and application frameworks for over a decade. We know what works and what doesn't about each of the existing solutions, and to this day have found no silver bullet solution.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Adding your own Queries and Mutations
|
||||
label: Custom Queries and Mutations
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
desc: Payload allows you to add your own GraphQL queries and mutations, simply set up GraphQL in your main Payload config by following these instructions.
|
||||
keywords: graphql, resolvers, mutations, custom, queries, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: graphql, resolvers, mutations, custom, queries, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
You can add your own GraphQL queries and mutations to Payload, making use of all the types that Payload has defined for you.
|
||||
@@ -25,11 +25,11 @@ This is Payload's GraphQL dependency. You should not install your own copy of Gr
|
||||
|
||||
This is a copy of the currently running Payload instance, which provides you with existing GraphQL types for all of your Collections and Globals - among other things.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Return value
|
||||
## Return value
|
||||
|
||||
Both `graphQL.queries` and `graphQL.mutations` functions should return an object with properties equal to your newly written GraphQL queries and mutations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
`payload.config.js`:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -68,7 +68,7 @@ export default buildConfig({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Resolver function
|
||||
## Resolver function
|
||||
|
||||
In your resolver, make sure you set `depth: 0` if you're returning data directly from the local API so that GraphQL can correctly resolve queries to nested values such as relationship data.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ An object containing the `req` and `res` objects that will provide you with the
|
||||
|
||||
Contextual information about the currently running GraphQL operation. You can get schema information from this as well as contextual information about where this resolver function is being run.
|
||||
|
||||
### Types
|
||||
## Types
|
||||
|
||||
We've exposed a few types and utilities to help you extend the API further. Payload uses the GraphQL.js package for which you can view the full list of available types in the [official documentation](https://graphql.org/graphql-js/type/).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -138,7 +138,7 @@ graphQL?: {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Best practices
|
||||
## Best practices
|
||||
|
||||
There are a few ways to structure your code, we recommend using a dedicated `graphql` directory so you can keep all of your logic in one place. You have total freedom of how you want to structure this but a common pattern is to group functions by type and with their resolver.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,12 +3,12 @@ title: GraphQL Schema
|
||||
label: GraphQL Schema
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
desc: Output your own GraphQL schema based on your collections and globals to a file.
|
||||
keywords: headless cms, typescript, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: headless cms, typescript, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
When working with GraphQL it is useful to have the schema for development of other projects that need to call on your GraphQL endpoint. In Payload the schema is controlled by your collections and globals and is made available to the developer or third parties, it is not necessary for developers using Payload to write schema types manually.
|
||||
|
||||
### Schema generation script
|
||||
## Schema generation script
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command in a Payload project to generate your project's GraphQL schema from Payload:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Run the following command in a Payload project to generate your project's GraphQ
|
||||
payload generate:graphQLSchema
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Field Schemas
|
||||
## Custom Field Schemas
|
||||
|
||||
For `array`, `block`, `group` and named `tab` fields, you can generate top level reusable interfaces. The following group field config:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ type Collection1 {
|
||||
|
||||
The above example outputs all your definitions to a file relative from your payload config as `./graphql/schema.graphql`. By default, the file will be output to your current working directory as `schema.graphql`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Adding an NPM script
|
||||
### Adding an NPM script
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
<strong>Important</strong>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: GraphQL Overview
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: Payload ships with a fully featured and extensible GraphQL API, which can be used in addition to the REST and Local APIs to give you more flexibility.
|
||||
keywords: graphql, resolvers, mutations, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: graphql, resolvers, mutations, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to its REST and Local APIs, Payload ships with a fully featured and extensible GraphQL API.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Collection Hooks
|
||||
label: Collections
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
desc: You can add hooks to any Collection, several hook types are available including beforeChange, afterRead, afterDelete and more.
|
||||
keywords: hooks, collections, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: hooks, collections, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Collections feature the ability to define the following hooks:
|
||||
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ import { CollectionBeforeOperationHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
const beforeOperationHook: CollectionBeforeOperationHook = async ({
|
||||
args, // original arguments passed into the operation
|
||||
operation, // name of the operation
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return args // return modified operation arguments as necessary
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ import { CollectionBeforeValidateHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
const beforeValidateHook: CollectionBeforeValidateHook = async ({
|
||||
data, // incoming data to update or create with
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
operation, // name of the operation ie. 'create', 'update'
|
||||
originalDoc, // original document
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
@@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ import { CollectionBeforeChangeHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
const beforeChangeHook: CollectionBeforeChangeHook = async ({
|
||||
data, // incoming data to update or create with
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
operation, // name of the operation ie. 'create', 'update'
|
||||
originalDoc, // original document
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
@@ -130,7 +130,7 @@ import { CollectionAfterChangeHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
const afterChangeHook: CollectionAfterChangeHook = async ({
|
||||
doc, // full document data
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
previousDoc, // document data before updating the collection
|
||||
operation, // name of the operation ie. 'create', 'update'
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
@@ -147,7 +147,7 @@ import { CollectionBeforeReadHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
const beforeReadHook: CollectionBeforeReadHook = async ({
|
||||
doc, // full document data
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
query, // JSON formatted query
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return doc
|
||||
@@ -163,7 +163,7 @@ import { CollectionAfterReadHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
const afterReadHook: CollectionAfterReadHook = async ({
|
||||
doc, // full document data
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
query, // JSON formatted query
|
||||
findMany, // boolean to denote if this hook is running against finding one, or finding many
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
@@ -179,7 +179,7 @@ Runs before the `delete` operation. Returned values are discarded.
|
||||
import { CollectionBeforeDeleteHook } from 'payload/types';
|
||||
|
||||
const beforeDeleteHook: CollectionBeforeDeleteHook = async ({
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
id, // id of document to delete
|
||||
}) => {...}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ Runs immediately after the `delete` operation removes records from the database.
|
||||
import { CollectionAfterDeleteHook } from 'payload/types';
|
||||
|
||||
const afterDeleteHook: CollectionAfterDeleteHook = async ({
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
id, // id of document to delete
|
||||
doc, // deleted document
|
||||
}) => {...}
|
||||
@@ -210,7 +210,7 @@ import { CollectionAfterOperationHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
const afterOperationHook: CollectionAfterOperationHook = async ({
|
||||
args, // arguments passed into the operation
|
||||
operation, // name of the operation
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
result, // the result of the operation, before modifications
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return result // return modified result as necessary
|
||||
@@ -225,7 +225,7 @@ For auth-enabled Collections, this hook runs during `login` operations where a u
|
||||
import { CollectionBeforeLoginHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
const beforeLoginHook: CollectionBeforeLoginHook = async ({
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
user, // user being logged in
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return user
|
||||
@@ -240,7 +240,7 @@ For auth-enabled Collections, this hook runs after successful `login` operations
|
||||
import { CollectionAfterLoginHook } from 'payload/types';
|
||||
|
||||
const afterLoginHook: CollectionAfterLoginHook = async ({
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
user, // user that was logged in
|
||||
token, // user token
|
||||
}) => {...}
|
||||
@@ -254,7 +254,7 @@ For auth-enabled Collections, this hook runs after `logout` operations.
|
||||
import { CollectionAfterLogoutHook } from 'payload/types';
|
||||
|
||||
const afterLogoutHook: CollectionAfterLogoutHook = async ({
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
}) => {...}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -266,8 +266,8 @@ For auth-enabled Collections, this hook runs after `refresh` operations.
|
||||
import { CollectionAfterRefreshHook } from 'payload/types';
|
||||
|
||||
const afterRefreshHook: CollectionAfterRefreshHook = async ({
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
res, // full express response
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
res, // full Response object
|
||||
token, // newly refreshed user token
|
||||
}) => {...}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -280,7 +280,7 @@ For auth-enabled Collections, this hook runs after `me` operations.
|
||||
import { CollectionAfterMeHook } from 'payload/types';
|
||||
|
||||
const afterMeHook: CollectionAfterMeHook = async ({
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
response, // response to return
|
||||
}) => {...}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Field Hooks
|
||||
label: Fields
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
desc: Hooks can be added to any fields, and optionally modify the return value of the field before the operation continues.
|
||||
keywords: hooks, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: hooks, fields, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Field-level hooks offer incredible potential for encapsulating your logic. They help to isolate concerns and package up
|
||||
@@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ Field Hooks receive one `args` argument that contains the following properties:
|
||||
| **`originalDoc`** | The full original document in `update` operations. In the `afterChange` hook, this is the resulting document of the operation. |
|
||||
| **`previousDoc`** | The document before changes were applied, only in `afterChange` hooks. |
|
||||
| **`previousSiblingDoc`** | The sibling data of the document before changes being applied, only in `beforeChange` and `afterChange` hook. |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object. It is mocked for Local API operations. |
|
||||
| **`req`** | The [Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) object. It is mocked for Local API operations. |
|
||||
| **`value`** | The value of the field. |
|
||||
| **`previousValue`** | The previous value of the field, before changes, only in `beforeChange` and `afterChange` hooks. |
|
||||
| **`context`** | Context passed to this hook. More info can be found under [Context](/docs/hooks/context) |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Global Hooks
|
||||
label: Globals
|
||||
order: 40
|
||||
desc: Hooks can be added to any Global and allow you to validate data, flatten locales, hide protected fields, remove fields and more.
|
||||
keywords: hooks, globals, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: hooks, globals, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Globals feature the ability to define the following hooks:
|
||||
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ import { GlobalBeforeValidateHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
const beforeValidateHook: GlobalBeforeValidateHook = async ({
|
||||
data, // incoming data to update or create with
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
originalDoc, // original document
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return data // Return data to update the document with
|
||||
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ import { GlobalBeforeChangeHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
const beforeChangeHook: GlobalBeforeChangeHook = async ({
|
||||
data, // incoming data to update or create with
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
originalDoc, // original document
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return data // Return data to update the document with
|
||||
@@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ import { GlobalAfterChangeHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
const afterChangeHook: GlobalAfterChangeHook = async ({
|
||||
doc, // full document data
|
||||
previousDoc, // document data before updating the collection
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return data
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ import { GlobalBeforeReadHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
const beforeReadHook: GlobalBeforeReadHook = async ({
|
||||
doc, // full document data
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
}) => {...}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -108,7 +108,7 @@ import { GlobalAfterReadHook } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
const afterReadHook: GlobalAfterReadHook = async ({
|
||||
doc, // full document data
|
||||
req, // full express request
|
||||
req, // full Request object
|
||||
findMany, // boolean to denote if this hook is running against finding one, or finding many (useful in versions)
|
||||
}) => {...}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Hooks Overview
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: Hooks allow you to add your own logic to Payload, including integrating with third-party APIs, adding auto-generated data, or modifing Payload's base functionality.
|
||||
keywords: hooks, overview, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: hooks, overview, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
@@ -28,15 +28,15 @@ Example uses:
|
||||
|
||||
There are many more use cases for Hooks and the sky is the limit.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Async vs. synchronous
|
||||
## Async vs. synchronous
|
||||
|
||||
All hooks can be written as either synchronous or asynchronous functions. If the Hook should modify data before a document is updated or created, and it relies on asynchronous actions such as fetching data from a third party, it might make sense to define your Hook as an asynchronous function, so you can be sure that your Hook completes before the operation's lifecycle continues. Async hooks are run in series - so if you have two async hooks defined, the second hook will wait for the first to complete before it starts.
|
||||
|
||||
If your Hook simply performs a side-effect, such as updating a CRM, it might be okay to define it synchronously, so the Payload operation does not have to wait for your hook to complete.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Server-only execution
|
||||
## Server-only execution
|
||||
|
||||
Payload Hooks are only triggered on the server. You can safely [remove your hooks](/docs/admin/webpack#aliasing-server-only-modules) from your Admin panel's client-side code by customizing the Webpack config, which not only keeps your Admin bundles' filesize small but also ensures that any server-side only code does not cause problems within browser environments.
|
||||
Payload Hooks are only triggered on the server and are automatically excluded from the Payload Admin bundle.
|
||||
|
||||
## Hook Types
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,30 +1,30 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Vercel Visual Editing
|
||||
label: Vercel Visual Editing
|
||||
title: Vercel Content Link
|
||||
label: Vercel Content Link
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: Payload + Vercel Visual Editing allows yours editors to navigate directly from the content rendered on your front-end to the fields in Payload that control it.
|
||||
keywords: vercel, vercel visual editing, visual editing, content source maps, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
desc: Payload + Vercel Content Link allows yours editors to navigate directly from the content rendered on your front-end to the fields in Payload that control it.
|
||||
keywords: vercel, vercel content link, content link, visual editing, content source maps, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
[Vercel Visual Editing](https://vercel.com/docs/workflow-collaboration/visual-editing) will allow your editors to navigate directly from the content rendered on your front-end to the fields in Payload that control it. This requires no changes to your front-end code and very few changes to your Payload config.
|
||||
[Vercel Content Link](https://vercel.com/docs/workflow-collaboration/edit-mode#content-link) will allow your editors to navigate directly from the content rendered on your front-end to the fields in Payload that control it. This requires no changes to your front-end code and very few changes to your Payload config.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
Vercel Visual Editing is an enterprise-only feature and only available for deployments hosted on
|
||||
Vercel Content Link is an enterprise-only feature and only available for deployments hosted on
|
||||
Vercel. If you are an existing enterprise customer, [contact our sales
|
||||
team](https://payloadcms.com/for-enterprise) for help with your integration.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### How it works
|
||||
## How it works
|
||||
|
||||
To power Vercel Visual Editing, Payload embeds Content Source Maps into its API responses. Content Source Maps are invisible, encoded JSON values that include a link back to the field in the CMS that generated the content. When rendered on the page, Vercel detects and decodes these values to display the Visual Editing interface.
|
||||
To power Vercel Content Link, Payload embeds Content Source Maps into its API responses. Content Source Maps are invisible, encoded JSON values that include a link back to the field in the CMS that generated the content. When rendered on the page, Vercel detects and decodes these values to display the Content Link interface.
|
||||
|
||||
For full details on how the encoding and decoding algorithm works, check out [`@vercel/stega`](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@vercel/stega).
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting Started
|
||||
## Getting Started
|
||||
|
||||
Setting up Payload with Vercel Visual Editing is easy. First, install the `@payloadcms/plugin-csm` plugin into your project. This plugin requires an API key to install, [contact our sales team](https://payloadcms.com/for-enterprise) if you don't already have one.
|
||||
Setting up Payload with Vercel Content Link is easy. First, install the `@payloadcms/plugin-csm` plugin into your project. This plugin requires an API key to install, [contact our sales team](https://payloadcms.com/for-enterprise) if you don't already have one.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm i @payloadcms/plugin-csm
|
||||
@@ -74,15 +74,15 @@ if (isDraftMode || process.env.VERCEL_ENV === 'preview') {
|
||||
|
||||
And that's it! You are now ready to enter Edit Mode and begin visually editing your content.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Edit Mode
|
||||
#### Edit Mode
|
||||
|
||||
To see Visual Editing on your site, you first need to visit any preview deployment on Vercel and login using the Vercel Toolbar. When Content Source Maps are detected on the page, a pencil icon will appear in the toolbar. Clicking this icon will enable Edit Mode, highlighting all editable fields on the page in blue.
|
||||
To see Content Link on your site, you first need to visit any preview deployment on Vercel and login using the Vercel Toolbar. When Content Source Maps are detected on the page, a pencil icon will appear in the toolbar. Clicking this icon will enable Edit Mode, highlighting all editable fields on the page in blue.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Troubleshooting
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
##### Dates
|
||||
### Date Fields
|
||||
|
||||
The plugin does not encode `date` fields by default, but for some cases like text that uses negative CSS letter-spacing, it may be necessary to split the encoded data out from the rendered text. This way you can safely use the cleaned data as expected.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -91,9 +91,9 @@ import { vercelStegaSplit } from '@vercel/stega'
|
||||
const { cleaned, encoded } = vercelStegaSplit(text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### Blocks
|
||||
### Block fields
|
||||
|
||||
All `blocks` fields by definition do not have plain text strings to encode. For this reason, blocks are given an additional `encodedSourceMap` key, which you can use to enable Visual Editing on entire sections of your site. You can then specify the editing container by adding the `data-vercel-edit-target` HTML attribute to any top-level element of your block.
|
||||
All `blocks` fields by definition do not have plain text strings to encode. For this reason, blocks are given an additional `encodedSourceMap` key, which you can use to enable Content Link on entire sections of your site. You can then specify the editing container by adding the `data-vercel-edit-target` HTML attribute to any top-level element of your block.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
<div data-vercel-edit-target>
|
||||
378
docs/lexical/converters.mdx
Normal file
378
docs/lexical/converters.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,378 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Lexical Converters
|
||||
label: Converters
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
desc: Conversion between lexical, markdown and html
|
||||
keywords: lexical, rich text, editor, headless cms, convert, html, mdx, markdown, md, conversion, export
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Lexical => HTML
|
||||
|
||||
Lexical saves data in JSON, but can also generate its HTML representation via two main methods:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Outputting HTML from the Collection:** Create a new field in your collection to convert saved JSON content to HTML. Payload generates and outputs the HTML for use in your frontend.
|
||||
2. **Generating HTML on any server** Convert JSON to HTML on-demand on the server.
|
||||
|
||||
The editor comes with built-in HTML serializers, simplifying the process of converting JSON to HTML.
|
||||
|
||||
### Outputting HTML from the Collection
|
||||
|
||||
To add HTML generation directly within the collection, follow the example below:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import type { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
import { HTMLConverterFeature, lexicalEditor, lexicalHTML } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
const Pages: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
slug: 'pages',
|
||||
fields: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'nameOfYourRichTextField',
|
||||
type: 'richText',
|
||||
editor: lexicalEditor({
|
||||
features: ({ defaultFeatures }) => [
|
||||
...defaultFeatures,
|
||||
// The HTMLConverter Feature is the feature which manages the HTML serializers.
|
||||
// If you do not pass any arguments to it, it will use the default serializers.
|
||||
HTMLConverterFeature({}),
|
||||
],
|
||||
}),
|
||||
},
|
||||
lexicalHTML('nameOfYourRichTextField', { name: 'nameOfYourRichTextField_html' }),
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `lexicalHTML()` function creates a new field that automatically converts the referenced lexical richText field into HTML through an afterRead hook.
|
||||
|
||||
### Generating HTML anywhere on the server:
|
||||
|
||||
If you wish to convert JSON to HTML ad-hoc, use this code snippet:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import type { SerializedEditorState } from 'lexical'
|
||||
import {
|
||||
type SanitizedEditorConfig,
|
||||
convertLexicalToHTML,
|
||||
consolidateHTMLConverters,
|
||||
} from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
async function lexicalToHTML(
|
||||
editorData: SerializedEditorState,
|
||||
editorConfig: SanitizedEditorConfig,
|
||||
) {
|
||||
return await convertLexicalToHTML({
|
||||
converters: consolidateHTMLConverters({ editorConfig }),
|
||||
data: editorData,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This method employs `convertLexicalToHTML` from `@payloadcms/richtext-lexical`, which converts the serialized editor state into HTML.
|
||||
|
||||
Because every `Feature` is able to provide html converters, and because the `htmlFeature` can modify those or provide their own, we need to consolidate them with the default html Converters using the `consolidateHTMLConverters` function.
|
||||
|
||||
### CSS
|
||||
|
||||
Payload's lexical HTML converter does not generate CSS for you, but it does add classes to the generated HTML. You can use these classes to style the HTML in your frontend.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is some "base" CSS you can use to ensure that nested lists render correctly:
|
||||
|
||||
```css
|
||||
/* Base CSS for Lexical HTML */
|
||||
.nestedListItem, .list-check {
|
||||
list-style-type: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating your own HTML Converter
|
||||
|
||||
HTML Converters are typed as `HTMLConverter`, which contains the node type it should handle, and a function that accepts the serialized node from the lexical editor, and outputs the HTML string. Here's the HTML Converter of the Upload node as an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import type { HTMLConverter } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
const UploadHTMLConverter: HTMLConverter<SerializedUploadNode> = {
|
||||
converter: async ({ node, payload }) => {
|
||||
const uploadDocument = await payload.findByID({
|
||||
id: node.value.id,
|
||||
collection: node.relationTo,
|
||||
})
|
||||
const url = (payload?.config?.serverURL || '') + uploadDocument?.url
|
||||
|
||||
if (!(uploadDocument?.mimeType as string)?.startsWith('image')) {
|
||||
// Only images can be serialized as HTML
|
||||
return ``
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return `<img src="${url}" alt="${uploadDocument?.filename}" width="${uploadDocument?.width}" height="${uploadDocument?.height}"/>`
|
||||
},
|
||||
nodeTypes: [UploadNode.getType()], // This is the type of the lexical node that this converter can handle. Instead of hardcoding 'upload' we can get the node type directly from the UploadNode, since it's static.
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, we have access to all the information saved in the node (for the Upload node, this is `value`and `relationTo`) and we can use that to generate the HTML.
|
||||
|
||||
The `convertLexicalToHTML` is part of `@payloadcms/richtext-lexical` automatically handles traversing the editor state and calling the correct converter for each node.
|
||||
|
||||
### Embedding the HTML Converter in your Feature
|
||||
|
||||
You can embed your HTML Converter directly within your custom `ServerFeature`, allowing it to be handled automatically by the `consolidateHTMLConverters` function. Here is an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { createNode } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
import type { FeatureProviderProviderServer } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
export const UploadFeature: FeatureProviderProviderServer<
|
||||
UploadFeatureProps,
|
||||
UploadFeaturePropsClient
|
||||
> = (props) => {
|
||||
/*...*/
|
||||
return {
|
||||
feature: () => {
|
||||
return {
|
||||
nodes: [
|
||||
createNode({
|
||||
converters: {
|
||||
html: yourHTMLConverter, // <= This is where you define your HTML Converter
|
||||
},
|
||||
node: UploadNode,
|
||||
//...
|
||||
}),
|
||||
],
|
||||
ClientComponent: UploadFeatureClientComponent,
|
||||
clientFeatureProps: clientProps,
|
||||
serverFeatureProps: props,
|
||||
/*...*/
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
key: 'upload',
|
||||
serverFeatureProps: props,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Headless Editor
|
||||
|
||||
Lexical provides a seamless way to perform conversions between various other formats:
|
||||
|
||||
- HTML to Lexical (or, importing HTML into the lexical editor)
|
||||
- Markdown to Lexical (or, importing Markdown into the lexical editor)
|
||||
- Lexical to Markdown
|
||||
|
||||
A headless editor can perform such conversions outside of the main editor instance. Follow this method to initiate a headless editor:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { createHeadlessEditor } from '@lexical/headless' // <= make sure this package is installed
|
||||
import { getEnabledNodes, sanitizeServerEditorConfig } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
const yourEditorConfig // <= your editor config here
|
||||
|
||||
const headlessEditor = createHeadlessEditor({
|
||||
nodes: getEnabledNodes({
|
||||
editorConfig: sanitizeServerEditorConfig(yourEditorConfig),
|
||||
}),
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting the editor config
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, you need to provide an editor config in order to create a headless editor. This is because the editor config is used to determine which nodes & features are enabled, and which converters are used.
|
||||
|
||||
To get the editor config, simply import the default editor config and adjust it - just like you did inside of the `editor: lexicalEditor({})` property:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { defaultEditorConfig, defaultEditorFeatures } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical' // <= make sure this package is installed
|
||||
|
||||
const yourEditorConfig = defaultEditorConfig
|
||||
|
||||
// If you made changes to the features of the field's editor config, you should also make those changes here:
|
||||
yourEditorConfig.features = [
|
||||
...defaultEditorFeatures,
|
||||
// Add your custom features here
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting the editor config from an existing field
|
||||
|
||||
If you have access to the sanitized collection config, you can get access to the lexical sanitized editor config & features, as every lexical richText field returns it. Here is an example how you can get it from another field's afterRead hook:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import type { CollectionConfig, RichTextField } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
import { createHeadlessEditor } from '@lexical/headless'
|
||||
import type { LexicalRichTextAdapter, SanitizedServerEditorConfig } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
import {
|
||||
getEnabledNodes,
|
||||
lexicalEditor
|
||||
} from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
export const MyCollection: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
slug: 'slug',
|
||||
fields: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'text',
|
||||
type: 'text',
|
||||
hooks: {
|
||||
afterRead: [
|
||||
({ value, collection }) => {
|
||||
const otherRichTextField: RichTextField = collection.fields.find(
|
||||
(field) => 'name' in field && field.name === 'richText',
|
||||
) as RichTextField
|
||||
|
||||
const lexicalAdapter: LexicalRichTextAdapter =
|
||||
otherRichTextField.editor as LexicalRichTextAdapter
|
||||
|
||||
const sanitizedServerEditorConfig: SanitizedServerEditorConfig =
|
||||
lexicalAdapter.editorConfig
|
||||
|
||||
const headlessEditor = createHeadlessEditor({
|
||||
nodes: getEnabledNodes({
|
||||
editorConfig: sanitizedServerEditorConfig,
|
||||
}),
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// Do whatever you want with the headless editor
|
||||
|
||||
return value
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'richText',
|
||||
type: 'richText',
|
||||
editor: lexicalEditor({
|
||||
features,
|
||||
}),
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## HTML => Lexical
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have your headless editor instance, you can use it to convert HTML to Lexical:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { $generateNodesFromDOM } from '@lexical/html'
|
||||
import { $getRoot, $getSelection } from 'lexical'
|
||||
import { JSDOM } from 'jsdom'
|
||||
|
||||
headlessEditor.update(
|
||||
() => {
|
||||
// In a headless environment you can use a package such as JSDom to parse the HTML string.
|
||||
const dom = new JSDOM(htmlString)
|
||||
|
||||
// Once you have the DOM instance it's easy to generate LexicalNodes.
|
||||
const nodes = $generateNodesFromDOM(headlessEditor, dom.window.document)
|
||||
|
||||
// Select the root
|
||||
$getRoot().select()
|
||||
|
||||
// Insert them at a selection.
|
||||
const selection = $getSelection()
|
||||
selection.insertNodes(nodes)
|
||||
},
|
||||
{ discrete: true },
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Do this if you then want to get the editor JSON
|
||||
const editorJSON = headlessEditor.getEditorState().toJSON()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Functions prefixed with a `$` can only be run inside an `editor.update()` or `editorState.read()` callback.
|
||||
|
||||
This has been taken from the [lexical serialization & deserialization docs](https://lexical.dev/docs/concepts/serialization#html---lexical).
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
<strong>Note:</strong>
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
Using the <code>discrete: true</code> flag ensures instant updates to the editor state. If
|
||||
immediate reading of the updated state isn't necessary, you can omit the flag.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
## Markdown => Lexical
|
||||
|
||||
Convert markdown content to the Lexical editor format with the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { $convertFromMarkdownString } from '@lexical/markdown'
|
||||
import { sanitizeServerEditorConfig } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
const yourSanitizedEditorConfig = sanitizeServerEditorConfig(yourEditorConfig) // <= your editor config here
|
||||
const markdown = `# Hello World`
|
||||
|
||||
headlessEditor.update(
|
||||
() => {
|
||||
$convertFromMarkdownString(markdown, yourSanitizedEditorConfig.features.markdownTransformers)
|
||||
},
|
||||
{ discrete: true },
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Do this if you then want to get the editor JSON
|
||||
const editorJSON = headlessEditor.getEditorState().toJSON()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Lexical => Markdown
|
||||
|
||||
Export content from the Lexical editor into Markdown format using these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Import your current editor state into the headless editor.
|
||||
2. Convert and fetch the resulting markdown string.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's the code for it:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { $convertToMarkdownString } from '@lexical/markdown'
|
||||
import { sanitizeServerEditorConfig } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
import type { SerializedEditorState } from 'lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
const yourSanitizedEditorConfig = sanitizeServerEditorConfig(yourEditorConfig) // <= your editor config here
|
||||
const yourEditorState: SerializedEditorState // <= your current editor state here
|
||||
|
||||
// Import editor state into your headless editor
|
||||
try {
|
||||
headlessEditor.setEditorState(headlessEditor.parseEditorState(yourEditorState)) // This should commit the editor state immediately
|
||||
} catch (e) {
|
||||
logger.error({ err: e }, 'ERROR parsing editor state')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Export to markdown
|
||||
let markdown: string
|
||||
headlessEditor.getEditorState().read(() => {
|
||||
markdown = $convertToMarkdownString(yourSanitizedEditorConfig?.features?.markdownTransformers)
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `.setEditorState()` function immediately updates your editor state. Thus, there's no need for the `discrete: true` flag when reading the state afterward.
|
||||
|
||||
## Lexical => Plain Text
|
||||
|
||||
Export content from the Lexical editor into plain text using these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Import your current editor state into the headless editor.
|
||||
2. Convert and fetch the resulting plain text string.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's the code for it:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import type { SerializedEditorState } from 'lexical'
|
||||
import { $getRoot } from 'lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
const yourEditorState: SerializedEditorState // <= your current editor state here
|
||||
|
||||
// Import editor state into your headless editor
|
||||
try {
|
||||
headlessEditor.setEditorState(headlessEditor.parseEditorState(yourEditorState)) // This should commit the editor state immediately
|
||||
} catch (e) {
|
||||
logger.error({ err: e }, 'ERROR parsing editor state')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Export to plain text
|
||||
const plainTextContent =
|
||||
headlessEditor.getEditorState().read(() => {
|
||||
return $getRoot().getTextContent()
|
||||
}) || ''
|
||||
```
|
||||
182
docs/lexical/migration.mdx
Normal file
182
docs/lexical/migration.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Lexical Migration
|
||||
label: Migration
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
desc: Migration from slate and payload-plugin-lexical to lexical
|
||||
keywords: lexical, rich text, editor, headless cms, migrate, migration
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Migrating from Slate
|
||||
|
||||
While both Slate and Lexical save the editor state in JSON, the structure of the JSON is different.
|
||||
|
||||
### Migration via SlateToLexicalFeature
|
||||
|
||||
One way to handle this is to just give your lexical editor the ability to read the slate JSON.
|
||||
|
||||
Simply add the `SlateToLexicalFeature` to your editor:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import type { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
import { SlateToLexicalFeature, lexicalEditor } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
const Pages: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
slug: 'pages',
|
||||
fields: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'nameOfYourRichTextField',
|
||||
type: 'richText',
|
||||
editor: lexicalEditor({
|
||||
features: ({ defaultFeatures }) => [...defaultFeatures, SlateToLexicalFeature({})],
|
||||
}),
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and done! Now, everytime this lexical editor is initialized, it converts the slate date to lexical on-the-fly. If the data is already in lexical format, it will just pass it through.
|
||||
|
||||
This is by far the easiest way to migrate from Slate to Lexical, although it does come with a few caveats:
|
||||
|
||||
- There is a performance hit when initializing the lexical editor
|
||||
- The editor will still output the Slate data in the output JSON, as the on-the-fly converter only runs for the admin panel
|
||||
|
||||
The easy way to solve this: Just save the document! This overrides the slate data with the lexical data, and the next time the document is loaded, the lexical data will be used. This solves both the performance and the output issue for that specific document.
|
||||
|
||||
### Migration via migration script
|
||||
|
||||
The method described above does not solve the issue for all documents, though. If you want to convert all your documents to lexical, you can use a migration script. Here's a simple example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import type { Payload } from 'payload'
|
||||
import type { YourDocumentType } from 'payload/generated-types'
|
||||
|
||||
import {
|
||||
cloneDeep,
|
||||
convertSlateToLexical,
|
||||
defaultSlateConverters,
|
||||
} from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
import { AnotherCustomConverter } from './lexicalFeatures/converters/AnotherCustomConverter'
|
||||
|
||||
export async function convertAll(payload: Payload, collectionName: string, fieldName: string) {
|
||||
const docs: YourDocumentType[] = await payload.db.collections[collectionName].find({}).exec() // Use MongoDB models directly to query all documents at once
|
||||
console.log(`Found ${docs.length} ${collectionName} docs`)
|
||||
|
||||
const converters = cloneDeep([...defaultSlateConverters, AnotherCustomConverter])
|
||||
|
||||
// Split docs into batches of 20.
|
||||
const batchSize = 20
|
||||
const batches = []
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < docs.length; i += batchSize) {
|
||||
batches.push(docs.slice(i, i + batchSize))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
let processed = 0 // Number of processed docs
|
||||
|
||||
for (const batch of batches) {
|
||||
// Process each batch asynchronously
|
||||
const promises = batch.map(async (doc: YourDocumentType) => {
|
||||
const richText = doc[fieldName]
|
||||
|
||||
if (richText && Array.isArray(richText) && !('root' in richText)) {
|
||||
// It's Slate data - skip already-converted data
|
||||
const converted = convertSlateToLexical({
|
||||
converters: converters,
|
||||
slateData: richText,
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
await payload.update({
|
||||
id: doc.id,
|
||||
collection: collectionName as any,
|
||||
depth: 0, // performance optimization. No need to run population.
|
||||
data: {
|
||||
[fieldName]: converted,
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// Wait for all promises in the batch to complete. Resolving batches of 20 asynchronously is faster than waiting for each doc to update individually
|
||||
await Promise.all(promises)
|
||||
|
||||
// Update the count of processed docs
|
||||
processed += batch.length
|
||||
console.log(`Converted ${processed} of ${docs.length}`)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `convertSlateToLexical` is the same method used in the `SlateToLexicalFeature` - it handles traversing the Slate JSON for you.
|
||||
|
||||
Do note that this script might require adjustment depending on your document structure, especially if you have nested richText fields or localization enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
### Converting custom Slate nodes
|
||||
|
||||
If you have custom Slate nodes, create a custom converter for them. Here's the Upload converter as an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import type { SerializedUploadNode } from '../uploadNode.'
|
||||
import type { SlateNodeConverter } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
export const SlateUploadConverter: SlateNodeConverter = {
|
||||
converter({ slateNode }) {
|
||||
return {
|
||||
fields: {
|
||||
...slateNode.fields,
|
||||
},
|
||||
format: '',
|
||||
relationTo: slateNode.relationTo,
|
||||
type: 'upload',
|
||||
value: {
|
||||
id: slateNode.value?.id || '',
|
||||
},
|
||||
version: 1,
|
||||
} as const as SerializedUploadNode
|
||||
},
|
||||
nodeTypes: ['upload'],
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It's pretty simple: You get a Slate node as input, and you return the lexical node. The `nodeTypes` array is used to determine which Slate nodes this converter can handle.
|
||||
|
||||
When using a migration script, you can add your custom converters to the `converters` property of the `convertSlateToLexical` props, as seen in the example above
|
||||
|
||||
When using the `SlateToLexicalFeature`, you can add your custom converters to the `converters` property of the `SlateToLexicalFeature` props:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import type { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
import {
|
||||
SlateToLexicalFeature,
|
||||
lexicalEditor,
|
||||
defaultSlateConverters,
|
||||
} from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
import { YourCustomConverter } from '../converters/YourCustomConverter'
|
||||
|
||||
const Pages: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
slug: 'pages',
|
||||
fields: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'nameOfYourRichTextField',
|
||||
type: 'richText',
|
||||
editor: lexicalEditor({
|
||||
features: ({ defaultFeatures }) => [
|
||||
...defaultFeatures,
|
||||
SlateToLexicalFeature({
|
||||
converters: [...defaultSlateConverters, YourCustomConverter],
|
||||
}),
|
||||
],
|
||||
}),
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Migrating from payload-plugin-lexical
|
||||
|
||||
Migrating from [payload-plugin-lexical](https://github.com/AlessioGr/payload-plugin-lexical) works similar to migrating from Slate.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead of a `SlateToLexicalFeature` there is a `LexicalPluginToLexicalFeature` you can use. And instead of `convertSlateToLexical` you can use `convertLexicalPluginToLexical`.
|
||||
179
docs/lexical/overview.mdx
Normal file
179
docs/lexical/overview.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,179 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Lexical Overview
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: Built by Meta, Lexical is an incredibly powerful rich text editor, and it works beautifully within Payload.
|
||||
keywords: lexical, rich text, editor, headless cms
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
One of Payload's goals is to build the best rich text editor experience that we possibly can. We want to combine the beauty and polish of the Medium editing experience with the strength and features of the Notion editor - all in one place.
|
||||
|
||||
Classically, we've used SlateJS to work toward this goal, but building custom elements into Slate has proven to be more difficult than we'd like, and we've been keeping our options open.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
Payload's Lexical rich text editor is currently in beta. It's stable enough to use as you build on
|
||||
Payload, so if you're up for helping us fine-tune it, you should use it. But if you're looking for
|
||||
stability, use Slate instead.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
Lexical is extremely impressive and trivializes a lot of the hard parts of building new elements into a rich text editor. It has a few distinct advantages over Slate, including the following:
|
||||
|
||||
1. A "/" menu, which allows editors to easily add new elements while never leaving their keyboard
|
||||
1. A "hover" toolbar that pops up if you select text
|
||||
1. It supports Payload blocks natively, directly within your rich text editor
|
||||
1. Custom elements, called "features", are much easier to build in Lexical vs. Slate
|
||||
|
||||
To use the Lexical editor, first you need to install it:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
npm install @payloadcms/richtext-lexical
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have it installed, you can pass it to your top-level Payload config as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { lexicalEditor } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
collections: [
|
||||
// your collections here
|
||||
],
|
||||
// Pass the Lexical editor to the root config
|
||||
editor: lexicalEditor({}),
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also override Lexical settings on a field-by-field basis as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import type { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
import { lexicalEditor } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
|
||||
export const Pages: CollectionConfig = {
|
||||
slug: 'pages',
|
||||
fields: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'content',
|
||||
type: 'richText',
|
||||
// Pass the Lexical editor here and override base settings as necessary
|
||||
editor: lexicalEditor({}),
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Extending the lexical editor with Features
|
||||
|
||||
Lexical has been designed with extensibility in mind. Whether you're aiming to introduce new functionalities or tweak the existing ones, Lexical makes it seamless for you to bring those changes to life.
|
||||
|
||||
### Features: The Building Blocks
|
||||
|
||||
At the heart of Lexical's customization potential are "features". While Lexical ships with a set of default features we believe are essential for most use cases, the true power lies in your ability to redefine, expand, or prune these as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
If you remove all the default features, you're left with a blank editor. You can then add in only the features you need, or you can build your own custom features from scratch.
|
||||
|
||||
### Integrating New Features
|
||||
|
||||
To weave in your custom features, utilize the `features` prop when initializing the Lexical Editor. Here's a basic example of how this is done:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import {
|
||||
BlocksFeature,
|
||||
LinkFeature,
|
||||
UploadFeature,
|
||||
lexicalEditor,
|
||||
} from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
|
||||
import { Banner } from '../blocks/Banner'
|
||||
import { CallToAction } from '../blocks/CallToAction'
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
editor: lexicalEditor({
|
||||
features: ({ defaultFeatures }) => [
|
||||
...defaultFeatures,
|
||||
LinkFeature({
|
||||
// Example showing how to customize the built-in fields
|
||||
// of the Link feature
|
||||
fields: ({ defaultFields }) => [
|
||||
...defaultFields,
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'rel',
|
||||
label: 'Rel Attribute',
|
||||
type: 'select',
|
||||
hasMany: true,
|
||||
options: ['noopener', 'noreferrer', 'nofollow'],
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
description:
|
||||
'The rel attribute defines the relationship between a linked resource and the current document. This is a custom link field.',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
}),
|
||||
UploadFeature({
|
||||
collections: {
|
||||
uploads: {
|
||||
// Example showing how to customize the built-in fields
|
||||
// of the Upload feature
|
||||
fields: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'caption',
|
||||
type: 'richText',
|
||||
editor: lexicalEditor(),
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}),
|
||||
// This is incredibly powerful. You can re-use your Payload blocks
|
||||
// directly in the Lexical editor as follows:
|
||||
BlocksFeature({
|
||||
blocks: [Banner, CallToAction],
|
||||
}),
|
||||
],
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Features overview
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an overview of all the included features:
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature Name | Included by default | Description |
|
||||
|--------------------------------|---------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **`BoldTextFeature`** | Yes | Handles the bold text format |
|
||||
| **`ItalicTextFeature`** | Yes | Handles the italic text format |
|
||||
| **`UnderlineTextFeature`** | Yes | Handles the underline text format |
|
||||
| **`StrikethroughTextFeature`** | Yes | Handles the strikethrough text format |
|
||||
| **`SubscriptTextFeature`** | Yes | Handles the subscript text format |
|
||||
| **`SuperscriptTextFeature`** | Yes | Handles the superscript text format |
|
||||
| **`InlineCodeTextFeature`** | Yes | Handles the inline-code text format |
|
||||
| **`ParagraphFeature`** | Yes | Handles paragraphs. Since they are already a key feature of lexical itself, this Feature mainly handles the Slash and Add-Block menu entries for paragraphs |
|
||||
| **`HeadingFeature`** | Yes | Adds Heading Nodes (by default, H1 - H6, but that can be customized) |
|
||||
| **`AlignFeature`** | Yes | Allows you to align text left, centered and right |
|
||||
| **`IndentFeature`** | Yes | Allows you to indent text with the tab key |
|
||||
| **`UnorderedListFeature`** | Yes | Adds unordered lists (ul) |
|
||||
| **`OrderedListFeature`** | Yes | Adds ordered lists (ol) |
|
||||
| **`CheckListFeature`** | Yes | Adds checklists |
|
||||
| **`LinkFeature`** | Yes | Allows you to create internal and external links |
|
||||
| **`RelationshipFeature`** | Yes | Allows you to create block-level (not inline) relationships to other documents |
|
||||
| **`BlockQuoteFeature`** | Yes | Allows you to create block-level quotes |
|
||||
| **`UploadFeature`** | Yes | Allows you to create block-level upload nodes - this supports all kinds of uploads, not just images |
|
||||
| **`HorizontalRuleFeature`** | Yes | Horizontal rules / separators. Basically displays an `<hr>` element |
|
||||
| **`InlineToolbarFeature`** | Yes | The inline toolbar is the floating toolbar which appears when you select text. This toolbar only contains actions relevant for selected text |
|
||||
| **`FixedToolbarFeature`** | No | This classic toolbar is pinned to the top and always visible. Both inline and fixed toolbars can be enabled at the same time. |
|
||||
| **`BlocksFeature`** | No | Allows you to use Payload's [Blocks Field](/docs/fields/blocks) directly inside your editor. In the feature props, you can specify the allowed blocks - just like in the Blocks field. |
|
||||
| **`TreeViewFeature`** | No | Adds a debug box under the editor, which allows you to see the current editor state live, the dom, as well as time travel. Very useful for debugging |
|
||||
|
||||
Notice how even the toolbars are features? That's how extensible our lexical editor is - you could theoretically create your own toolbar if you wanted to!
|
||||
|
||||
## Creating your own, custom Feature
|
||||
|
||||
Creating your own custom feature requires deep knowledge of the Lexical editor. We recommend you take a look at the [Lexical documentation](https://lexical.dev/docs/intro) first - especially the "concepts" section.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, take a look at the [features we've already built](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/packages/richtext-lexical/src/field/features) - understanding how they work will help you understand how to create your own. There is no difference between the features included by default and the ones you create yourself - since those features are all isolated from the "core", you have access to the same APIs, whether the feature is part of payload or not!
|
||||
|
||||
## Coming Soon
|
||||
|
||||
Lots more documentation will be coming soon, which will show in detail how to create your own custom features within Lexical.
|
||||
|
||||
For now, take a look at the TypeScript interfaces and let us know if you need a hand. Much more will be coming from the Payload team on this topic soon.
|
||||
292
docs/live-preview/client.mdx
Normal file
292
docs/live-preview/client.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,292 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Client-side Live Preview
|
||||
label: Client-side
|
||||
order: 40
|
||||
desc: Learn how to implement Live Preview in your client-side front-end application.
|
||||
keywords: live preview, frontend, react, next.js, vue, nuxt.js, svelte, hook, useLivePreview
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
If your front-end application supports Server Components like the [Next.js App Router](https://nextjs.org/docs/app), etc., we suggest setting up [server-side Live Preview](./server) instead.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
While using Live Preview, the Admin panel emits a new `window.postMessage` event every time your document has changed. Your front-end application can listen for these events and re-render accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
If your front-end application is built with [React](#react) or [Vue](#vue), use the `useLivePreview` hooks that Payload provides. In the future, all other major frameworks like Svelte will be officially supported. If you are using any of these frameworks today, you can still integrate with Live Preview yourself using the underlying tooling that Payload provides. See [building your own hook](#building-your-own-hook) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, all hooks accept the following args:
|
||||
|
||||
| Path | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`serverURL`** \* | The URL of your Payload server. |
|
||||
| **`initialData`** | The initial data of the document. The live data will be merged in as changes are made. |
|
||||
| **`depth`** | The depth of the relationships to fetch. Defaults to `0`. |
|
||||
| **`apiRoute`** | The path of your API route as defined in `routes.api`. Defaults to `/api`. |
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
And return the following values:
|
||||
|
||||
| Path | Description |
|
||||
| --------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`data`** | The live data of the document, merged with the initial data. |
|
||||
| **`isLoading`** | A boolean that indicates whether or not the document is loading. |
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
If your front-end is tightly coupled to required fields, you should ensure that your UI does not
|
||||
break when these fields are removed. For example, if you are rendering something like
|
||||
`data.relatedPosts[0].title`, your page will break once you remove the first related post. To get
|
||||
around this, use conditional logic, optional chaining, or default values in your UI where needed.
|
||||
For example, `data?.relatedPosts?.[0]?.title`.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
It is important that the `depth` argument matches exactly with the depth of your initial page request. The depth property is used to populated relationships and uploads beyond their IDs. See [Depth](../getting-started/concepts#depth) for more information.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
## React
|
||||
|
||||
If your front-end application is built with client-side [React](https://react.dev) like [Next.js Pages Router](https://nextjs.org/docs/pages), you can use the `useLivePreview` hook that Payload provides.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install the `@payloadcms/live-preview-react` package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm install @payloadcms/live-preview-react
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, use the `useLivePreview` hook in your React component:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
'use client'
|
||||
import { useLivePreview } from '@payloadcms/live-preview-react'
|
||||
import { Page as PageType } from '@/payload-types'
|
||||
|
||||
// Fetch the page in a server component, pass it to the client component, then thread it through the hook
|
||||
// The hook will take over from there and keep the preview in sync with the changes you make
|
||||
// The `data` property will contain the live data of the document
|
||||
export const PageClient: React.FC<{
|
||||
page: {
|
||||
title: string
|
||||
}
|
||||
}> = ({ page: initialPage }) => {
|
||||
const { data } = useLivePreview<PageType>({
|
||||
initialData: initialPage,
|
||||
serverURL: PAYLOAD_SERVER_URL,
|
||||
depth: 2,
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return <h1>{data.title}</h1>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Vue
|
||||
|
||||
If your front-end application is built with [Vue 3](https://vuejs.org) or [Nuxt 3](https://nuxt.js), you can use the `useLivePreview` composable that Payload provides.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install the `@payloadcms/live-preview-vue` package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm install @payloadcms/live-preview-vue
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, use the `useLivePreview` hook in your Vue component:
|
||||
|
||||
```vue
|
||||
<script setup lang="ts">
|
||||
import type { PageData } from '~/types';
|
||||
import { defineProps } from 'vue';
|
||||
import { useLivePreview } from '@payloadcms/live-preview-vue';
|
||||
|
||||
// Fetch the initial data on the parent component or using async state
|
||||
const props = defineProps<{ initialData: PageData }>();
|
||||
|
||||
// The hook will take over from here and keep the preview in sync with the changes you make.
|
||||
// The `data` property will contain the live data of the document only when viewed from the Preview view of the Admin UI.
|
||||
const { data } = useLivePreview<PageData>({
|
||||
initialData: props.initialData,
|
||||
serverURL: "<PAYLOAD_SERVER_URL>",
|
||||
depth: 2,
|
||||
});
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
|
||||
<template>
|
||||
<h1>{{ data.title }}</h1>
|
||||
</template>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Building your own hook
|
||||
|
||||
No matter what front-end framework you are using, you can build your own hook using the same underlying tooling that Payload provides.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install the base `@payloadcms/live-preview` package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm install @payloadcms/live-preview
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This package provides the following functions:
|
||||
|
||||
| Path | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`subscribe`** | Subscribes to the Admin panel's `window.postMessage` events and calls the provided callback function. |
|
||||
| **`unsubscribe`** | Unsubscribes from the Admin panel's `window.postMessage` events. |
|
||||
| **`ready`** | Sends a `window.postMessage` event to the Admin panel to indicate that the front-end is ready to receive messages. |
|
||||
| **`isLivePreviewEvent`** | Checks if a `MessageEvent` originates from the Admin panel and is a Live Preview event, i.e. debounced form state. |
|
||||
|
||||
The `subscribe` function takes the following args:
|
||||
|
||||
| Path | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`callback`** \* | A callback function that is called with `data` every time a change is made to the document. |
|
||||
| **`serverURL`** \* | The URL of your Payload server. |
|
||||
| **`initialData`** | The initial data of the document. The live data will be merged in as changes are made. |
|
||||
| **`depth`** | The depth of the relationships to fetch. Defaults to `0`. |
|
||||
|
||||
With these functions, you can build your own hook using your front-end framework of choice:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { subscribe, unsubscribe } from '@payloadcms/live-preview'
|
||||
|
||||
// To build your own hook, subscribe to Live Preview events using the `subscribe` function
|
||||
// It handles everything from:
|
||||
// 1. Listening to `window.postMessage` events
|
||||
// 2. Merging initial data with active form state
|
||||
// 3. Populating relationships and uploads
|
||||
// 4. Calling the `onChange` callback with the result
|
||||
// Your hook should also:
|
||||
// 1. Tell the Admin panel when it is ready to receive messages
|
||||
// 2. Handle the results of the `onChange` callback to update the UI
|
||||
// 3. Unsubscribe from the `window.postMessage` events when it unmounts
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of what the same `useLivePreview` React hook from above looks like under the hood:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { subscribe, unsubscribe, ready } from '@payloadcms/live-preview'
|
||||
import { useCallback, useEffect, useState, useRef } from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export const useLivePreview = <T extends any>(props: {
|
||||
depth?: number
|
||||
initialData: T
|
||||
serverURL: string
|
||||
}): {
|
||||
data: T
|
||||
isLoading: boolean
|
||||
} => {
|
||||
const { depth = 0, initialData, serverURL } = props
|
||||
const [data, setData] = useState<T>(initialData)
|
||||
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState<boolean>(true)
|
||||
const hasSentReadyMessage = useRef<boolean>(false)
|
||||
|
||||
const onChange = useCallback((mergedData) => {
|
||||
// When a change is made, the `onChange` callback will be called with the merged data
|
||||
// Set this merged data into state so that React will re-render the UI
|
||||
setData(mergedData)
|
||||
setIsLoading(false)
|
||||
}, [])
|
||||
|
||||
useEffect(() => {
|
||||
// Listen for `window.postMessage` events from the Admin panel
|
||||
// When a change is made, the `onChange` callback will be called with the merged data
|
||||
const subscription = subscribe({
|
||||
callback: onChange,
|
||||
depth,
|
||||
initialData,
|
||||
serverURL,
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// Once subscribed, send a `ready` message back up to the Admin panel
|
||||
// This will indicate that the front-end is ready to receive messages
|
||||
if (!hasSentReadyMessage.current) {
|
||||
hasSentReadyMessage.current = true
|
||||
|
||||
ready({
|
||||
serverURL,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// When the component unmounts, unsubscribe from the `window.postMessage` events
|
||||
return () => {
|
||||
unsubscribe(subscription)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, [serverURL, onChange, depth, initialData])
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
data,
|
||||
isLoading,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
When building your own hook, ensure that the args and return values are consistent with the ones
|
||||
listed at the top of this document. This will ensure that all hooks follow the same API.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
For a working demonstration of this, check out the official [Live Preview Example](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/live-preview/payload). There you will find examples of various front-end frameworks and how to integrate each one of them, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Next.js App Router](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/live-preview/next-app)
|
||||
- [Next.js Pages Router](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/live-preview/next-pages)
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
### Relationships and/or uploads are not populating
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using relationships or uploads in your front-end application, and your front-end application runs on a different domain than your Payload server, you may need to configure [CORS](../configuration/overview) to allow requests to be made between the two domains. This includes sites that are running on a different port or subdomain. Similarly, if you are protecting resources behind user authentication, you may also need to configure [CSRF](../authentication/overview#csrf-protection) to allow cookies to be sent between the two domains. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
// If your site is running on a different domain than your Payload server,
|
||||
// This will allows requests to be made between the two domains
|
||||
cors: {
|
||||
[
|
||||
'http://localhost:3001' // Your front-end application
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
// If you are protecting resources behind user authentication,
|
||||
// This will allow cookies to be sent between the two domains
|
||||
csrf: {
|
||||
[
|
||||
'http://localhost:3001' // Your front-end application
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Relationships and/or uploads disappear after editing a document
|
||||
|
||||
It is possible that either you are setting an improper [`depth`](../getting-started/concepts#depth) in your initial request and/or your `useLivePreview` hook, or they're mismatched. Ensure that the `depth` parameter is set to the correct value, and that it matches exactly in both places. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// Your initial request
|
||||
const { docs } = await payload.find({
|
||||
collection: 'pages',
|
||||
depth: 1, // Ensure this is set to the proper depth for your application
|
||||
where: {
|
||||
slug: {
|
||||
equals: 'home',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// Your hook
|
||||
const { data } = useLivePreview<PageType>({
|
||||
initialData: initialPage,
|
||||
serverURL: PAYLOAD_SERVER_URL,
|
||||
depth: 1, // Ensure this matches the depth of your initial request
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Iframe refuses to connect
|
||||
|
||||
If your front-end application has set a [Content Security Policy](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP) (CSP) that blocks the Admin Panel from loading your front-end application, the iframe will not be able to load your site. To resolve this, you can whitelist the Admin Panel's domain in your CSP by setting the `frame-ancestors` directive:
|
||||
|
||||
```plaintext
|
||||
frame-ancestors: "self" localhost:* https://your-site.com;
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,279 +1,16 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implementing Live Preview in your app
|
||||
label: Frontend Implementation
|
||||
title: Implementing Live Preview in your frontend
|
||||
label: Frontend
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
desc: Learn how to implement Live Preview in your front-end application.
|
||||
keywords: live preview, frontend, react, next.js, vue, nuxt.js, svelte, hook, useLivePreview
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
While using Live Preview, the Admin panel emits a new `window.postMessage` event every time a change is made to the document. Your front-end application can listen for these events and re-render accordingly.
|
||||
There are two ways to use Live Preview in your own application depending on whether your front-end framework supports Server Components:
|
||||
|
||||
Wiring your front-end into Live Preview is easy. If your front-end application is built with React, Next.js, Vue or Nuxt.js, use the `useLivePreview` hook that Payload provides. In the future, all other major frameworks like Svelte will be officially supported. If you are using any of these frameworks today, you can still integrate with Live Preview yourself using the underlying tooling that Payload provides. See [building your own hook](#building-your-own-hook) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, all hooks accept the following args:
|
||||
|
||||
| Path | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`serverURL`** \* | The URL of your Payload server. |
|
||||
| **`initialData`** | The initial data of the document. The live data will be merged in as changes are made. |
|
||||
| **`depth`** | The depth of the relationships to fetch. Defaults to `0`. |
|
||||
| **`apiRoute`** | The path of your API route as defined in `routes.api`. Defaults to `/api`. |
|
||||
|
||||
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
|
||||
|
||||
And return the following values:
|
||||
|
||||
| Path | Description |
|
||||
| --------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`data`** | The live data of the document, merged with the initial data. |
|
||||
| **`isLoading`** | A boolean that indicates whether or not the document is loading. |
|
||||
- [Server-side Live Preview (suggested)](./server)
|
||||
- [Client-side Live Preview](./client)
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
If your front-end is tightly coupled to required fields, you should ensure that your UI does not
|
||||
break when these fields are removed. For example, if you are rendering something like
|
||||
`data.relatedPosts[0].title`, your page will break once you remove the first related post. To get
|
||||
around this, use conditional logic, optional chaining, or default values in your UI where needed.
|
||||
For example, `data?.relatedPosts?.[0]?.title`.
|
||||
We suggest using server-side Live Preview if your framework supports Server Components, it is both simpler to setup and more performant to run than the client-side alternative.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
It is important that the `depth` argument matches exactly with the depth of your initial page request. The depth property is used to populated relationships and uploads beyond their IDs. See [Depth](../getting-started/concepts#depth) for more information.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
### React
|
||||
|
||||
If your front-end application is built with React or Next.js, you can use the `useLivePreview` hook that Payload provides.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install the `@payloadcms/live-preview-react` package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm install @payloadcms/live-preview-react
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, use the `useLivePreview` hook in your React component:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
'use client'
|
||||
import { useLivePreview } from '@payloadcms/live-preview-react'
|
||||
import { Page as PageType } from '@/payload-types'
|
||||
|
||||
// Fetch the page in a server component, pass it to the client component, then thread it through the hook
|
||||
// The hook will take over from there and keep the preview in sync with the changes you make
|
||||
// The `data` property will contain the live data of the document
|
||||
export const PageClient: React.FC<{
|
||||
page: {
|
||||
title: string
|
||||
}
|
||||
}> = ({ page: initialPage }) => {
|
||||
const { data } = useLivePreview<PageType>({
|
||||
initialData: initialPage,
|
||||
serverURL: PAYLOAD_SERVER_URL,
|
||||
depth: 2,
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return <h1>{data.title}</h1>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Vue
|
||||
|
||||
If your front-end application is built with Vue 3 or Nuxt 3, you can use the `useLivePreview` composable that Payload provides.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install the `@payloadcms/live-preview-vue` package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm install @payloadcms/live-preview-vue
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, use the `useLivePreview` hook in your Vue component:
|
||||
|
||||
```vue
|
||||
<script setup lang="ts">
|
||||
import type { PageData } from '~/types';
|
||||
import { defineProps } from 'vue';
|
||||
import { useLivePreview } from '@payloadcms/live-preview-vue';
|
||||
|
||||
// Fetch the initial data on the parent component or using async state
|
||||
const props = defineProps<{ initialData: PageData }>();
|
||||
|
||||
// The hook will take over from here and keep the preview in sync with the changes you make.
|
||||
// The `data` property will contain the live data of the document only when viewed from the Preview view of the Admin UI.
|
||||
const { data } = useLivePreview<PageData>({
|
||||
initialData: props.initialData,
|
||||
serverURL: "<PAYLOAD_SERVER_URL>",
|
||||
depth: 2,
|
||||
});
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
|
||||
<template>
|
||||
<h1>{{ data.title }}</h1>
|
||||
</template>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Building your own hook
|
||||
|
||||
No matter what front-end framework you are using, you can build your own hook using the same underlying tooling that Payload provides.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install the base `@payloadcms/live-preview` package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm install @payloadcms/live-preview
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This package provides the following functions:
|
||||
|
||||
| Path | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| **`subscribe`** | Subscribes to the Admin panel's `window.postMessage` events and calls the provided callback function. |
|
||||
| **`unsubscribe`** | Unsubscribes from the Admin panel's `window.postMessage` events. |
|
||||
| **`ready`** | Sends a `window.postMessage` event to the Admin panel to indicate that the front-end is ready to receive messages. |
|
||||
|
||||
The `subscribe` function takes the following args:
|
||||
|
||||
| Path | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **`callback`** \* | A callback function that is called with `data` every time a change is made to the document. |
|
||||
| **`serverURL`** \* | The URL of your Payload server. |
|
||||
| **`initialData`** | The initial data of the document. The live data will be merged in as changes are made. |
|
||||
| **`depth`** | The depth of the relationships to fetch. Defaults to `0`. |
|
||||
|
||||
With these functions, you can build your own hook using your front-end framework of choice:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { subscribe, unsubscribe } from '@payloadcms/live-preview'
|
||||
|
||||
// To build your own hook, subscribe to Live Preview events using the`subscribe` function
|
||||
// It handles everything from:
|
||||
// 1. Listening to `window.postMessage` events
|
||||
// 2. Merging initial data with active form state
|
||||
// 3. Populating relationships and uploads
|
||||
// 4. Calling the `onChange` callback with the result
|
||||
// Your hook should also:
|
||||
// 1. Tell the Admin panel when it is ready to receive messages
|
||||
// 2. Handle the results of the `onChange` callback to update the UI
|
||||
// 3. Unsubscribe from the `window.postMessage` events when it unmounts
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of what the same `useLivePreview` React hook from above looks like under the hood:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { subscribe, unsubscribe, ready } from '@payloadcms/live-preview'
|
||||
import { useCallback, useEffect, useState, useRef } from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export const useLivePreview = <T extends any>(props: {
|
||||
depth?: number
|
||||
initialData: T
|
||||
serverURL: string
|
||||
}): {
|
||||
data: T
|
||||
isLoading: boolean
|
||||
} => {
|
||||
const { depth = 0, initialData, serverURL } = props
|
||||
const [data, setData] = useState<T>(initialData)
|
||||
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState<boolean>(true)
|
||||
const hasSentReadyMessage = useRef<boolean>(false)
|
||||
|
||||
const onChange = useCallback((mergedData) => {
|
||||
// When a change is made, the `onChange` callback will be called with the merged data
|
||||
// Set this merged data into state so that React will re-render the UI
|
||||
setData(mergedData)
|
||||
setIsLoading(false)
|
||||
}, [])
|
||||
|
||||
useEffect(() => {
|
||||
// Listen for `window.postMessage` events from the Admin panel
|
||||
// When a change is made, the `onChange` callback will be called with the merged data
|
||||
const subscription = subscribe({
|
||||
callback: onChange,
|
||||
depth,
|
||||
initialData,
|
||||
serverURL,
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// Once subscribed, send a `ready` message back up to the Admin panel
|
||||
// This will indicate that the front-end is ready to receive messages
|
||||
if (!hasSentReadyMessage.current) {
|
||||
hasSentReadyMessage.current = true
|
||||
|
||||
ready({
|
||||
serverURL,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// When the component unmounts, unsubscribe from the `window.postMessage` events
|
||||
return () => {
|
||||
unsubscribe(subscription)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, [serverURL, onChange, depth, initialData])
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
data,
|
||||
isLoading,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
When building your own hook, ensure that the args and return values are consistent with the ones
|
||||
listed at the top of this document. This will ensure that all hooks follow the same API.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
For a working demonstration of this, check out the official [Live Preview Example](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/live-preview/payload). There you will find examples of various front-end frameworks and how to integrate each one of them, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Next.js App Router](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/live-preview/next-app)
|
||||
- [Next.js Pages Router](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/live-preview/next-pages)
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relationships and/or uploads are not populating
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using relationships or uploads in your front-end application, and your front-end application runs on a different domain than your Payload server, you may need to configure [CORS](../configuration/overview) to allow requests to be made between the two domains. This includes sites that are running on a different port or subdomain. Similarly, if you are protecting resources behind user authentication, you may also need to configure [CSRF](../authentication/overview#csrf-protection) to allow cookies to be sent between the two domains. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
// If your site is running on a different domain than your Payload server,
|
||||
// This will allows requests to be made between the two domains
|
||||
cors: {
|
||||
[
|
||||
'http://localhost:3001' // Your front-end application
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
// If you are protecting resources behind user authentication,
|
||||
// This will allow cookies to be sent between the two domains
|
||||
csrf: {
|
||||
[
|
||||
'http://localhost:3001' // Your front-end application
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relationships and/or uploads disappear after editing a document
|
||||
|
||||
It is possible that either you are setting an improper [`depth`](../getting-started/concepts#depth) in your initial request and/or your `useLivePreview` hook, or they're mismatched. Ensure that the `depth` parameter is set to the correct value, and that it matches exactly in both places. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// Your initial request
|
||||
const { docs } = await payload.find({
|
||||
collection: 'pages',
|
||||
depth: 1, // Ensure this is set to the proper depth for your application
|
||||
where: {
|
||||
slug: {
|
||||
equals: 'home',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// Your hook
|
||||
const { data } = useLivePreview<PageType>({
|
||||
initialData: initialPage,
|
||||
serverURL: PAYLOAD_SERVER_URL,
|
||||
depth: 1, // Ensure this matches the depth of your initial request
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ keywords: live preview, preview, live, iframe, iframe preview, visual editing, d
|
||||
|
||||
**With Live Preview you can render your front-end application directly within the Admin panel. As you type, your changes take effect in real-time. No need to save a draft or publish your changes.**
|
||||
|
||||
Live Preview works by rendering an iframe on the page that loads your front-end application. The Admin panel communicates with your app through [`window.postMessage`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window/postMessage) events. These events are emitted every time a change is made to the document. Your app then listens for these events and re-renders itself with the data it receives.
|
||||
Live Preview works by rendering an iframe on the page that loads your front-end application. The Admin panel communicates with your app through [`window.postMessage`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window/postMessage) events. These events are emitted every time a change is made to the document. Your app then listens for these events and re-renders itself with the data it receives. Live Preview works in both server-side as well as client-side environments. See [Front-End](./frontend) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
{/* IMAGE OF LIVE PREVIEW HERE */}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
191
docs/live-preview/server.mdx
Normal file
191
docs/live-preview/server.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,191 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Server-side Live Preview
|
||||
label: Server-side
|
||||
order: 30
|
||||
desc: Learn how to implement Live Preview in your server-side front-end application.
|
||||
keywords: live preview, frontend, react, next.js, vue, nuxt.js, svelte, hook, useLivePreview
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
Server-side Live Preview is only for front-end frameworks that support the concept of Server Components, i.e. [React Server Components](https://react.dev/reference/rsc/server-components). If your front-end application is built with a client-side framework like the [Next.js Pages Router](https://nextjs.org/docs/pages), [React Router](https://reactrouter.com), [Vue 3](https://vuejs.org), etc., see [client-side Live Preview](./client).
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
Server-side Live Preview works by making a roundtrip to the server every time your document is saved, i.e. draft save, autosave, or publish. While using Live Preview, the Admin panel emits a new `window.postMessage` event which your front-end application can use to invoke this process. In Next.js, this means simply calling `router.refresh()` which will hydrate the HTML using new data straight from the [Local API](../local-api/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
It is recommended that you enable [Autosave](../versions/autosave) alongside Live Preview to make the experience feel more responsive.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
If your front-end application is built with [React](#react), you can use the `RefreshRouteOnChange` function that Payload provides. In the future, all other major frameworks like Vue and Svelte will be officially supported. If you are using any of these frameworks today, you can still integrate with Live Preview yourself using the underlying tooling that Payload provides. See [building your own router refresh component](#building-your-own-router-refresh-component) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
## React
|
||||
|
||||
If your front-end application is built with server-side [React](https://react.dev) like [Next.js App Router](https://nextjs.org/docs/app), you can use the `RefreshRouteOnSave` component that Payload provides.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install the `@payloadcms/live-preview-react` package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm install @payloadcms/live-preview-react
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, render the `RefreshRouteOnSave` component anywhere in your `page.tsx`. Here's an example:
|
||||
|
||||
`page.tsx`:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { RefreshRouteOnSave } from './RefreshRouteOnSave.tsx'
|
||||
import { getPayloadHMR } from '@payloadcms/next'
|
||||
import config from '../payload.config'
|
||||
|
||||
export default async function Page() {
|
||||
const payload = await getPayloadHMR({ config })
|
||||
|
||||
const page = await payload.find({
|
||||
collection: 'pages',
|
||||
draft: true
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<Fragment>
|
||||
<RefreshRouteOnSave />
|
||||
<h1>{page.title}</h1>
|
||||
</Fragment>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`RefreshRouteOnSave.tsx`:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
'use client'
|
||||
import { RefreshRouteOnSave as PayloadLivePreview } from '@payloadcms/live-preview-react'
|
||||
import { useRouter } from 'next/navigation.js'
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export const RefreshRouteOnSave: React.FC = () => {
|
||||
const router = useRouter()
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<PayloadLivePreview
|
||||
refresh={() => router.refresh()}
|
||||
serverURL={process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_PAYLOAD_URL}
|
||||
/>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Building your own router refresh component
|
||||
|
||||
No matter what front-end framework you are using, you can build your own component using the same underlying tooling that Payload provides.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install the base `@payloadcms/live-preview` package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm install @payloadcms/live-preview
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This package provides the following functions:
|
||||
|
||||
| Path | Description |
|
||||
| --------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| **`ready`** | Sends a `window.postMessage` event to the Admin panel to indicate that the front-end is ready to receive messages. |
|
||||
| **`isDocumentEvent`** | Checks if a `MessageEvent` originates from the Admin panel and is a document-level event, i.e. draft save, autosave, publish, etc. |
|
||||
|
||||
With these functions, you can build your own hook using your front-end framework of choice:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { ready, isDocumentEvent } from '@payloadcms/live-preview'
|
||||
|
||||
// To build your own component:
|
||||
// 1. Listen for document-level `window.postMessage` events sent from the Admin panel
|
||||
// 2. Tell the Admin panel when it is ready to receive messages
|
||||
// 3. Refresh the route every time a new document-level event is received
|
||||
// 4. Unsubscribe from the `window.postMessage` events when it unmounts
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of what the same `RefreshRouteOnSave` React component from above looks like under the hood:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
'use client'
|
||||
|
||||
import type React from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
import { isDocumentEvent, ready } from '@payloadcms/live-preview'
|
||||
import { useCallback, useEffect, useRef } from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export const RefreshRouteOnSave: React.FC<{
|
||||
apiRoute?: string
|
||||
depth?: number
|
||||
refresh: () => void
|
||||
serverURL: string
|
||||
}> = (props) => {
|
||||
const { apiRoute, depth, refresh, serverURL } = props
|
||||
const hasSentReadyMessage = useRef<boolean>(false)
|
||||
|
||||
const onMessage = useCallback(
|
||||
(event: MessageEvent) => {
|
||||
if (isDocumentEvent(event, serverURL)) {
|
||||
if (typeof refresh === 'function') {
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
[refresh, serverURL],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
useEffect(() => {
|
||||
if (typeof window !== 'undefined') {
|
||||
window.addEventListener('message', onMessage)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!hasSentReadyMessage.current) {
|
||||
hasSentReadyMessage.current = true
|
||||
|
||||
ready({
|
||||
serverURL,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return () => {
|
||||
if (typeof window !== 'undefined') {
|
||||
window.removeEventListener('message', onMessage)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, [serverURL, onMessage, depth, apiRoute])
|
||||
|
||||
return null
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
For a working demonstration of this, check out the official [Live Preview Example](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/examples/live-preview/payload). There you will find a fully working example of how to implement Live Preview in your Next.js App Router application.
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
### Updates do not appear as fast as client-side Live Preview
|
||||
|
||||
If you are noticing that updates feel less snappy than client-side Live Preview (i.e. the `useLivePreview` hook), this is because of how the two differ in how they work—instead of emitting events against _form state_, server-side Live Preview refreshes the route after a new document is _saved_.
|
||||
|
||||
Use [Autosave](../versions/autosave) to mimic this effect server-side. Try decreasing the value of `versions.autoSave.interval` to make the experience feel more responsive:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// collection.ts
|
||||
{
|
||||
versions: {
|
||||
drafts: {
|
||||
autosave: {
|
||||
interval: 375,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Iframe refuses to connect
|
||||
|
||||
If your front-end application has set a [Content Security Policy](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP) (CSP) that blocks the Admin Panel from loading your front-end application, the iframe will not be able to load your site. To resolve this, you can whitelist the Admin Panel's domain in your CSP by setting the `frame-ancestors` directive:
|
||||
|
||||
```plaintext
|
||||
frame-ancestors: "self" localhost:* https://your-site.com;
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Local API
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: The Payload Local API allows you to interact with your database and execute the same operations that are available through REST and GraphQL within Node, directly on your server.
|
||||
keywords: local api, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: local api, config, configuration, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
The Payload Local API gives you the ability to execute the same operations that are available through REST and GraphQL
|
||||
@@ -23,14 +23,14 @@ can interact directly with your database.
|
||||
Here are some common examples of how you can use the Local API:
|
||||
|
||||
- Seeding data via Node seed scripts that you write and maintain
|
||||
- Opening custom Express routes which feature additional functionality but still rely on Payload
|
||||
- Opening custom routes which feature additional functionality but still rely on Payload
|
||||
- Within access control and hook functions
|
||||
|
||||
### Accessing payload
|
||||
## Accessing payload
|
||||
|
||||
You can gain access to the currently running `payload` object via two ways:
|
||||
|
||||
##### Importing it
|
||||
#### Importing it
|
||||
|
||||
You can import or require `payload` into your own files after it's been initialized, but you need to make sure that
|
||||
your `import` / `require` statements come **after** you call `payload.init()`—otherwise Payload won't have been
|
||||
@@ -49,9 +49,9 @@ const afterChangeHook: CollectionAfterChangeHook = async () => {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### Accessing from the `req`
|
||||
#### Accessing from the `req`
|
||||
|
||||
Payload is available anywhere you have access to the Express `req` - including within your access control and hook
|
||||
Payload is available anywhere you have access to the `req` - including within your access control and hook
|
||||
functions.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ const afterChangeHook: CollectionAfterChangeHook = async ({ req: { payload } })
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Local options available
|
||||
## Local options available
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify more options within the Local API vs. REST or GraphQL due to the server-only context that they are
|
||||
executed in.
|
||||
@@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ _There are more options available on an operation by operation basis outlined be
|
||||
|
||||
The following Collection operations are available through the Local API:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Create
|
||||
### Create
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// The created Post document is returned
|
||||
@@ -127,7 +127,7 @@ const post = await payload.create({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Find
|
||||
### Find
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Result will be a paginated set of Posts.
|
||||
@@ -148,7 +148,7 @@ const result = await payload.find({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Find by ID
|
||||
### Find by ID
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Result will be a Post document.
|
||||
@@ -164,7 +164,7 @@ const result = await payload.findByID({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Count
|
||||
### Count
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Result will be an object with:
|
||||
@@ -180,7 +180,7 @@ const result = await payload.count({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Update by ID
|
||||
### Update by ID
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Result will be the updated Post document.
|
||||
@@ -211,7 +211,7 @@ const result = await payload.update({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Update Many
|
||||
### Update Many
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Result will be an object with:
|
||||
@@ -249,7 +249,7 @@ const result = await payload.update({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Delete
|
||||
### Delete
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Result will be the now-deleted Post document.
|
||||
@@ -265,7 +265,7 @@ const result = await payload.delete({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Delete Many
|
||||
### Delete Many
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Result will be an object with:
|
||||
@@ -293,7 +293,7 @@ const result = await payload.delete({
|
||||
If a collection has [`Authentication`](/docs/authentication/overview) enabled, additional Local API operations will be
|
||||
available:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Login
|
||||
### Login
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// result will be formatted as follows:
|
||||
@@ -310,7 +310,7 @@ const result = await payload.login({
|
||||
email: 'dev@payloadcms.com',
|
||||
password: 'rip',
|
||||
},
|
||||
req: req, // pass an Express `req` which will be provided to all hooks
|
||||
req: req, // pass a Request object to be provided to all hooks
|
||||
res: res, // used to automatically set an HTTP-only auth cookie
|
||||
depth: 2,
|
||||
locale: 'en',
|
||||
@@ -320,7 +320,7 @@ const result = await payload.login({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Forgot Password
|
||||
### Forgot Password
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Returned token will allow for a password reset
|
||||
@@ -330,11 +330,11 @@ const token = await payload.forgotPassword({
|
||||
// required
|
||||
email: 'dev@payloadcms.com',
|
||||
},
|
||||
req: req, // pass an Express `req` which will be provided to all hooks
|
||||
req: req, // pass a Request object to be provided to all hooks
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Reset Password
|
||||
### Reset Password
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Result will be formatted as follows:
|
||||
@@ -349,12 +349,12 @@ const result = await payload.resetPassword({
|
||||
password: req.body.password, // the new password to set
|
||||
token: 'afh3o2jf2p3f...', // the token generated from the forgotPassword operation
|
||||
},
|
||||
req: req, // pass an Express `req` which will be provided to all hooks
|
||||
req: req, // pass a Request object to be provided to all hooks
|
||||
res: res, // used to automatically set an HTTP-only auth cookie
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Unlock
|
||||
### Unlock
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Returned result will be a boolean representing success or failure
|
||||
@@ -364,12 +364,12 @@ const result = await payload.unlock({
|
||||
// required
|
||||
email: 'dev@payloadcms.com',
|
||||
},
|
||||
req: req, // pass an Express `req` which will be provided to all hooks
|
||||
req: req, // pass a Request object to be provided to all hooks
|
||||
overrideAccess: true,
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Verify
|
||||
### Verify
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Returned result will be a boolean representing success or failure
|
||||
@@ -383,7 +383,7 @@ const result = await payload.verifyEmail({
|
||||
|
||||
The following Global operations are available through the Local API:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Find
|
||||
### Find
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Result will be the Header Global.
|
||||
@@ -398,7 +398,7 @@ const result = await payload.findGlobal({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Update
|
||||
### Update
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Result will be the updated Header Global.
|
||||
@@ -427,10 +427,10 @@ const result = await payload.updateGlobal({
|
||||
## Next.js Conflict with Local API
|
||||
|
||||
There is a known issue when using the Local API with Next.js version `13.4.13` and higher. Next.js executes within a
|
||||
separate child process, and Payload has not been initalized yet in these instances. That means that unless you
|
||||
separate child process, and Payload has not been initialized yet in these instances. That means that unless you
|
||||
explicitly initialize Payload within your operation, it will not be running and return no data / an empty object.
|
||||
|
||||
As a workaround, we recommend leveraging the following pattern to determine and ensure Payload is initalized:
|
||||
As a workaround, we recommend leveraging the following pattern to determine and ensure Payload is initialized:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import dotenv from 'dotenv'
|
||||
|
||||
804
docs/migration-guide/overview.mdx
Normal file
804
docs/migration-guide/overview.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,804 @@
|
||||
# 🚧 **DRAFT:** 3.0 Migration Guide / Breaking Changes
|
||||
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> This document will continue to be updated and cleaned up until the 3.0 release.
|
||||
|
||||
## What has changed?
|
||||
|
||||
The core logic and principles of Payload remain the same for 3.0. The brunt of the changes are at the HTTP layer and the Admin Panel. These aspects were moved to be based upon Next.js.
|
||||
|
||||
## To migrate from Payload 2.0 to 3.0:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Delete the `admin.bundler` property from your Payload config:
|
||||
|
||||
Payload no longer bundles the admin panel. Instead, we rely directly on Next.js for bundling. This also means that the `@payloadcms/bundler-webpack` and `@payloadcms/bundler-vite` packages have been deprecated. You can completely uninstall those from your project by removing them from your `package.json` file and re-running your package manager’s installation process, i.e. `pnpm i`.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Add the `secret` property to your Payload config. This used to be set in the `payload.init()` function of your `server.ts` file. Move it to `payload.config.ts` instead:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
|
||||
buildConfig({
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
secret: process.env.PAYLOAD_SECRET
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. The `admin.css` and `admin.scss` properties in the Payload config have been removed:
|
||||
|
||||
Instead for any global styles you can:
|
||||
|
||||
- use `(payload)/custom.scss` to import or add your own styles, eg. for tailwind
|
||||
- plugins that need to inject global styles should do so via the provider config at `admin.components.providers` :
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// payload.config.js
|
||||
|
||||
//...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
providers: [
|
||||
MyProvider
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
//...
|
||||
|
||||
// MyProvider.tsx
|
||||
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
import './globals.css'
|
||||
|
||||
const MyProvider: React.FC<{children?: any}= ({ children }) ={
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<React.fragment>
|
||||
{children}
|
||||
</React.fragment>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default Provider
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. The `admin.indexHTML` property has been removed.
|
||||
5. The `collection.admin.hooks` property has been removed.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, use the new `beforeDuplicate` field-level hook which take the usual field hook arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// TODO: add snippet here of old vs new
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Import all Payload React components via the `@payloadcms/ui` package instead of `payload`:
|
||||
|
||||
If you were previously importing components into your app from the `payload` package, for example to create a custom component, you will need to:
|
||||
|
||||
- Change your import paths (see below)
|
||||
- Migrate your component (if necessary, see next bullet)
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import { Button } from '@payloadcms/ui/elements/Button'
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: Add new full list of exports
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
7. Migrate all Custom Components to Server Components.
|
||||
|
||||
All Custom Components are now server-rendered, and therefore, cannot use state or hooks directly. If you’re using Custom Components in your app that requires state or hooks, define your component in a separate file with the `'use client'` directive at the top, then render *that* client component within your server component. Remember you can only pass serializable props to this component, so props cannot be blindly spread.
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
import type { ServerOnlyProps } from './types.ts'
|
||||
import MyClientComponent from './client.tsx'
|
||||
|
||||
export const MyServerComponent: React.FC<ServerOnlyProps= (serverOnlyProps) ={
|
||||
const clientOnlyProps = {
|
||||
// ... sanitize server-only props here as needed
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<MyClientComponent {...clientOnlyProps} />
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. The `custom` property in the Payload config, i.e. collections, globals, blocks, and fields are now ***server only***.
|
||||
|
||||
Use `admin.custom` properties will be available in both server and client bundles.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
|
||||
buildConfig({
|
||||
// Server Only
|
||||
custom: {
|
||||
someProperty: 'value'
|
||||
},
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
custom: {
|
||||
name: 'Customer portal' // Available in server and client
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
9. The `admin.description` property on field configs no longer attaches `data` to its args:
|
||||
|
||||
This is because we cannot pass your `description` function to the client for execution (functions are not serializable, and state is held on the client). To display dynamic descriptions that use current `data` or `path`, you must now pass a custom component and subscribe to the field’s state yourself using Payload’s React hooks:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// TODO: add config snippet for total clarity
|
||||
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
// TODO: get rest of imports
|
||||
|
||||
export const CustomFieldDescriptionComponent: DescriptionComponent = () ={
|
||||
const { path } = useFieldProps()
|
||||
const { value } = useFormFields(([fields]) =fields[path])
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
{`Component description: ${path} - ${value}`}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
10. The `admin.label` property on the `collapsible` field no longer attaches `data` to its args.
|
||||
|
||||
This is because we cannot pass your `label` function to the client for execution (functions are not serializable, and state is held on the client). To display dynamic labels that use current `data` or `path`, you must now pass a custom component and subscribe to the field’s state yourself using Payload’s React hooks:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// TODO: add config snippet for total clarity
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
// TODO: get rest of imports
|
||||
|
||||
export const CustomFieldLabelComponent: LabelComponent = () => {
|
||||
const { path } = useFieldProps()
|
||||
const { value } = useFormFields(([fields]) =fields[path])
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
{`Component label: ${path} - ${value}`}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
11. The `admin.components.Cell` no longer receives `rowData` or `cellData`.
|
||||
|
||||
If using a custom component, you must now get the data yourself via the `useTableCell` hook, i.e. `const { cellData, rowData } = useTableCell()`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// TODO: add config snippet for total clarity
|
||||
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
// TODO: get rest of imports
|
||||
|
||||
export const CustomCellComponent: CellComponent = () ={
|
||||
const { cellData, rowData } = useTableCell()
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
{`Component cell: ${cellData}`}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
12. `admin.components.RowLabel` no longer accepts a function, instead use a custom component and make use of the `useRowLabel` hook:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
// Field config
|
||||
{
|
||||
type: 'array',
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
RowLabel: ({ data }) ={
|
||||
console.log(data)
|
||||
return data?.title || 'Untitled'
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
// Field config
|
||||
{
|
||||
type: 'array',
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
RowLabel: ArrayRowLabel
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Custom Component
|
||||
'use client'
|
||||
|
||||
import type { RowLabelComponent } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
import { useRowLabel } from '@payloadcms/ui/forms/RowLabel/Context'
|
||||
import React from 'react'
|
||||
|
||||
export const ArrayRowLabel: RowLabelComponent = () ={
|
||||
const { data } = useRowLabel<{ title: string }>()
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>{data.title || 'Untitled'}</div>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
13. The `admin.components.views[].Tab.pillLabel` has been replaced with `admin.components.views[].Tab.Pill`
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// Collection.ts
|
||||
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: {
|
||||
Tab: {
|
||||
pillLabel: '',
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
components: {
|
||||
views: {
|
||||
Edit: {
|
||||
Tab: {
|
||||
Pill: MyPill,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
14. The `useTitle` hook has been absorbed by the `useDocumentInfo` hook.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can get title directly from document info context, i.e. `const { title } = useDocumentInfo()`.
|
||||
|
||||
15. The `Fields` type was renamed to `FormState`:
|
||||
|
||||
This was changed for improved semantics. If you were previously importing this type in your own application, simply change the import name:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
import type { Fields } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
import type { FormState } from 'payload/types'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
16. The `useDocumentInfo` hook no longer returns a `SanizitedCollectionConfig` or `SanitizedGlobalConfig`:
|
||||
|
||||
This is because the configs themselves are not serializable and so they cannot be thread through to the client, i.e. the `DocumentInfoContext`. Instead, various properties of the config are passed instead, like `collectionSlug` and `globalSlug`. You can use these to access a client-side config, if needed, through the `useConfig` hook (see next bullet).
|
||||
|
||||
17. The `useConfig` hook now returns a `ClientConfig` and not a `SanizitedConfig`.
|
||||
|
||||
This is because the config itself is not serializable and so it is not able to be thread through to the client, i.e. the `ConfigContext`.
|
||||
|
||||
18. `DocumentTabProps` no longer contains `id` or `isEditing`.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead you can use the `useDocumentInfo` hook to get this information (see above).
|
||||
|
||||
19. The args of the `livePreview.url` function have changed.
|
||||
|
||||
It no longer receives `documentInfo` as an arg, and instead, now has `collectionConfig` and `globalConfig`.
|
||||
|
||||
20. The `href` and `isActive` functions in the view tab config no longer sends the `match` or `location` arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
This is is a property specific to React Router, not Next.js. If you need to do fancy matching similar to this, use a custom tab that fires of some hooks, i.e. `usePathname()` and run it through your own utility functions.
|
||||
|
||||
21. The `views.Edit` or `views.Edit.Default` or `views.Edit.Default.Component` properties are no longer of type `AdminViewComponent` like the other views.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, their new type is `React.FC<EditViewProps>` where you now only receive the config slug. This is because of how custom edit views need to be rendered server-side, then returned by a client-component (i.e. the document drawer). There’s an example of this adapter pattern in the first sections of this page.
|
||||
|
||||
22. `beforeDuplicate` field hooks have been added to `unique` fields to automatically add “- Copy” to the end.
|
||||
23. The `useCollapsible` hook has had slight changes to its property names:
|
||||
|
||||
`collapsed` is now `isCollapsed` and `withinCollapsible` is now `isWithinCollapsible`.
|
||||
|
||||
24. Components that return a function have webpack errors.
|
||||
|
||||
Will need to document the following (if intended as a breaking change)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
25. The `admin.favicon` property is now `admin.icons` and the types have changed
|
||||
|
||||
Reference: https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/pull/6347
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
favicon: 'path-to-favicon.svg'
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
icons: [{
|
||||
path: 'path-to-favicon.svg',
|
||||
sizes: '32x32'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See also: https://nextjs.org/docs/app/api-reference/functions/generate-metadata#icons
|
||||
|
||||
26. The `admin.meta.ogImage` property has been replaced by `admin.meta.openGraph.images`
|
||||
|
||||
Reference: https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/pull/6227
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
{
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
meta: {
|
||||
ogImage: ''
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
meta: {
|
||||
openGraph: {
|
||||
images: []
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See also : https://nextjs.org/docs/app/api-reference/functions/generate-metadata#opengraph
|
||||
|
||||
27. The `admin.logoutRoute` and `admin.inactivityRoute` properties have been consolidated into a single `admin.routes` property
|
||||
|
||||
Reference: https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/pull/6354
|
||||
|
||||
To migrate, simply move those two keys as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// payload.config.ts
|
||||
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
logoutRoute: '/custom-logout',
|
||||
inactivityRoute: '/custom-inactivity'
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
admin: {
|
||||
routes: {
|
||||
logout: '/custom-logout',
|
||||
inactivity: '/custom-inactivity'
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Environment variables
|
||||
|
||||
- Environment variables prefixed with `PAYLOAD_PUBLIC` will no longer be available on the client. In order to access them on the client, those will now have to be prefixed with `NEXT_PUBLIC` instead
|
||||
|
||||
## i18n
|
||||
|
||||
- `useTranslation()` hook no longer takes any options, any translations using shorthand accessors will need to use the entire `group:key`
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
const { i18n, t } = useTranslation('general')
|
||||
return <p>{t('cancel')}</p>
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
const { i18n, t } = useTranslation()
|
||||
return <p>{t('general:cancel')}</p>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `react-i18n` was removed, the `Trans` component from react-i18n has been replaced with a payload provided solution. You can instead `import { Translation } from "@payloadcms/ui"`
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// Translation string example
|
||||
// "loggedInChangePassword": "To change your password, go to your <0>account</0> and edit your password there."
|
||||
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
<Trans i18nKey="loggedInChangePassword" t={t}>
|
||||
<Link to={`${admin}/account`}>account</Link>
|
||||
</Trans>
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
<Translation
|
||||
t={t}
|
||||
i18nKey="authentication:loggedInChangePassword"
|
||||
elements={{
|
||||
'0': ({ children }) => <Link href={`${admin}/account`} children={children} />,
|
||||
}}
|
||||
/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Description and Label handling
|
||||
|
||||
https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/pull/6264
|
||||
|
||||
- Globals config: `admin.description` no longer accepts a custom component. You will have to move it to `admin.components.elements.Description`
|
||||
- Collections config: `admin.description` no longer accepts a custom component. You will have to move it to `admin.components.edit.Description`
|
||||
- All Fields: `field.admin.description` no longer accepts a custom component. You will have to move it to `field.admin.components.Description`
|
||||
- Collapsible Field: `field.label` no longer accepts a custom component. You will have to move it to `field.admin.components.RowLabel`
|
||||
- Array Field: `field.admin.components.RowLabel` no longer accepts strings or records
|
||||
- If you are using our exported field components in your own app, their `labelProps` property has been stripped down and no longer contains the `label` and `required` prop. Those can now only be configured at the top-level.
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom Endpoints
|
||||
|
||||
- `root` endpoints no longer exist on the config. If you want to create a “root” endpoint, you can add them to the api folder within your Payload application. See Next docs: https://nextjs.org/docs/app/api-reference/file-conventions/route
|
||||
- Endpoint handlers
|
||||
- arguments
|
||||
- ❌ Before: `(req, res, next)`
|
||||
- ✅ After: `(req)`
|
||||
- return
|
||||
- ❌ Before: `res.json`, `res.send`, etc.
|
||||
- ✅ After: a valid HTTP [`Response`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Response)
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
path: '/whoami/:parameter',
|
||||
method: 'post',
|
||||
handler: (req, res) => {
|
||||
res.json({
|
||||
parameter: req.params.parameter,
|
||||
name: req.body.name,
|
||||
age: req.body.age,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
path: '/whoami/:parameter',
|
||||
method: 'post',
|
||||
handler: (req) => {
|
||||
return Response.json({
|
||||
parameter: req.routeParams.parameter,
|
||||
// ^^ `params` is now `routeParams`
|
||||
name: req.data.name,
|
||||
age: req.data.age,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Handlers no longer resolve `data` for you on the request, use `req.json()` or you can use our utilities
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
path: '/whoami/:parameter',
|
||||
method: 'post',
|
||||
handler: async (req) => {
|
||||
return Response.json({
|
||||
name: req.data.name, // data will be undefined
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
import { addDataAndFileToRequest } from '@payloadcms/next/utilities'
|
||||
{
|
||||
path: '/whoami/:parameter',
|
||||
method: 'post',
|
||||
handler: async (req) => {
|
||||
// mutates req, must be awaited
|
||||
await addDataAndFileToRequest(req)
|
||||
|
||||
return Response.json({
|
||||
name: req.data.name, // data is now available
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Handlers no longer resolve `locale` and `fallbackLocale` for you
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
path: '/whoami/:parameter',
|
||||
method: 'post',
|
||||
handler: async (req) => {
|
||||
return Response.json({
|
||||
// will be undefined
|
||||
fallbackLocale: req.fallbackLocale,
|
||||
locale: req.locale,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
import { addLocalesToRequest } from '@payloadcms/next/utilities'
|
||||
{
|
||||
path: '/whoami/:parameter',
|
||||
method: 'post',
|
||||
handler: async (req) => {
|
||||
// mutates req
|
||||
addLocalesToRequest(req)
|
||||
|
||||
return Response.json({
|
||||
fallbackLocale: req.fallbackLocale,
|
||||
locale: req.locale,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Req (Hooks, Access-control, etc)
|
||||
|
||||
- The `req` used to extend the Express Request, now it extends the [Web Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request). So you may need to change things in your code, for example if you are relying on `req.headers['content-type']` you will now need to to use `req.headers.get('content-type')`
|
||||
|
||||
## Uploads
|
||||
|
||||
- `staticDir` must now be an absolute path. Before it would attempt to use the location of the payload config and merge the relative path set for staticDir.
|
||||
- `staticURL` has been removed. If you were using this format URLs when using an external provider, you can leverage the `generateFileURL` functions in order to do the same.
|
||||
|
||||
## Email Adapters
|
||||
|
||||
Email functionality has been abstracted out into email adapters.
|
||||
|
||||
- All existing nodemailer functionality was abstracted into the `@payloadcms/email-nodemailer` package
|
||||
- No longer configured with ethereal.email by default.
|
||||
- Ability to pass email into the `init` function has been removed.
|
||||
- Warning will be given on startup if email not configured. Any `sendEmail` call will simply log the To address and subject.
|
||||
- A Resend adapter is now also available via the `@payloadcms/email-resend` package.
|
||||
|
||||
### If you used the default email configuration in 2.0 (nodemailer):
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
// via payload.init
|
||||
payload.init({
|
||||
email: {
|
||||
transport: someNodemailerTransport
|
||||
fromName: 'hello',
|
||||
fromAddress: 'hello@example.com',
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
// or via email in payload.config.ts
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
email: {
|
||||
transport: someNodemailerTransport
|
||||
fromName: 'hello',
|
||||
fromAddress: 'hello@example.com',
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
// Using new nodemailer adapter package
|
||||
|
||||
import { nodemailerAdapter } from '@payloadcms/email-nodemailer'
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
email: nodemailerAdapter() // This will be the old ethereal.email functionality
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// or pass in transport
|
||||
|
||||
export default buildConfig({
|
||||
email: nodemailerAdapter({
|
||||
defaultFromAddress: 'info@payloadcms.com',
|
||||
defaultFromName: 'Payload',
|
||||
transport: await nodemailer.createTransport({
|
||||
host: process.env.SMTP_HOST,
|
||||
port: 587,
|
||||
auth: {
|
||||
user: process.env.SMTP_USER,
|
||||
pass: process.env.SMTP_PASS,
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
})
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Removal of rate-limiting
|
||||
|
||||
- Now only available if using custom server and using express or similar
|
||||
|
||||
# Plugins
|
||||
|
||||
- *All* plugins have been standardized to use *named exports* (as opposed to default exports). Most also have a suffix of `Plugin` to make it clear what is being imported.
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
import seo from '@payloadcms/plugin-seo'
|
||||
import stripePlugin from '@payloadcms/plugin-stripe'
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
import { seoPlugin } from '@payloadcms/plugin-seo'
|
||||
import { stripePlugin } from '@payloadcms/plugin-stripe'
|
||||
|
||||
// etc.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## `@payloadcms/plugin-cloud-storage`
|
||||
|
||||
- The adapters that are exported from `@payloadcms/plugin-cloud-storage` (ie. `@payloadcms/plugin-cloud-storage/s3`) package have been removed.
|
||||
- New *standalone* packages have been created for each of the existing adapters. Please see the documentation for the one that you use.
|
||||
- `@payloadcms/plugin-cloud-storage` is still fully supported but should only to be used if you are providing a custom adapter that does not have a dedicated package.
|
||||
- If you have created a custom adapter, the type must now provide a `name` property.
|
||||
|
||||
| Service | Package |
|
||||
| -------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Vercel Blob | https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/beta/packages/storage-vercel-blob |
|
||||
| AWS S3 | https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/beta/packages/storage-s3 |
|
||||
| Azure | https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/beta/packages/storage-azure |
|
||||
| Google Cloud Storage | https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/beta/packages/storage-gcs |
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ❌ Before (required peer dependencies depending on adapter)
|
||||
|
||||
import { cloudStorage } from '@payloadcms/plugin-cloud-storage'
|
||||
import { s3Adapter } from '@payloadcms/plugin-cloud-storage/s3'
|
||||
|
||||
plugins: [
|
||||
cloudStorage({
|
||||
collections: {
|
||||
[mediaSlug]: {
|
||||
adapter: s3Adapter({
|
||||
bucket: process.env.S3_BUCKET,
|
||||
config: {
|
||||
credentials: {
|
||||
accessKeyId: process.env.S3_ACCESS_KEY_ID,
|
||||
secretAccessKey: process.env.S3_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY,
|
||||
},
|
||||
region: process.env.S3_REGION,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}),
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}),
|
||||
],
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
|
||||
import { s3Storage } from '@payloadcms/storage-s3'
|
||||
|
||||
plugins: [
|
||||
s3Storage({
|
||||
collections: {
|
||||
[mediaSlug]: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
bucket: process.env.S3_BUCKET,
|
||||
config: {
|
||||
credentials: {
|
||||
accessKeyId: process.env.S3_ACCESS_KEY_ID,
|
||||
secretAccessKey: process.env.S3_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY,
|
||||
},
|
||||
region: process.env.S3_REGION,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}),
|
||||
],
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## `@payloadcms/plugin-form-builder`
|
||||
|
||||
- Field overrides for form and form submission collections now accept a function with a `defaultFields` inside the args instead of an array of config
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
fields: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'custom',
|
||||
type: 'text',
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
fields: ({ defaultFields }) => {
|
||||
return [
|
||||
...defaultFields,
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'custom',
|
||||
type: 'text',
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## `@payloadcms/plugin-redirects`
|
||||
|
||||
- Field overrides for the redirects collection now accepts a function with a `defaultFields` inside the args instead of an array of config
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// ❌ Before
|
||||
|
||||
fields: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'custom',
|
||||
type: 'text',
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
// ✅ After
|
||||
fields: ({ defaultFields }) => {
|
||||
return [
|
||||
...defaultFields,
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: 'custom',
|
||||
type: 'text',
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## `@payloadcms/richtext-lexical`
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: Needs comprehensive breaking changes / migration steps
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Features
|
||||
|
||||
- Previously, a Feature would contain both server code (e.g. population promises) and client code (e.g. toolbar items). Now, they have been split up into server features and client features
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Building Your Own Plugin
|
||||
label: Build Your Own
|
||||
order: 50
|
||||
desc: Starting to build your own plugin? Find everything you need and learn best practices with the Payload plugin template.
|
||||
keywords: plugins, template, config, configuration, extensions, custom, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: plugins, template, config, configuration, extensions, custom, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Building your own plugin is easy, and if you're already familiar with Payload then you'll have everything you need to get started. You can either start from scratch or use the Payload plugin template to get up and running quickly.
|
||||
@@ -22,11 +22,11 @@ Our plugin template includes everything you need to build a full life-cycle plug
|
||||
|
||||
By abstracting your code into a plugin, you'll be able to reuse your feature across multiple projects and make it available for other developers to use.
|
||||
|
||||
### Plugins Recap
|
||||
## Plugins Recap
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a brief recap of how to integrate plugins with Payload, to learn more head back to the [plugin overview page](https://payloadcms.com/docs/plugins/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
#### How to install a plugin
|
||||
### How to install a plugin
|
||||
|
||||
To install any plugin, simply add it to your Payload config in the plugins array.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ const config = buildConfig({
|
||||
export default config;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Initialization
|
||||
### Initialization
|
||||
|
||||
The initialization process goes in the following order:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ The initialization process goes in the following order:
|
||||
4. Sanitization cleans and validates data
|
||||
5. Final config gets initialized
|
||||
|
||||
### Plugin Template
|
||||
## Plugin Template
|
||||
|
||||
In the [Payload plugin template](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload-plugin-template), you will see a common file structure that is used across plugins:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -63,14 +63,14 @@ In the [Payload plugin template](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload-plugin-te
|
||||
2. /src folder - everything related to the plugin
|
||||
3. /dev folder - sanitized test project for development
|
||||
|
||||
#### Root
|
||||
### The root folder
|
||||
|
||||
In the root folder, you will see various files related to the configuration of the plugin. We set up our environment in a similar manner in Payload core and across other projects. The only two files you need to modify are:
|
||||
|
||||
- **README**.md - This contains instructions on how to use the template. When you are ready, update this to contain instructions on how to use your Plugin.
|
||||
- **package**.json - Contains necessary scripts and dependencies. Overwrite the metadata in this file to describe your Plugin.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dev
|
||||
### The dev folder
|
||||
|
||||
The purpose of the **dev** folder is to provide a sanitized local Payload project. so you can run and test your plugin while you are actively developing it.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ When you're ready to start development, navigate into this folder with `cd
|
||||
|
||||
And then start the project with `yarn dev` and pull up `http://localhost:3000` in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
### Testing
|
||||
## Testing
|
||||
|
||||
Another benefit of the dev folder is that you have the perfect environment established for testing.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ describe('Plugin tests', () => {
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Seeding data
|
||||
## Seeding data
|
||||
|
||||
For development and testing, you will likely need some data to work with. You can streamline this process by seeding and dropping your database - instead of manually entering data.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -159,7 +159,7 @@ export const seed = async (payload: Payload): Promise<void> => {
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Src
|
||||
## Overview of the src folder
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have our environment setup and dev project ready to go - it's time to build the plugin!
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -188,7 +188,7 @@ export const samplePlugin =
|
||||
3. From here, you can extend the config however you like!
|
||||
4. Finally, return the config and you're all set.
|
||||
|
||||
### Spread Syntax
|
||||
## Spread Syntax
|
||||
|
||||
[Spread syntax](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Spread_syntax) (or the spread operator) is a feature in JavaScript that uses the dot notation **(...)** to spread elements from arrays, strings, or objects into various contexts.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -235,23 +235,7 @@ If you wish to add to the `onInit`, you must include the async/await. We don&apo
|
||||
|
||||
In the template, we have stubbed out a basic `onInitExtension` file that you can use, if not needed feel free to delete it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Webpack
|
||||
|
||||
If any of your files use server only packages such as fs, stripe, nodemailer, etc, they will need to be removed from the browser bundle. To do that, you can [alias the file imports with webpack](https://payloadcms.com/docs/admin/webpack#aliasing-server-only-modules).
|
||||
|
||||
When files are bundled for the browser, the import paths are essentially crawled to determine what files to include in the bundle. To prevent the server only files from making it into the bundle, we can alias their import paths to a file that can be included in the browser. This will short-circuit the import path crawling and ensure browser only code is bundled.
|
||||
|
||||
Webpack is another part of the Payload config that can be a little more tricky to extend. To help here, the template includes a helper function `extendWebpackConfig()` which takes care of spreading the existing webpack, so you can just add your new stuff:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
config.admin = {
|
||||
...(config.admin || {}),
|
||||
// Add your aliases to the helper function below
|
||||
webpack: extendWebpackConfig(incomingConfig)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Types
|
||||
## Types
|
||||
|
||||
If your plugin has options, you should define and provide types for these options in a separate file which gets exported from the main `index.ts`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -268,26 +252,26 @@ export interface PluginTypes {
|
||||
|
||||
If possible, include [JSDoc comments](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/jsdoc-supported-types.html#types-1) to describe the options and their types. This allows a developer to see details about the options in their editor.
|
||||
|
||||
### Best practices
|
||||
## Best practices
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the setup covered above, here are other best practices to follow:
|
||||
|
||||
##### Providing an enable / disable option:
|
||||
### Providing an enable / disable option
|
||||
|
||||
For a better user experience, provide a way to disable the plugin without uninstalling it. This is especially important if your plugin adds additional webpack aliases, this will allow you to still let the webpack run to prevent errors.
|
||||
For a better user experience, provide a way to disable the plugin without uninstalling it.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Include tests in your GitHub CI workflow:
|
||||
### Include tests in your GitHub CI workflow
|
||||
|
||||
If you've configured tests for your package, integrate them into your workflow to run the tests each time you commit to the plugin repository. Learn more about [how to configure tests into your GitHub CI workflow.](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/automating-builds-and-tests/building-and-testing-nodejs)
|
||||
|
||||
##### Publish your finished plugin to NPM:
|
||||
### Publish your finished plugin to NPM
|
||||
|
||||
The best way to share and allow others to use your plugin once it is complete is to publish an NPM package. This process is straightforward and well documented, find out more about [creating and publishing a NPM package here](https://docs.npmjs.com/creating-and-publishing-scoped-public-packages/).
|
||||
|
||||
##### Add payload-plugin topic tag:
|
||||
### Add payload-plugin topic tag
|
||||
|
||||
Apply the tag **payload-plugin** to your GitHub repository. This will boost the visibility of your plugin and ensure it gets listed with [existing payload plugins](https://github.com/topics/payload-plugin).
|
||||
|
||||
##### Use [Semantic Versioning](https://semver.org/) (SemVer):
|
||||
### Use Semantic Versioning (SemVer)
|
||||
|
||||
With the SemVer system you release version numbers that reflect the nature of changes (major, minor, patch). Ensure all major versions reference their Payload compatibility.
|
||||
With the [Semantic Versioning](https://semver.org/) (SemVer) system you release version numbers that reflect the nature of changes (major, minor, patch). Ensure all major versions reference their Payload compatibility.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ Forms can be as simple or complex as you need, from a basic contact form, to a m
|
||||
with as much detail as possible.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
##### Core Features
|
||||
## Core Features
|
||||
|
||||
- Build completely dynamic forms directly from the admin panel for a variety of use cases
|
||||
- Render forms on your front-end using your own UI components and match your brand's design system
|
||||
@@ -64,9 +64,9 @@ const config = buildConfig({
|
||||
export default config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Options
|
||||
## Options
|
||||
|
||||
#### `fields` (option)
|
||||
### `fields` (option)
|
||||
|
||||
The `fields` property is an object of field types to allow your admin editors to build forms with. To override default settings, pass either a boolean value or a partial [Payload Block](https://payloadcms.com/docs/fields/blocks#block-configs) _keyed to the block's slug_. See [Fields](#fields) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ formBuilder({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### `redirectRelationships`
|
||||
### `redirectRelationships`
|
||||
|
||||
The `redirectRelationships` property is an array of collection slugs that, when enabled, are populated as options in the form's `redirect` field. This field is used to redirect the user to a dedicated confirmation page upon form submission (optional).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ formBuilder({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### `beforeEmail`
|
||||
### `beforeEmail`
|
||||
|
||||
The `beforeEmail` property is a [beforeChange](<[beforeChange](https://payloadcms.com/docs/hooks/globals#beforechange)>) hook that is called just after emails are prepared, but before they are sent. This is a great place to inject your own HTML template to add custom styles.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -119,7 +119,7 @@ formBuilder({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### `formOverrides`
|
||||
### `formOverrides`
|
||||
|
||||
Override anything on the `forms` collection by sending a [Payload Collection Config](https://payloadcms.com/docs/configuration/collections) to the `formOverrides` property.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -143,7 +143,7 @@ formBuilder({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### `formSubmissionOverrides`
|
||||
### `formSubmissionOverrides`
|
||||
|
||||
Override anything on the `form-submissions` collection by sending a [Payload Collection Config](https://payloadcms.com/docs/configuration/collections) to the `formSubmissionOverrides` property.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -166,7 +166,7 @@ formBuilder({
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### `handlePayment`
|
||||
### `handlePayment`
|
||||
|
||||
The `handlePayment` property is a [beforeChange](<[beforeChange](https://payloadcms.com/docs/hooks/globals#beforechange)>) hook that is called upon form submission. You can integrate into any third-party payment processing API here to accept payment based on form input. You can use the `getPaymentTotal` function to calculate the total cost after all conditions have been applied. This is only applicable if the form has enabled the `payment` field.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -206,7 +206,7 @@ Each field represents a form input. To override default settings pass either a b
|
||||
of a collection_ which are set via `formOverrides.fields`.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Text
|
||||
### Text
|
||||
|
||||
Maps to a `text` input in your front-end. Used to collect a simple string.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -218,7 +218,7 @@ Maps to a `text` input in your front-end. Used to collect a simple string.
|
||||
| `width` | string | The width of the field on the front-end. |
|
||||
| `required` | checkbox | Whether or not the field is required when submitted. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Textarea
|
||||
### Textarea
|
||||
|
||||
Maps to a `textarea` input on your front-end. Used to collect a multi-line string.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -230,7 +230,7 @@ Maps to a `textarea` input on your front-end. Used to collect a multi-line strin
|
||||
| `width` | string | The width of the field on the front-end. |
|
||||
| `required` | checkbox | Whether or not the field is required when submitted. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Select
|
||||
### Select
|
||||
|
||||
Maps to a `select` input on your front-end. Used to display a list of options.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -243,7 +243,7 @@ Maps to a `select` input on your front-end. Used to display a list of options.
|
||||
| `required` | checkbox | Whether or not the field is required when submitted. |
|
||||
| `options` | array | An array of objects with `label` and `value` properties. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Email (field)
|
||||
### Email (field)
|
||||
|
||||
Maps to a `text` input with type `email` on your front-end. Used to collect an email address.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -255,7 +255,7 @@ Maps to a `text` input with type `email` on your front-end. Used to collect an e
|
||||
| `width` | string | The width of the field on the front-end. |
|
||||
| `required` | checkbox | Whether or not the field is required when submitted. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### State
|
||||
### State
|
||||
|
||||
Maps to a `select` input on your front-end. Used to collect a US state.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -267,7 +267,7 @@ Maps to a `select` input on your front-end. Used to collect a US state.
|
||||
| `width` | string | The width of the field on the front-end. |
|
||||
| `required` | checkbox | Whether or not the field is required when submitted. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Country
|
||||
### Country
|
||||
|
||||
Maps to a `select` input on your front-end. Used to collect a country.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -279,7 +279,7 @@ Maps to a `select` input on your front-end. Used to collect a country.
|
||||
| `width` | string | The width of the field on the front-end. |
|
||||
| `required` | checkbox | Whether or not the field is required when submitted. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Checkbox
|
||||
### Checkbox
|
||||
|
||||
Maps to a `checkbox` input on your front-end. Used to collect a boolean value.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -291,7 +291,7 @@ Maps to a `checkbox` input on your front-end. Used to collect a boolean value.
|
||||
| `width` | string | The width of the field on the front-end. |
|
||||
| `required` | checkbox | Whether or not the field is required when submitted. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Number
|
||||
### Number
|
||||
|
||||
Maps to a `number` input on your front-end. Used to collect a number.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -303,7 +303,7 @@ Maps to a `number` input on your front-end. Used to collect a number.
|
||||
| `width` | string | The width of the field on the front-end. |
|
||||
| `required` | checkbox | Whether or not the field is required when submitted. | | `defaultValue` | number | The default value of the field. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Message
|
||||
### Message
|
||||
|
||||
Maps to a `RichText` component on your front-end. Used to display an arbitrary message to the user anywhere in the form.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -311,7 +311,7 @@ Maps to a `RichText` component on your front-end. Used to display an arbitrary m
|
||||
| --------- | -------- | ----------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `message` | richText | The message to display on the form. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Payment
|
||||
### Payment
|
||||
|
||||
Add this field to your form if it should collect payment. Upon submission, the `handlePayment` callback is executed with the form and submission data. You can use this to integrate with any third-party payment processing API.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -324,7 +324,7 @@ Add this field to your form if it should collect payment. Upon submission, the `
|
||||
| `required` | checkbox | Whether or not the field is required when submitted. |
|
||||
| `priceConditions` | array | An array of objects that define the price conditions. See below for more details. |
|
||||
|
||||
##### Price Conditions
|
||||
#### Price Conditions
|
||||
|
||||
Each of the `priceConditions` are executed by the `getPaymentTotal` utility that this plugin provides. You can call this function in your `handlePayment` callback to dynamically calculate the total price of a form upon submission based on the user's input. For example, you could create a price condition that says "if the user selects 'yes' for this checkbox, add $10 to the total price".
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -337,7 +337,7 @@ Each of the `priceConditions` are executed by the `getPaymentTotal` utility that
|
||||
| `valueType` | string | The type of value to use to determine the price. |
|
||||
| `value` | string | The value to use to determine the price. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Field Overrides
|
||||
### Field Overrides
|
||||
|
||||
You can provide your own custom fields by passing a new [Payload Block](https://payloadcms.com/docs/fields/blocks#block-configs) object into `fields`. You can override or extend any existing fields by first importing the `fields` from the plugin:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -392,7 +392,7 @@ The [Examples Directory](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/example
|
||||
|
||||
Below are some common troubleshooting tips. To help other developers, please contribute to this section as you troubleshoot your own application.
|
||||
|
||||
##### SendGrid 403 Forbidden Error
|
||||
#### SendGrid 403 Forbidden Error
|
||||
|
||||
- If you are using [SendGrid Link Branding](https://docs.sendgrid.com/ui/account-and-settings/how-to-set-up-link-branding) to remove the "via sendgrid.net" part of your email, you must also setup [Domain Authentication](https://docs.sendgrid.com/ui/account-and-settings/how-to-set-up-domain-authentication). This means you can only send emails from an address on this domain — so the `from` addresses in your form submission emails **_cannot_** be anything other than `something@your_domain.com`. This means that from `{{email}}` will not work, but `website@your_domain.com` will. You can still send the form's email address in the body of the email.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ but different parents.
|
||||
with as much detail as possible.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
##### Core features
|
||||
## Core features
|
||||
|
||||
- Automatically adds a `parent` relationship field to each document
|
||||
- Allows for parent/child relationships between documents within the same collection
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Plugins
|
||||
label: Overview
|
||||
order: 10
|
||||
desc: Plugins provide a great way to modularize Payload functionalities into easy-to-use enhancements and extensions of your Payload apps.
|
||||
keywords: plugins, config, configuration, extensions, custom, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, express
|
||||
keywords: plugins, config, configuration, extensions, custom, documentation, Content Management System, cms, headless, javascript, node, react, nextjs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Payload comes with a built-in Plugins infrastructure that allows developers to build their own modular and easily reusable sets of functionality.
|
||||
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ Writing plugins is no more complex than writing regular JavaScript. If you know
|
||||
- Integrate all `upload`-enabled collections with a third-party file host like S3 or Cloudinary
|
||||
- Add custom endpoints or GraphQL queries / mutations with any type of custom functionality that you can think of
|
||||
|
||||
### How to install plugins
|
||||
## How to install plugins
|
||||
|
||||
The base Payload config allows for a `plugins` property which takes an `array` of [`Plugins`](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/packages/payload/src/config/types.ts).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -39,12 +39,7 @@ import passwordProtect from 'payload-password-protect'
|
||||
import { mongooseAdapter } from '@payloadcms/db-mongodb'
|
||||
import { postgresAdapter } from '@payloadcms/db-postgres'
|
||||
|
||||
import { viteBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-vite'
|
||||
import { webpackBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-webpack'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
const config = buildConfig({
|
||||
bundler: webpackBundler() // or viteBundler(),
|
||||
collections: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
slug: 'pages',
|
||||
@@ -82,7 +77,7 @@ const config = buildConfig({
|
||||
export default config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### When Plugins are initialized
|
||||
### When Plugins are initialized
|
||||
|
||||
Payload Plugins are executed _after_ the incoming config is validated, but before it is sanitized and had default options merged in.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -142,7 +137,7 @@ const addLastModified: Plugin = (incomingConfig: Config): Config => {
|
||||
export default addLastModified
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Available Plugins
|
||||
## Available Plugins
|
||||
|
||||
You can discover existing plugins by browsing the `payload-plugin` topic on [GitHub](https://github.com/topics/payload-plugin).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ For example, if you have a page at `/about` and you want to change it to `/about
|
||||
with as much detail as possible.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
##### Core features
|
||||
## Core features
|
||||
|
||||
- Adds a `redirects` collection to your config that:
|
||||
- includes a `from` and `to` fields
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ This plugin is a great way to implement a fast, immersive search experience such
|
||||
with as much detail as possible.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
##### Core Features
|
||||
## Core Features
|
||||
|
||||
- Automatically adds an indexed `search` collection to your database
|
||||
- Automatically creates, syncs, and deletes search records as you manage your documents
|
||||
|
||||
133
docs/plugins/sentry.mdx
Normal file
133
docs/plugins/sentry.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Sentry Plugin
|
||||
label: Sentry
|
||||
order: 20
|
||||
desc: Integrate Sentry error tracking into your Payload application
|
||||
keywords: plugins, sentry, error, tracking, monitoring, logging, bug, reporting, performance
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@payloadcms/plugin-sentry)
|
||||
|
||||
This plugin allows you to integrate [Sentry](https://sentry.io/) seamlessly with your [Payload](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload) application.
|
||||
|
||||
## What is Sentry?
|
||||
|
||||
Sentry is a powerful error tracking and performance monitoring tool that helps developers identify, diagnose, and resolve issues in their applications.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="success">
|
||||
Sentry does smart stuff with error data to make bugs easier to find and fix. - [sentry.io](https://sentry.io/)
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
This multi-faceted software offers a range of features that will help you manage errors with greater ease and ultimately ensure your application is running smoothly:
|
||||
|
||||
## Core Features
|
||||
|
||||
- **Error Tracking**: Instantly captures and logs errors as they occur in your application
|
||||
- **Performance Monitoring**: Tracks application performance to identify slowdowns and bottlenecks
|
||||
- **Detailed Reports**: Provides comprehensive insights into errors, including stack traces and context
|
||||
- **Alerts and Notifications**: Send and customize event-triggered notifications
|
||||
- **Issue Grouping, Filtering and Search**: Automatically groups similar errors, and allows filtering and searching issues by custom criteria
|
||||
- **Breadcrumbs**: Records user actions and events leading up to an error
|
||||
- **Integrations**: Connects with various tools and services for enhanced workflow and issue management
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="info">
|
||||
This plugin is completely open-source and the [source code can be found here](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/packages/plugin-sentry). If you need help, check out our [Community Help](https://payloadcms.com/community-help). If you think you've found a bug, please [open a new issue](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/issues/new?assignees=&labels=plugin%3A%20seo&template=bug_report.md&title=plugin-seo%3A) with as much detail as possible.
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Install the plugin using any JavaScript package manager like [Yarn](https://yarnpkg.com), [NPM](https://npmjs.com), or [PNPM](https://pnpm.io):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yarn add @payloadcms/plugin-sentry
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Basic Usage
|
||||
|
||||
In the `plugins` array of your [Payload config](https://payloadcms.com/docs/configuration/overview), call the plugin and pass in your Sentry DSN as an option.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { sentry } from '@payloadcms/plugin-sentry'
|
||||
import { Pages, Media } from './collections'
|
||||
|
||||
const config = buildConfig({
|
||||
collections: [Pages, Media],
|
||||
plugins: [
|
||||
sentry({
|
||||
dsn: 'https://61edebas776889984d323d777@o4505289711681536.ingest.sentry.io/4505357433352176',
|
||||
}),
|
||||
],
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
export default config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Options
|
||||
|
||||
- `dsn` : string | **required**
|
||||
|
||||
Sentry automatically assigns a DSN when you create a project, the unique DSN informs Sentry where to send events so they are associated with the correct project.
|
||||
|
||||
<Banner type="warning">
|
||||
You can find your project DSN (Data Source Name) by visiting [sentry.io](sentry.io) and navigating to your [Project] > Settings > Client Keys (DSN).
|
||||
</Banner>
|
||||
|
||||
- `enabled`: boolean | optional
|
||||
|
||||
Set to false to disable the plugin. Defaults to true.
|
||||
|
||||
- `init` : ClientOptions | optional
|
||||
|
||||
Sentry allows a variety of options to be passed into the Sentry.init() function, see the full list of options [here](https://docs.sentry.io/platforms/node/guides/express/configuration/options).
|
||||
|
||||
- `requestHandler` : RequestHandlerOptions | optional
|
||||
|
||||
Accepts options that let you decide what data should be included in the event sent to Sentry, checkout the options [here](https://docs.sentry.io/platforms/node/guides/express/configuration/options).
|
||||
|
||||
- `captureErrors`: number[] | optional
|
||||
|
||||
By default, `Sentry.errorHandler` will capture only errors with a status code of 500 or higher. To capture additional error codes, pass the values as numbers in an array.
|
||||
|
||||
To see all options available, visit the [Sentry Docs](https://docs.sentry.io/platforms/node/guides/express/configuration/options).
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
|
||||
Configure any of these options by passing them to the plugin:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
|
||||
import { sentry } from '@payloadcms/plugin-sentry'
|
||||
import { Pages, Media } from './collections'
|
||||
|
||||
const config = buildConfig({
|
||||
collections: [Pages, Media],
|
||||
plugins: [
|
||||
sentry({
|
||||
dsn: 'https://61edebas777689984d323d777@o4505289711681536.ingest.sentry.io/4505357433352176',
|
||||
options: {
|
||||
init: {
|
||||
debug: true,
|
||||
environment: 'development',
|
||||
tracesSampleRate: 1.0,
|
||||
},
|
||||
requestHandler: {
|
||||
serverName: false,
|
||||
user: ['email'],
|
||||
},
|
||||
captureErrors: [400, 403, 404],
|
||||
},
|
||||
}),
|
||||
],
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
export default config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
All types can be directly imported:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
import { PluginOptions } from '@payloadcms/plugin-sentry/types'
|
||||
```
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user