* feat: update templates to 2.0 and support create-payload-app
* chore: rich text updates
* chore(templates): remove mongoURL
* chore: migrates rich text fields in website
* chore: manually aliases dotenv in templates
* chore: installs new beta in website template
* chore: type issues
* chore (template): add alias for fs to website template
* chore: more template updates
---------
Co-authored-by: James <james@trbl.design>
Co-authored-by: Dan Ribbens <dan.ribbens@gmail.com>
BREAKING CHANGE: If your config has a `admin.components.routes` array, you will need to key them into the `admin.components.views` object. The configuration options should remain unchanged.
* chore: WIP id type validation for richtext upload
* chore: fix richtext fields test ID placeholder replacements
* chore: use getIDType in relationship validation for consistency
* chore: make getIDType safer in case payload.db.defaultIDType is null
---------
Co-authored-by: Dan Ribbens <dan.ribbens@gmail.com>
BREAKING: config (SanitizedConfig) is now a new, mandatory property to be passed into .validate(, options) functions. In order to accommodate that, other functions which may call validate now also have a new, mandatory config property. These are:
* buildStateFromSchema
* addFieldStatePromise
feat: breaking: richtext-lexical: block node validations
* ci: cache entire build to share with future jobs
* chore: pnpm setup for tests job
* chore: use build cache in db adapter builds
* chore: troubleshoot db builds
* chore: add back db-mongodb
* chore: add back db-postgres, cleanup
* chore: separate type gen into separate job
* chore: run tests separately for each db adapter
* chore: use matrix for tests w/ db
* chore: explicit ip and port for postgres
* chore: exportPointerFiles script
* chore: handle creation of subfolders which may not exist
* chore: add json to copyfiles
* chore: do not use exports property for publishConfig
* chore: add clean:unix command
* chore: modify clean:unix command to also delete any tsconfig.tsbuildinfo files
* chore: remove exports properties from db adapter packages
* chore: cleanup tsconfigs and fix db-mongodb builds
* chore: make the db adapters depend on payload
* chore: fix tsconfig for test directory
* chore: fix packages/db-mongodb not building
BREAKING CHANGE:
- Unhandled Errors are now omitted by default. This can be breaking if people depend on those error messages. Now, it will just say "Something went wrong.".
* chore: slightly improved testing of registration via graphql
Signed-off-by: Vsevolod Volkov <st.lyn4@gmail.com>
* chore: hiding details of internal errors from responses
Signed-off-by: Vsevolod Volkov <st.lyn4@gmail.com>
* feat: ability to remove authorization tokens from response bodies
Signed-off-by: Vsevolod Volkov <st.lyn4@gmail.com>
* chore: add section for design contributions in contributing.md
* feat: add afterOperation hook (#2697)
* feat: add afterOperation hook for Find operation
* docs: change #afterOperation to #afteroperation
* chore: extract afterOperation in function
* chore: implement afterChange in operations
* docs: use proper CollectionAfterOperationHook
* chore: remove outdated info
* chore: types afterOperation hook
* chore: improves afterOperation tests
* docs: updates description of afterOperation hook
* chore: improve typings
* chore: improve types
* chore: rename index.tsx => index.ts
---------
Co-authored-by: Jacob Fletcher <jacobsfletch@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alessio Gravili <alessio@gravili.de>
* chore: remove swc version pin (#3179)
* fix: WhereBuilder component does not accept all valid Where queries (#3087)
* chore: add jsDocs for ListControls
* chore: add jsDocs for ListView
* chore: add jsDocs for WhereBuilder
* chore: add comment
* chore: remove unnecessary console log
* chore: improve operator type
* fix: transform where queries which aren't necessarily incorrect, and improve their validation
* chore: add type to import
* fix: do not merge existing old query params with new ones if the existing old ones got transformed and are not valid, as that would cause duplicates
* chore: sort imports and remove extra validation
* fix: transformWhereQuery logic
* chore: add back extra validation
* chore: add e2e tests
* chore(test): adds test to ensure relationship returns over 10 docs (#3181)
* chore(test): adds test to ensure relationship returns over 10 docs
* chore: remove unnecessary movieDocs variable
* fix: passes in height to resizeOptions upload option to allow height resize (#3171)
* docs: fixes syntax error in rich-text.mdx that was breaking build
* docs: removes auto-formatting from rich-text.mdx (#3188)
* feat: Improve admin dashboard accessibility (#3053)
Co-authored-by: Alessio Gravili <alessio@gravili.de>
* feat: improve field ops (#3172)
Co-authored-by: PatrikKozak <patrik@trbl.design>
* chore: file cleanup (#3190)
* chore(release): v1.14.0
* chore: improve ts typing in sanitization functions (#3194)
* chore(templates): default port on website
* chore(templates): safely handles bad network requests
* chore(templates): implements draft preview and on-demand revalidation
* chore(templates): renders static cart page fallback
* chore(examples): updates draft-preview next-app example to use revalidateTag (#3199)
* feat: query support for geo within and intersects + dynamic GraphQL operator types (#3183)
Co-authored-by: Lucas Blancas <lablancas@gmail.com>
* chore: improve checkboxes (#3191)
* chore: improve filtering for hasMany number field (#3193)
* chore: improve fiiltering for hasMany number field
* chore: add translation for 'items' and replace rows with items
* chore: new exceededLimit key
* Revert "chore: add translation for 'items' and replace rows with items"
This reverts commit 3a91dabdfd.
* chore: undo adding items key in translation schema
* chore: new limitReached key
* chore: remove unnecessary exceededLimit key
* chore: spelling improvements
* chore: update test build config import
---------
Signed-off-by: Vsevolod Volkov <st.lyn4@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Vsevolod Volkov <st.lyn4@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Jarrod Flesch <30633324+JarrodMFlesch@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Alessio Gravili <alessio@gravili.de>
Co-authored-by: ibr-hin95 <ibr.hin95@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Seied Ali Mirkarimi <dasmergo@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: muathkhatib <mkhatib.dev@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: ibr-hin95 <40246707+ibr-hin95@users.noreply.github.com>
fix: recursiveNestedPaths not merging existing fields when hoisting row/collapsible fields (#2769)
fix: exclude monaco code editor from ltr due to microsoft/monaco-editor#2371
BREAKING CHANGE:
- The admin hook for `useLocale` now returns a Locale object of the currently active locale. Previously this would only return the code as a string. Any custom components built which had `locale = useLocale()` should be replaced with `{ code: locale } = useLocale()` to maintain the same functionality.
- The property `localization.locales` of `SanitizedConfig` type has changed. This was an array of strings and is now an array of Locale objects having: `label: string`, `code: string` and `rtl: boolean`. If you are using localization.locales from the config you will need to adjust your project or plugin accordingly.
* chore: disable slug pluralization for versions model
* chore: disable slug pluralizations for globals version model
* chore: disable auto slug pluralization for globals collection
* feat: autoPluralization option for mongoose adapter
* Update isActive.tsx
This change allows us to define toggling of custom types in Slate. Specifically, this fixes the ability to toggle Alignment on nodes that use other active elements.
isElementActive(editor, format, TEXT_ALIGN_TYPES.includes(format) ? 'align' : 'type');
Type is the default for elements, allowing us to use a custom field lets us greater extend the functionality of Slate in Payload without causing any breaking changes
* Update toggle.tsx
Added to toggleElement public function
* Update isActive.tsx
* Update toggle.tsx
Added Rich Text Alignment, updated toggle function, added tests and doc updates
* added margin to void elements
* fix: list alignment
* removed textAlign from elements and added docs
* chore: fix typo
---------
Co-authored-by: Alessio Gravili <alessio@gravili.de>
* feat: make PAYLOAD_CONFIG_PATH optional
* hardcode common search paths
* docs: update docs regarding PAYLOAD_CONFIG_PATH
* make the tsConfig parser less prone to errors
* feat(ImageResize): add support for resize options
* fix(ImageUpload): reuse name for accidental duplicate
* fix(ImageResize): e2e tests for added media size
* chore: simplify fileExists method
* fix: typo
* feat(ImageResize): update name to be more transparent
* fix: use fileExists in file removal
* improve names, comments and clarity of needsResize function
* fix: jsDoc params
* fix: incorrect needsResize condition and add failing test case
* chore: improve comment
* fix: merge conflict error
---------
Co-authored-by: Alessio Gravili <70709113+AlessioGr@users.noreply.github.com>
* chore: add jsDocs for buildQuery
* feat: where instead of id for updateOne and deleteOne
* feat: find => findOne
* sort order => sort direction
* fix: typing of Global buildQuery
* cleanup
* fix: init payload's i18n for error message
* fix: incorrect use of FindArgs in findByID
* move deleteOne call to adapter
* re-order
* deleteVersions
* versions stuff
* more version stuff
* moar version stuff
* global stuff
* global stuff
* move combineQueries inside the findGlobal
* global stuff
* fix type
* more global stuff
* move docWithFilenameExists to adapter pattern
* chore: remove unnecessary comments
* perf: make everything lean, disable virtuals, ++performance
* chore: remove unnecessary Model
* chore: add jsdocs for limit
* moar jsdocs
* Replace find in deleteByID
* (check this:) add missing locale
* move findByID
* Make findByID return only one document
* _id => id
* _id => id
* Improve version types
* Improve sortOrder types
* move version stuff over
* version stuff
* fix: sort types
* fix params
* fix: findVersionByID generic
* fix: type error for versions
* remove unused value
* fix: Document import
* add todo
* feat: updateOne to mongoose
* remove unnecessary Model
* more update stuff
* remove unnecessary imports
* remove unnecessary function arguments
* fix: auth db update calls
* fix: bad updateByID which made tests fail
* fix: update returned docs to fix tests
* fix: update from version using mongoose directly even though the Model does not exist
* feat: implement deleteOne
* fix: assign verificationToken only when it exists - fixes test
* migrate saveVersion partly
* feat: make dev:generate-graphql-schema work even without specifying extra argument
* fix: this.db can be null
* chore: use destructured locale where possible
* chore: improve variable name
* fix: SanitizedConfig type
* feat: findGlobal database adapter
* fix: flaky e2e test
* chore: improve incorrect comment
* chore: undo diffs
* fix: id types
* fix: id typing
* added custom config extension points
* Added custom field to documentation
* fix: not building due to incorrect typings
* Upload dist
* point to number array test
* feat: hasMany for number field
* fix: types
* Fix: incorrectly styles input for hasMany
* Revert "point to number array test"
This reverts commit 5a5162a803.
* Revert "Merge branch 'production-with-custom' into number-hasmany-v2"
This reverts commit dfc3ac523e, reversing
changes made to a3b1b7dd67.
* test: adds test for numbers with hasMany
* test: add number field e2e
* Fix updated index.tsx
* Fix updated index.tsx
* chore: add jsDocs for hasMany property
* chore: rename isMultiText to isCreatable, as it makes more sense
* fix: incorrect double space in comments
* chore: rename onMultiTextChange to handleHasManyChange
* chore: improve ordering
* docs: add documentation for hasMany
* docs: add more jsdocs for number field
* fix: new value not transformed to number
* improve types
* fix: only allow numbers as input using filterOption
* fix: Option / value type breaking sortable selects
* fix: typings and add id for sorting
* add animation to react select
* undo transitions due to glitches
* fix: keyboard handler for select for empty input values
* fix: validation for hasMany numbers
* feat: perform validation in the filter as well
* attempt to fix duplicate key issue
* add todo
* remove console logs
* fix: stupid key warning
* fix: validation tests
* feat: add filterOption to keydown listener
* feat: numberOnly for react-select
* chore: improve variable naming
* fix: allow numbers for relationship value by stringifying those for sortable react-selects
* feat: generated types for hasMany number field
* graphql typings part 1
* graphql defaults type
* better typing for number in buildObjectType
* fix: default graphql type disregarding hasMany for relationship field
* feat: minRows and maxRows for hasMany numbers
* simplify joi schema
* working minRows and maxRows validation!
* jesus christ: fix incorrect translations for number & relationship fields for greaterThanMax and lessThanMin
* fix weird type error
* move validation tests to validations.spec.ts and fix them
* fix: make sure filterOption only passes a number array to validate function
* fix: adds missing dark-mode styles for version differences view (#2812)
Co-authored-by: Tylan Davis <tylan@Tylans-MacBook-Pro.local>
* fix: #2821 i18n ui field label (#2823)
* chore: version diff styles (#2824)
Co-authored-by: Tylan Davis <tylan@Tylans-MacBook-Pro.local>
* chore: remove --legacy-peer-deps from gh actions workflow (#2814)
* chore: removes cms text from instances of payload name (#2793)
* chore(release): v1.9.2
* chore: update changelog release notes v1.9.2
* chore: cleans up graphql-schema-gen test folder
* fix: adds custom property to ui field in joi validation (#2835)
* adjust validation
* improve isnumber function
* Update number.mdx
---------
Co-authored-by: Teun Mooij <tmooij@infinitaslearning.com>
Co-authored-by: Dan Ribbens <dan.ribbens@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Tylan Davis <89618855+tylandavis@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Tylan Davis <tylan@Tylans-MacBook-Pro.local>
Co-authored-by: Dan Ribbens <DanRibbens@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Jacob Fletcher <jacobsfletch@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Jarrod Flesch <jarrodmflesch@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Jarrod Flesch <30633324+JarrodMFlesch@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix: deprecate min/max in exchange for minRows and maxRows for relationship
* fix: update validations unit tests with minRows and maxRows
* fix: incorrect types
* move to sanitize
**BREAKING CHANGES**
Preferences have been overhauled to be abstracted as a Payload collection and no longer explicitly defined by Payload. They previously used the slug `_preferences` as a collection name and url route and are now
If any of the following are true you will need to take action:
- You have existing preferences you wish to keep for your admin users you must migrate data in the _preferences collection to the new shape. To migrate the preferences in the database you must update the shape of each _preferences document from:
```js
{
user: ObjectId("abc"),
userCollection: "users",
/** other fields remain the same **/
}
```
to:
```js
{
user: {
value: 'abc',
relationTo: 'users",
}
/** other fields remain the same **/
}
```
- You have code external of Payload or custom code within Payload using the API endpoint `api/_preferences`, you should update any applications to use `api/payload-preferences` instead.
- You were using the preferences GraphQL implementation. This was removed and is instead provided the same way as Payload handles any other. In this way the queries, mutation and schemas have changed. These are now generated as any other collection within your payload project.
- You were using the Payload's exported Preference type for your typescript code. Now you can instead import the generated type from your project.
* chore: colocates gql schema field types with operators
* chore: adds missing `json` gql field schema
* fix: corrects graphql `id` type from JSON to String
* Add paginatedType to graphQL on collections types
* Refactor config query and mutation extension into a reusable type
* Export paginatedListType and payload's version of graphql
* Revert prettier's automatic changes
* Fix requested changes
* Add additional documentation for extending GraphQL
* Add information about the resolver's first argument
* Refactor imageResizer.ts to allow for keeping original size in certain cases
* revert new property for keeping desired size
* add unit tests for maintained image size feature
* feat: support full URL for upload.staticURL
* feat: Update documentation about upload.staticURL property
* feat: Add reproduction test for absolute staticURL
* chore: ensures example configs are being exported when necessary
* chore: adds note regarding updating of hidden fields
---------
Co-authored-by: Jessica Boezwinkle <jessica@trbl.design>
* feat: support email configuration in payload config
* feat: set email defaults if no email config
* chore: leftover line from testing
* feat: add warning if email configure in both init and config
* chore: use correct locale when querying relationship for list view
* chore: make sure the relationships are re-queried when the locale changes
* chore: cleans up localization test ts-types
---------
Co-authored-by: Jarrod Flesch <jarrodmflesch@gmail.com>
Fixes ERROR (payload): TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading '<field.name>')
at promise (...\payload\src\fields\hooks\afterChange\promise.ts:68:23)
at ...\payload\src\fields\hooks\afterChange\traverseFields.ts:31:26
at Array.forEach (<anonymous>)
at traverseFields (...\payload\src\fields\hooks\afterChange\traverseFields.ts:30:10)
at promise (...\payload\src\fields\hooks\afterChange\promise.ts:154:27)
at ...\payload\src\fields\hooks\afterChange\traverseFields.ts:31:26
at Array.forEach (<anonymous>)
at traverseFields (...\payload\src\fields\hooks\afterChange\traverseFields.ts:30:10)
at promise (...\payload\src\fields\hooks\afterChange\promise.ts:170:27)
at ...\payload\src\fields\hooks\afterChange\traverseFields.ts:31:26
## Description
Fixed a wrong translation
- I have read and understand the CONTRIBUTING.md document in this repository
## Type of change
- fix of tiny error of translation
* fix: adds RTE provider, to allow for disabledRTE relationships from breaking other drawers
* chore: updates hook name
* chore: simplifies list drawer rendering
* chore: simplify types
* chore: adds arg to determine what listType drawer to render
* chore: renames listType to contentType, fix upload field drawer
* chore: requires collectionSlugs in useListDrawer
* chore(test): adds tests for list drawers, relationships and uploads
* chore: formatting
* chore: cleans up types, collectionSlugs are required for useListDrawer
* chore: removes RichTextProvider
* chore: removes hoc in favor of FC hoc
* chore: fixes fc hoc
* Fix Local API update typing
Payload allows for updating doc with only partial data, but the inferred type requires the whole collection type.
#2009
* fix typos
* chore: further typing of update operation
---------
Co-authored-by: Elliot DeNolf <denolfe@gmail.com>
* fix: corrects type for required named tab fields
* chore: tabs and groups are always required
* chore: adjusts tab and group type to omit required since a group/named-tab will always exist
* Update README.md
- updates logo approach to work with npm and github
- updates badge style
- fixes twitter badge
- removes duplicative links for discord and website
- moves feature request link
* changes h1 to p tag, changes h2 to h3 - both done to remove ugly bottom border
* adds target blank to a few anchor tags
* chore: ensures relationship fields react to locale changes in the admin panel - fixes#1870
* chore: patches in default values for fields, and localized fields using fallbacks - fixes#1859
* chore: organizes field localization and sanitizing
* Revert "Feat/1180 loading UI enhancements"
* Feat/1180 loading UI enhancements
* chore: safely sets tab if name field, only sets fallback value if it exists
* chore: adds test to ensure text fields use fallback locale value when empty
* fix: hides fallback locale checkbox when field localization is set to false
* fix: updates fallback locale checkbox logic
* chore: updates naming convention
* Upgraded the packages to latest patch versions where non breaking
* Upgraded the packages to latest minor versions where non breaking
Co-authored-by: TomDoFuture <108644869+TomDoFuture@users.noreply.github.com>
* Run connectMongoose before starting payload init
* - reverted changes
- added deprecated to init
- docs: changed all payload.init to payload.initAsync
- changed all internal init calls
* forgotten inits in docs
* reverted back - removed init and renamed initAsync to init
* chore: README header logo
* updates conditionally rendered logo for light/dark mode
* adds img folder with light and dark logos to utilize gh conditional
* moves payload logos to avoid polluting root directory
Co-authored-by: Sean Zubrickas <zubricks@gmail.com>
* refines readme banner image, badges and headings
* chore: spruce up README a bit more
* adds dark/light mode support for logo
Co-authored-by: Elliot DeNolf <denolfe@gmail.com>
BREAKING CHANGE: replaced the useAPIKey authentication header format to use the collection slug instead of the collection label. Previous: `${collection.labels.singular} API-Key ${apiKey}`, updated: `${collection.slug} API-Key ${apiKey}`
* feat: adds document level access endpoints so admin ui can now accurately reflect document level access control
* chore(docs): new doc access callout, updates useDocumentInfo props from change
BREAKING CHANGE: collection slugs are no longer automatically sanitized to be kebab case. This will only be an issue if your current slugs were in camel case. The upgrade path will be to change those slugs to the kebab case version that the slug was automatically being sanitized to on the backend.
If you only use kebab case or single word slugs: no action needed.
If you have existing slugs with camel case and populated data: you'll need to convert these to the kebab case version to match the previously sanitized value.
ie. myOldSlug is your slug, you should convert it to my-old-slug.
Any future slugs after updating will be used as-is.
Co-authored-by: shikhantmaungs <shinkhantmaungs@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Thomas Ghysels <info@thomasg.be>
Co-authored-by: Kokutse Djoguenou <kokutse@Kokutses-MacBook-Pro.local>
Co-authored-by: Christian Gil <47041342+ChrisGV04@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Łukasz Rabiec <lukaszrabiec@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Jenny <jennifer.eberlei@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Hung Vu <hunghvu2017@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Shin Khant Maung <101539335+shinkhantmaungs@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carlo Brualdi <carlo.brualdi@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Ariel Tonglet <ariel.tonglet@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Roman Ryzhikov <general+github@ya.ru>
Co-authored-by: maekoya <maekoya@stromatolite.jp>
Co-authored-by: Emilia Trollros <3m1l1a@emiliatrollros.se>
Co-authored-by: Kokutse J Djoguenou <90865585+Julesdj@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Mitch Dries <mitch.dries@gmail.com>
BREAKING CHANGE: If you assigned labels to collections, globals or block names, you need to update your config! Your GraphQL schema and generated Typescript interfaces may have changed. Payload no longer uses labels for code based naming. To prevent breaking changes to your GraphQL API and typescript types in your project, you can assign the below properties to match what Payload previously generated for you from labels.
On Collections
Use `graphQL.singularName`, `graphQL.pluralName` for GraphQL schema names.
Use `typescript.interface` for typescript generation name.
On Globals
Use `graphQL.name` for GraphQL Schema name.
Use `typescript.interface` for typescript generation name.
On Blocks (within Block fields)
Use `graphQL.singularName` for graphQL schema names.
* feat: Added to types.ts the default Max Field Length
* feat: Added the defaultMaxFieldLength to the schema.ts
* feat: applying defaultMaxFieldLength to 3 validators
* feat: renamed defaultMaxFieldLength to defaultMaxTextLength , adding defaultMax and min nums
* feat: validating numbers with new defaultminnum and defaultmaxnum
* feat: FIXED BUG, do not return an error message on the defaultmaxnum and minnum override checks
* Added test fields
* Eslint compliance
* feat : eslint compliacnce
* Added tests, though a reasonable payload config needs to be imported to them
* Removed my failed jest tests, relying on the yarn dev test instead
* Increased default num max and min range to JS safe integer
* Jmi suggestions
* feat: removing the superfluous number max and min default
* Added test for max text field
Co-authored-by: Tom Do <tom@iifuture.com>
Co-authored-by: TomDoFuture <108644869+TomDoFuture@users.noreply.github.com>
*Note:* Feature requests should be opened as [discussions](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/discussions/new?category=feature-requests-ideas).
- type:input
id:reproduction-link
attributes:
label:Link to reproduction
description:Please add a link to a reproduction. See the fork [reproduction-guide](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/.github/reproduction-guide.md) for more information.
validations:
required:true
- type:textarea
attributes:
label:To Reproduce
description:Steps to reproduce the behavior, please provide a clear description of how to reproduce the issue, based on the linked minimal reproduction. Screenshots can be provided in the issue body below. If using code blocks, make sure that [syntax highlighting is correct](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/writing-on-github/working-with-advanced-formatting/creating-and-highlighting-code-blocks#syntax-highlighting) and double check that the rendered preview is not broken.
validations:
required:true
- type:textarea
attributes:
label:Describe the Bug
validations:
required:true
- type:input
id:version
attributes:
label:Payload Version
description:What version of Payload are you running?
validations:
required:true
- type:input
id:adapters-plugins
attributes:
label:Adapters and Plugins
description:What adapters and plugins are you using? ie. db-mongodb, db-postgres, bundler-webpack, etc.
- type:markdown
attributes:
value:Before submitting the issue, go through the steps you've written down to make sure the steps provided are detailed and clear.
- type:markdown
attributes:
value:Contributors should be able to follow the steps provided in order to reproduce the bug.
- type:markdown
attributes:
value:These steps are used to add integration tests to ensure the same issue does not happen again. Thanks in advance!
1. [fork](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/fork) this repo
2. run `yarn` to install dependencies
3. open up the `test/_community` directory
4. add any necessary `collections/globals/fields` in this directory to recreate the issue you are experiencing
5. run `yarn dev _community` to start the admin panel
**NOTE:** The goal is to isolate the problem by reducing the number of `collections/globals/fields` you add to the `test/_community` folder. This folder is _not_ meant for you to copy your project into, but rather recreate the issue you are experiencing with minimal config.
## Example test directory file tree
```text
.
├── config.ts
├── int.spec.ts
├── e2e.spec.ts
└── payload-types.ts
```
-`config.ts` - This is the _granular_ Payload config for testing. It should be as lightweight as possible. Reference existing configs for an example
-`int.spec.ts` [Optional] - This is the test file run by jest. Any test file must have a `*int.spec.ts` suffix.
-`e2e.spec.ts` [Optional] - This is the end-to-end test file that will load up the admin UI using the above config and run Playwright tests.
-`payload-types.ts` - Generated types from `config.ts`. Generate this file by running `yarn dev:generate-types _community`.
The directory split up in this way specifically to reduce friction when creating tests and to add the ability to boot up Payload with that specific config. You should modify the files in `test/_community` to get started.
<br />
## Testing is optional but encouraged
An issue does not need to have failing tests — reproduction steps with your forked repo are enough at this point. Some people like to dive deeper and we want to give you the guidance/tools to do so. Read more below:
### Running integration tests (Payload API tests)
First install [Jest Runner for VSVode](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=firsttris.vscode-jest-runner).
There are a couple ways run integration tests:
- **Granularly** - you can run individual tests in vscode by installing the Jest Runner plugin and using that to run individual tests. Clicking the `debug` button will run the test in debug mode allowing you to set break points.
Once they are installed you can open the `testing` tab in vscode sidebar and drill down to the test you want to run, i.e. `/test/_community/e2e.spec.ts`
- It is recommended to add the test credentials (located in `test/credentials.ts`) to your autofill for `localhost:3000/admin` as this will be required on every nodemon restart. The default credentials are `dev@payloadcms.com` as email and `test` as password.
node-linker=isolated # due to a typescript bug, isolated mode requires @types/express-serve-static-core, terser and monaco-editor to be installed https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/issues/47663#issuecomment-1519138189 along with two other changes in the code which I've marked with (tsbugisolatedmode) in the code
Below you'll find a set of guidelines for how to contribute to Payload.
## Opening issues
Before you submit an issue, please check all existing [open and closed issues](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/issues) to see if your issue has previously been resolved or is already known. If there is already an issue logged, feel free to upvote it by adding a :thumbsup: [reaction](https://github.com/blog/2119-add-reactions-to-pull-requests-issues-and-comments). If you would like to submit a new issue, please fill out our Issue Template to the best of your ability so we can accurately understand your report.
## Security issues & vulnerabilities
If you come across an issue related to security, or a potential attack vector within Payload or one of its dependencies, please DO NOT create a publicly viewable issue. Instead, please contact us directly at [`dev@payloadcms.com`](mailto:dev@payloadcms.com). We will do everything we can to respond to the issue as soon as possible.
If you find a vulnerability within the core Payload repository, and we determine that it is remediable and of significant nature, we will be happy to pay you a reward for your findings and diligence. [`Contact us`](mailto:dev@payloadcms.com) to find out more.
## Documentation edits
Payload documentation can be found directly within its codebase and you can feel free to make changes / improvements to any of it through opening a PR. We utilize these files directly in our website and will periodically deploy documentation updates as necessary.
## Building additional features
If you're an incredibly awesome person and want to help us make Payload even better through new features or additions, we would be thrilled to work with you.
## Design Contributions
When it comes to design-related changes or additions, it's crucial for us to ensure a cohesive user experience and alignment with our broader design vision. Before embarking on any implementation that would affect the design or UI/UX, we ask that you **first share your design proposal** with us for review and approval.
Our design review ensures that proposed changes fit seamlessly with other components, both existing and planned. This step is meant to prevent unintentional design inconsistencies and to save you from investing time in implementing features that might need significant design alterations later.
### Before Starting
To help us work on new features, you can create a new feature request post in [GitHub Discussion](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/discussions) or discuss it in our [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/payload). New functionality often has large implications across the entire Payload repo, so it is best to discuss the architecture and approach before starting work on a pull request.
### Code
Most new functionality should keep testing in mind. With 1.0, testability of new features has been vastly improved. All top-level directories within the `test/` directory are for testing a specific category: `fields`, `collections`, etc.
If it makes sense to add your feature to an existing test directory, please do so.
A typical directory with `test/` will be structured like this:
```text
.
├── config.ts
├── int.spec.ts
├── e2e.spec.ts
└── payload-types.ts
```
-`config.ts` - This is the _granular_ Payload config for testing. It should be as lightweight as possible. Reference existing configs for an example
-`int.spec.ts` - This is the test file run by jest. Any test file must have a `*int.spec.ts` suffix.
-`e2e.spec.ts` - This is the end-to-end test file that will load up the admin UI using the above config and run Playwright tests. These tests are typically only needed if a large change is being made to the Admin UI.
-`payload-types.ts` - Generated types from `config.ts`. Generate this file by running `pnpm dev:generate-types my-test-dir`.
The directory split up in this way specifically to reduce friction when creating tests and to add the ability to boot up Payload with that specific config.
The following command will start Payload with your config: `pnpm dev my-test-dir`. This command will start up Payload using your config and refresh a test database on every restart.
By default, it will automatically log you in with the default credentials. To disable that, you can either pass in the --no-auto-login flag (example: `pnpm dev my-test-dir --no-auto-login`) or set the `PAYLOAD_PUBLIC_DISABLE_AUTO_LOGIN` environment variable to `false`.
If you wish to use to your own Mongo database for the `test` directory instead of using the in memory database, all you need to do is add the following env vars to the `test/dev.ts` file:
-`process.env.NODE_ENV`
-`process.env.PAYLOAD_TEST_MONGO_URL`
- Simply set `process.env.NODE_ENV` to `test` and set `process.env.PAYLOAD_TEST_MONGO_URL` to your mongo url e.g. `mongodb://127.0.0.1/your-test-db`.
NOTE: It is recommended to add the test credentials (located in `test/credentials.ts`) to your autofill for `localhost:3000/admin` as this will be required on every nodemon restart. The default credentials are `dev@payloadcms.com` as E-Mail and `test` as password.
### Commits
We use [Conventional Commits](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0/) for our commit messages. Please follow this format when creating commits. Here are some examples:
-`feat: adds new feature`
-`fix: fixes bug`
-`docs: adds documentation`
-`chore: does chore`
Here's a breakdown of the format. At the top-level, we use the following types to categorize our commits:
-`feat`: new feature that adds functionality. These are automatically added to the changelog when creating new releases.
-`fix`: a fix to an existing feature. These are automatically added to the changelog when creating new releases.
-`docs`: changes to [docs](./docs) only. These do not appear in the changelog.
-`chore`: changes to code that is neither a fix nor a feature (e.g. refactoring, adding tests, etc.). These do not appear in the changelog.
If you are committing to [templates](./templates) or [examples](./examples), use the `chore` type with the proper scope, like this:
-`chore(templates): adds feature to template`
-`chore(examples): fixes bug in example`
## Pull Requests
For all Pull Requests, you should be extremely descriptive about both your problem and proposed solution. If there are any affected open or closed issues, please leave the issue number in your PR message.
To report an issue, please follow the steps below:
1. Fork this repository
2. Add necessary collections/globals/fields to the `test/_community` directory to recreate the issue you are experiencing
3. Create an issue and add a link to your forked repo
**The goal is to isolate the problem by reducing the number of fields/collections you add to the test/\_community folder. This folder is not meant for you to copy your project into, but to recreate the issue you are experiencing with minimal config.**
## Test directory file tree explanation
```text
.
├── config.ts
├── int.spec.ts
├── e2e.spec.ts
└── payload-types.ts
```
-`config.ts` - This is the _granular_ Payload config for testing. It should be as lightweight as possible. Reference existing configs for an example
-`int.spec.ts` [Optional] - This is the test file run by jest. Any test file must have a `*int.spec.ts` suffix.
-`e2e.spec.ts` [Optional] - This is the end-to-end test file that will load up the admin UI using the above config and run Playwright tests.
-`payload-types.ts` - Generated types from `config.ts`. Generate this file by running `pnpm dev:generate-types _community`.
The directory split up in this way specifically to reduce friction when creating tests and to add the ability to boot up Payload with that specific config. You should modify the files in `test/_community` to get started.
## How to start test collection admin UI
To start the admin panel so you can manually recreate your issue, you can run the following command:
```bash
# This command will start up Payload using your config
# NOTE: it will wipe the test database on restart
pnpm dev _community
```
## Testing is optional but encouraged
An issue does not need to have failing tests — reproduction steps with your forked repo are enough at this point. Some people like to dive deeper and we want to give you the guidance/tools to do so. Read more below.
### How to run integration tests (Payload API tests)
There are a couple ways to do this:
- **Granularly** - you can run individual tests in vscode by installing the Jest Runner plugin and using that to run individual tests. Clicking the `debug` button will run the test in debug mode allowing you to set break points.
Once they are installed you can open the `testing` tab in vscode sidebar and drill down to the test you want to run, i.e. `/test/_community/e2e.spec.ts`
- It is recommended to add the test credentials (located in `test/credentials.ts`) to your autofill for `localhost:3000/admin` as this will be required on every nodemon restart. The default credentials are `dev@payloadcms.com` as email and `test` as password.
<img src="https://payloadcms.com/images/og-image.jpg" alt="Payload headless CMS Admin panel built with React" />
</a>
### 🎉 Payload 2.0 is now available! Read more in the [announcement post](https://payloadcms.com/blog/payload-2-0).
### Features
<h3>Benefits over a regular CMS</h3>
<ul>
<li>Don’t hit some third-party SaaS API, hit your own API</li>
<li>Use your own database and own your data</li>
<li>It's just Express - do what you want outside of Payload</li>
<li>No need to learn how Payload works - if you know JS, you know Payload</li>
<li>No vendor lock-in</li>
<li>Avoid microservices hell - get everything (even auth) in one place</li>
<li>Never touch ancient WP code again</li>
<li>Build faster, never hit a roadblock</li>
<li>Both admin and backend are 100% extensible</li>
</ul>
## ☁️ Deploy instantly with Payload Cloud.
Create a cloud account, connect your GitHub, and [deploy in minutes](https://payloadcms.com/new).
## 🚀 Get started by self-hosting completely free, forever.
Before beginning to work with Payload, make sure you have all of the [required software](https://payloadcms.com/docs/getting-started/installation).
```text
npx create-payload-app
```
Alternatively, it only takes about five minutes to [create an app from scratch](https://payloadcms.com/docs/getting-started/installation#from-scratch).
## 🖱️ One-click templates
Jumpstart your next project by starting with a pre-made template. These are production-ready, end-to-end solutions designed to get you to market as fast as possible.
Eliminate the need to combine Shopify and a CMS, and instead do it all with Payload + Stripe. Comes with a beautiful, fully functional front-end complete with shopping cart, checkout, orders, and much more.
Build any kind of website, blog, or portfolio from small to enterprise. Comes with a beautiful, fully functional front-end complete with posts, projects, comments, and much more.
We're constantly adding more templates to our [Templates Directory](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/templates). If you maintain your own template, consider adding the `payload-template` topic to your GitHub repository for others to find.
Payload is a CMS that has been designed for developers from the ground up to deliver them what they need to build great digital products. If you know JavaScript, you know Payload. It's a _code-first_ CMS, which allows us to do a lot of things right:
- Payload gives you everything you need, but then steps back and lets you build what you want in JavaScript or TypeScript - with no unnecessary complexity brought by GUIs. You'll understand how your CMS works because you will have written it exactly how you want it.
- Bring your own Express server and do whatever you need on top of Payload. Payload doesn't impose anything on you or your app.
- Completely control the Admin panel by using your own React components. Swap out fields or even entire views with ease.
- Use your data however and wherever you need thanks to auto-generated, yet fully extensible REST, GraphQL, and Local Node APIs.
### Quick Start
Before beginning to work with Payload, make sure you have all of the [required software](https://payloadcms.com/docs/getting-started/installation).
From there, the easiest way to get started with Payload is to use the `create-payload-app` package:
```
npx create-payload-app
```
Alternatively, it only takes about five minutes to [create an app from scratch](https://payloadcms.com/docs/getting-started/installation#from-scratch).
### Documentation
## 🗒️ Documentation
Check out the [Payload website](https://payloadcms.com/docs/getting-started/what-is-payload) to find in-depth documentation for everything that Payload offers.
### Contributing
If you want to add contributions to this repository, please follow the instructions in [contributing.md](./contributing.md).
Migrating from v1 to v2? Check out the [2.0 Release Notes](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/releases/tag/v2.0.0) on how to do it.
### Other Resources
## 🙋 Contributing
##### Discussions
If you want to add contributions to this repository, please follow the instructions in [contributing.md](./CONTRIBUTING.md).
There are lots of good conversations and resources in our [GitHub Discussions board](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/discussions). If you're struggling with something, chances are, someone's already solved what you're up against. Searching Discussions will often provide very helpful tips and tricks.
## 📚 Examples
##### Discord
The [Examples Directory](./examples) is a great resource for learning how to setup Payload in a variety of different ways, but you can also find great examples in our blog and throughout our social media.
Join [Payload's Discord channel](https://discord.com/invite/r6sCXqVk3v) to interact with Payload developers in realtime.
Payload is highly extensible and allows you to install or distribute plugins that add or remove functionality. There are both officially-supported and community-supported plugins available. If you maintain your own plugin, consider adding the `payload-plugin` topic to your GitHub repository for others to find.
There are lots of good conversations and resources in our Github Discussions board and our Discord Server. If you're struggling with something, chances are, someone's already solved what you're up against. :point_down:
Below you'll find a set of guidelines for how to contribute to Payload CMS.
## Opening issues
Before you submit an issue, please check all existing [open and closed issues](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/issues) to see if your issue has previously been resolved or is already known. If there is already an issue logged, feel free to upvote it by adding a :thumbsup: [reaction](https://github.com/blog/2119-add-reactions-to-pull-requests-issues-and-comments). If you would like to submit a new issue, please fill out our Issue Template to the best of your ability so we can accurately understand your report.
## Security issues & vulnerabilities
If you come across an issue related to security, or a potential attack vector within Payload or one of its dependencies, please DO NOT create a publicly viewable issue. Instead, please contact us directly at [`dev@payloadcms.com`](mailto:dev@payloadcms.com). We will do everything we can to respond to the issue as soon as possible.
If you find a vulnerability within the core Payload repository, and we determine that it is remediable and of significant nature, we will be happy to pay you a reward for your findings and diligence. [`Contact us`](mailto:dev@payloadcms.com) to find out more.
## Documentation edits
Payload documentation can be found directly within its codebase and you can feel free to make changes / improvements to any of it through opening a PR. We utilize these files directly in our website and will periodically deploy documentation updates as necessary.
## Building additional features
If you're an incredibly awesome person and want to help us make Payload even better through new features or additions, we would be thrilled to work with you.
### Before Starting
To help us work on new features, you can create a new feature request post in [GitHub Discussion](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/discussions) or discuss it in our [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/r6sCXqVk3v). New functionality often has large implications across the entire Payload repo, so it is best to discuss the architecture and approach before starting work on a pull request.
### Code
Most new functionality should keep testing in mind. With 1.0, testability of new features has been vastly improved. All top-level directories within the `test/` directory are for testing a specific category: `fields`, `collections`, etc.
If it makes sense to add your feature to an existing test directory, please do so.
A typical directory with `test/` will be structured like this:
```text
.
├── config.ts
├── int.spec.ts
├── e2e.spec.ts
└── payload-types.ts
```
-`config.ts` - This is the _granular_ Payload config for testing. It should be as lightweight as possible. Reference existing configs for an example
-`int.spec.ts` - This is the test file run by jest. Any test file must have a `*int.spec.ts` suffix.
-`e2e.spec.ts` - This is the end-to-end test file that will load up the admin UI using the above config and run Playwright tests. These tests are typically only needed if a large change is being made to the Admin UI.
-`payload-types.ts` - Generated types from `config.ts`. Generate this file by running `yarn dev:generate-types my-test-dir`.
The directory split up in this way specifically to reduce friction when creating tests and to add the ability to boot up Payload with that specific config.
The following command will start Payload with your config: `yarn dev my-test-dir`. This command will start up Payload using your config and refresh a test database on every restart.
NOTE: It is recommended to add the test credentials to your autofill for `localhost:3000/admin` as this will be required on every nodemon restart.
## Pull Requests
For all Pull Requests, you should be extremely descriptive about both your problem and proposed solution. If there are any affected open or closed issues, please leave the issue number in your PR message.
| **`req`** | The Express `request` object containing the currently authenticated `user` |
| **`id`** | `id` of the document being read |
| **`doc`** | The full document data. |
| **`siblingData`** | Immediately adjacent field data of the document being read. |
| **`id`** | `id` of the document being read |
| **`doc`** | The full document data. |
| **`siblingData`** | Immediately adjacent field data of the document being read. |
### Update
Returns a boolean which allows or denies the ability to update a field's value. If `false` is returned, any passed values will be discarded.
If `false` is returned and you attempt to update the field's value, the operation will **not** throw an error however the field will be omitted from the update operation and the value will remain unchanged.
Access control within Payload is extremely powerful while remaining easy and intuitive to manage. Declaring who should have access to what documents is no more complex than writing a simple JavaScript function that either returns a `boolean` or a [`query`](/docs/queries/overview) constraint to restrict which documents users can interact with.
<YouTube id="DoPLyXG26Dg" title="Overview of Payload Access Control" />
**Example use cases:**
- Allowing anyone `read` access to all `Post`s
@@ -27,13 +29,18 @@ Access control within Payload is extremely powerful while remaining easy and int
In the Local API, all Access Control functions are skipped by default, allowing your server to do whatever it needs. But, you can opt back in by setting the option <strong>overrideAccess</strong> to <strong>true</strong>.
<strong>Note:</strong>
<br />
In the Local API, all Access Control functions are skipped by default, allowing your server to do
whatever it needs. But, you can opt back in by setting the option <strong>
overrideAccess
</strong>{' '}
to <strong>false</strong>.
</Banner>
### Access Control Types
@@ -44,12 +51,13 @@ You can manage access within Payload on three different levels:
- [Fields](/docs/access-control/fields)
- [Globals](/docs/access-control/globals)
### When Access Control is Executed
<Banner type="success">
<strong>Note:</strong><br/>
Access control functions are utilized in two places. It's important to understand how and when your access control is executed.
<strong>Note:</strong>
<br />
Access control functions are utilized in two places. It's important to understand how and when
your access control is executed.
</Banner>
#### As you execute operations
@@ -65,8 +73,11 @@ To accomplish this, Payload ships with an `Access` operation, which is executed
### Argument Availability
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Important:</strong><br/>
When your access control functions are executed via the <strong>access</strong> operation, the <strong>id</strong> and <strong>data</strong> arguments will be <strong>undefined</strong>, because Payload is executing your functions without referencing a specific document.
<strong>Important:</strong>
<br />
When your access control functions are executed via the <strong>access</strong> operation, the{' '}
<strong>id</strong> and <strong>data</strong> arguments will be <strong>undefined</strong>,
because Payload is executing your functions without referencing a specific document.
</Banner>
If you use `id` or `data` within your access control functions, make sure to check that they are defined first. If they are not, then you can assume that your access control is being executed via the `access` operation, to determine solely what the user can do within the Admin UI.
desc: Bundlers are used to bundle the code that serves Payload's Admin Panel.
---
Payload has two official bundlers, the [Webpack Bundler](/docs/admin/webpack) and the [Vite Bundler](/docs/admin/vite). You must install a bundler to use the admin panel.
##### Install a bundler
Webpack (recommended):
```text
yarn add @payloadcms/bundler-webpack
```
Vite (beta):
```text
yarn add @payloadcms/bundler-vite
```
##### Configure the bundler
```ts
// payload.config.ts
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
import { webpackBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-webpack'
// import { viteBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-vite'
export default buildConfig({
// highlight-start
admin: {
bundler: webpackBundler() // or viteBundler()
},
// highlight-end
})
```
### What are bundlers?
At their core, a bundler's main goal is to take a bunch of files and turn them into a few optimized files that you ship to the browser. The admin UI has a root `index.html` entry point, and from there the bundler traverses the dependency tree, bundling all of the files that are required from that point on.
Since the bundled file is sent to the browser, it can't include any server-only code. You will need to remove any server-only code from your admin UI before bundling it. You can learn more about [excluding server code](/docs/admin/excluding-server-code) section.
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Using environment variables in the admin UI</strong>
<br />
Bundles should not contain sensitive information. By default, Payload
excludes env variables from the bundle. If you need to use env variables in your payload config,
you need to prefix them with `PAYLOAD_PUBLIC_` to make them available to the client-side code.
While designing the Payload Admin panel, we determined it should be as minimal and straightforward as possible to allow easy customization and control. There are many times where you may want to completely control how a whole view or a field works. You might even want to add in your own routes entirely. In order for Payload to support that level of customization without introducing versioning / future-proofing issues, Payload provides for a pattern to supply your own React components via your Payload config.
While designing the Payload Admin panel, we determined it should be as minimal and straightforward as possible to allow easy customization and control. There are many times where you may want to completely control how a whole view or a field works. You might even want to add in new views entirely. In order for Payload to support this level of customization without introducing versioning / future-proofing issues, Payload provides for a pattern to supply your own React components via your Payload config.
To swap in your own React component, first, consult the list of available component overrides below. Determine the scope that corresponds to what you are trying to accomplish, and then author your React component accordingly.
<Banner type="success">
<strong>Tip:</strong><br/>
Custom components will automatically be provided with all props that the default component would accept.
<strong>Tip:</strong>
<br />
Custom components will automatically be provided with all props that the default component normally
accepts.
</Banner>
### Base Component Overrides
You can override a set of admin panel-wide components by providing a component to your base Payload config's `admin.components` property. The following options are available:
| Path | Description |
| --------------------- | -------------|
| **`Nav`** | Contains the sidebar and mobile Nav in its entirety. |
| **`BeforeDashboard`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Dashboard, _before_ the default dashboard contents. |
| **`AfterDashboard`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Dashboard, _after_ the default dashboard contents. [Demo](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/master/test/admin/components/AfterDashboard/index.tsx)|
| **`BeforeLogin`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Login, _before_ the default login form. |
| **`AfterLogin`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Login, _after_ the default login form. |
| **`BeforeNavLinks`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Nav, _before_ the links themselves. |
| **`AfterNavLinks`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Nav, _after_ the links. |
| **`views.Account`** | The Account view is used to show the currently logged in user's Account page. |
| **`views.Dashboard`** | The main landing page of the Admin panel. |
| **`graphics.Icon`** | Used as a graphic within the `Nav` component. Often represents a condensed version of a full logo. |
| **`graphics.Logo`** | The full logo to be used in contexts like the `Login` view. |
| **`routes`** | Define your own routes to add to the Payload Admin UI. [More](#custom-routes) |
| **`providers`** | Define your own provider components that will wrap the Payload Admin UI. [More](#custom-providers) |
| **`Nav`** | Contains the sidebar / mobile menu in its entirety. |
| **`BeforeNavLinks`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Nav, _before_ the links themselves. |
| **`AfterNavLinks`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Nav, _after_ the links. |
| **`BeforeDashboard`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Dashboard, _before_ the default dashboard contents. |
| **`AfterDashboard`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Dashboard, _after_ the default dashboard contents. [Demo](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/main/test/admin/components/AfterDashboard/index.tsx) |
| **`BeforeLogin`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Login, _before_ the default login form. |
| **`AfterLogin`** | Array of components to inject into the built-in Login, _after_ the default login form. |
| **`logout.Button`** | A custom React component. |
| **`graphics.Icon`** | Used as a graphic within the `Nav` component. Often represents a condensed version of a full logo. |
| **`graphics.Logo`** | The full logo to be used in contexts like the `Login` view. |
| **`providers`** | Define your own provider components that will wrap the Payload Admin UI. [More](#custom-providers) |
| **`views`** | Override or create new views within the Payload Admin UI. [More](#views) |
#### Full example:
Here is a full example showing how to swap some of these components for your own.
`payload.config.js`
```ts
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
import {
MyCustomNav,
MyCustomLogo,
@@ -47,7 +50,7 @@ import {
MyCustomAccount,
MyCustomDashboard,
MyProvider,
} from './customComponents';
} from './customComponents'
export default buildConfig({
admin: {
@@ -64,44 +67,394 @@ export default buildConfig({
providers: [MyProvider],
},
},
});
})
```
*For more examples regarding how to customize components, look at the following [examples](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/master/test/admin/components).*
#### Views
You can easily swap entire views with your own by using the `admin.components.views` property. At the root level, Payload renders the following views dy default, all of which can be overridden:
| **`Account`** | The Account view is used to show the currently logged in user's Account page. |
| **`Dashboard`** | The main landing page of the Admin panel. |
To swap out any of these views, simply pass in your custom component to the `admin.components.views` property of your Payload config. For example:
```ts
// payload.config.ts
{
// ...
admin: {
components: {
views: {
Account: MyCustomAccountView,
Dashboard: MyCustomDashboardView,
},
},
},
}
```
For more granular control, pass a configuration object instead. Payload exposes all of the properties of `<Route />` component in [React Router v5](https://v5.reactrouter.com):
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
#### Adding new views
To add a _new_ view to the Admin Panel, simply add another key to the `views` object with at least a `path` and `Component` property. For example:
```ts
// payload.config.ts
{
// ...
admin: {
components: {
views: {
MyCustomView: {
Component: MyCustomView,
path: '/my-custom-view',
},
},
},
},
}
```
_For more examples regarding how to customize components, look at the following [examples](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/master/test/admin/components)._
For help on how to build your own custom view components, see [building a custom view component](#building-a-custom-view-component).
### Collections
You can override components on a Collection-by-Collection basis via each Collection's `admin` property.
You can override components on a collection-by-collection basis via their `admin` property.
| Path | Description |
| ---------------- | -------------|
| **`views.Edit`** | Used while a document within this Collection is being edited. |
| **`views.List`** | The `List` view is used to render a paginated, filterable table of Documents in this Collection. |
| **`BeforeList`** | Array of components to inject _before_ the built-in List view |
| **`BeforeListTable`** | Array of components to inject _before_ the built-in List view's table |
| **`AfterList`** | Array of components to inject _after_ the built-in List view |
| **`AfterListTable`** | Array of components to inject _after_ the built-in List view's table |
| **`edit.SaveButton`** | Replace the default `Save` button with a custom component. Drafts must be disabled |
| **`edit.SaveDraftButton`** | Replace the default `Save Draft` button with a custom component. Drafts must be enabled and autosave must be disabled. |
| **`edit.PublishButton`** | Replace the default `Publish` button with a custom component. Drafts must be enabled. |
| **`edit.PreviewButton`** | Replace the default `Preview` button with a custom component. |
| **`views`** | Override or create new views within the Payload Admin UI. [More](#collection-views) |
Here is a full example showing how to swap some of these components for your own:
To swap out entire views on collections, you can use the `admin.components.views` property on the collection's config. Payload renders the following views dy default, all of which can be overridden:
| **`Edit`** | The Edit view is used to edit a single document for a given collection. |
| **`List`** | The List view is used to show a list of documents for a given collection. |
To swap out any of these views, simply pass in your custom component to the `admin.components.views` property of your Payload config. This will replace the entire view, including the page breadcrumbs, title, tabs, etc, _as well as all nested routes_.
```ts
// Collection.ts
{
// ...
admin: {
components: {
views: {
Edit: MyCustomEditView,
List: MyCustomListView,
},
},
},
}
```
_For help on how to build your own custom view components, see [building a custom view component](#building-a-custom-view-component)._
To swap specific _nested_ views within the parent `Edit` view, you can use the `admin.components.views.Edit` property on the globals's config. This will only replace the nested view, leaving the page breadcrumbs, title, tabs, etc intact.
```ts
// Collection.ts
{
// ...
admin: {
components: {
views: {
Edit: {
Default: MyCustomDefaultTab,
},
},
},
},
}
```
You can also add _new_ tabs to the `Edit` view by adding another key to the `components.views.Edit[key]` object with a `path` and `Component` property. See [Custom Tabs](#custom-tabs) for more information.
### Globals
As with Collections, You can override components on a global-by-global basis via their `admin` property.
As with Collections, you can override components on a global-by-global basis via their `admin` property.
| Path | Description |
| ---------------- | -------------|
| **`views.Edit`** | Used while this Global is being edited. |
| **`edit.SaveButton`** | Replace the default `Save` button with a custom component. Drafts must be disabled |
| **`edit.SaveDraftButton`** | Replace the default `Save Draft` button with a custom component. Drafts must be enabled and autosave must be disabled. |
| **`edit.PublishButton`** | Replace the default `Publish` button with a custom component. Drafts must be enabled. |
| **`edit.PreviewButton`** | Replace the default `Preview` button with a custom component. |
| **`views`** | Override or create new views within the Payload Admin UI. [More](#global-views) |
#### Global views
To swap out views for globals, you can use the `admin.components.views` property on the global's config. Payload renders the following views dy default, all of which can be overridden:
| **`Edit`** | The Edit view is used to edit a single document for a given Global. |
To swap out any of these views, simply pass in your custom component to the `admin.components.views` property of your Payload config. This will replace the entire view, including the page breadcrumbs, title, and tabs, _as well as all nested views_.
```ts
// Global.ts
{
// ...
admin: {
components: {
views: {
Edit: MyCustomEditView,
},
},
},
}
```
_For help on how to build your own custom view components, see [building a custom view component](#building-a-custom-view-component)._
To swap specific _nested_ views within the parent `Edit` view, you can use the `admin.components.views.Edit` property on the globals's config. This will only replace the nested view, leaving the page breadcrumbs, title, and tabs intact.
```ts
// Global.ts
{
// ...
admin: {
components: {
views: {
Edit: {
Default: MyCustomDefaultTab,
},
},
},
},
}
```
You can also add _new_ tabs to the `Edit` view by adding another key to the `components.views.Edit[key]` object with a `path` and `Component` property. See [Custom Tabs](#custom-tabs) for more information.
### Custom Tabs
You can easily swap individual collection or global edit views. To do this, pass an _object_ to the `admin.components.views.Edit` property of the config. Payload renders the following views dy default, all of which can be overridden:
Edit: { // You can also define `components.views.Edit` as a component, this will override _all_ nested views
Default: MyCustomDefaultTab,
Versions: MyCustomVersionsTab,
Version: MyCustomVersionTab,
API: MyCustomAPITab,
LivePreview: MyCustomLivePreviewTab,
},
},
},
},
}
```
To add a _new_ tab to the `Edit` view, simply add another key to `components.views.Edit[key]` with at least a `path` and `Component` property. For example:
| **`user`** | The currently logged in user. Will be `null` if no user is logged in. |
| **`canAccessAdmin`** \* | If the currently logged in user is allowed to access the admin panel or not. |
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Note:</strong>
<br />
It's up to you to secure your custom views. If your view requires a user to be logged in or to
have certain access rights, you should handle that within your view component yourself.
</Banner>
#### Example
You can find examples of custom views in the [Payload source code `/test/admin/components/views` folder](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/master/test/admin/components/views). There, you'll find two custom views:
1. A custom view that uses the `DefaultTemplate`, which is the built-in Payload template that displays the sidebar and "eyebrow nav"
1. A custom view that uses the `MinimalTemplate` - which is just a centered template used for things like logging in or out
To see how to pass in your custom views to create custom views of your own, take a look at the `admin.components.views` property of the [Payload test admin config](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/master/test/admin/config.ts).
### Fields
All Payload fields support the ability to swap in your own React components. So, for example, instead of rendering a default Text input, you might need to render a color picker that provides the editor with a custom color picker interface to restrict the data entered to colors only.
<Banner type="success">
<strong>Tip:</strong><br/>
Don't see a built-in field type that you need? Build it! Using a combination of custom validation and custom components, you can override the entirety of how a component functions within the admin panel and effectively create your own field type.
<strong>Tip:</strong>
<br />
Don't see a built-in field type that you need? Build it! Using a combination of custom validation
and custom components, you can override the entirety of how a component functions within the admin
panel and effectively create your own field type.
</Banner>
**Fields support the following custom components:**
| Component | Description |
| --------------- | -------------|
| **`Filter`** | Override the text input that is presented in the `List` view when a user is filtering documents by the customized field. |
| **`Cell`** | Used in the `List` view's table to represent a table-based preview of the data stored in the field. |
| **`Field`** | Swap out the field itself within all `Edit` views. |
When writing your own custom components you can make use of a number of hooks to set data, get reactive changes to other fields, get the id of the document or interact with a context from a custom provider.
There are times when a custom field component needs to have access to data from other fields. This can be done using `getDataByPath` from `useWatchForm` as follows:
```tsx
import { useWatchForm } from 'payload/components/forms';
<span>The fee is ${(amount * feePercentage) / 100}</span>
);
}
};
```
### Getting the document ID
The document ID can be very useful for certain custom components. You can get the `id` from the `useDocumentInfo` hook. Here is an example of a `UI` field using `id` to link to related collections:
```tsx
import { useDocumentInfo } from 'payload/components/utilities';
You can easily add your own custom routes to the Payload Admin panel using the `admin.components.routes` property. Payload currently uses the extremely powerful React Router v5.x and custom routes support all the properties of the React Router `<Route />` component.
**Custom routes support the following properties:**
| Property | Description |
| ----------------- | -------------|
| **`Component`** * | Pass in the component that should be rendered when a user navigates to this route. |
| **`path`** * | React Router `path`. [See the React Router docs](https://v5.reactrouter.com/web/api/Route/path-string-string) for more info. |
*\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required.*
#### Custom route components
Your custom route components will be given all the props that a React Router `<Route />` typically would receive, as well as two props from Payload:
| Prop | Description |
| ---------------------- | -------------|
| **`user`** | The currently logged in user. Will be `null` if no user is logged in. |
| **`canAccessAdmin`** * | If the currently logged in user is allowed to access the admin panel or not. |
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Note:</strong><br/>
It's up to you to secure your custom routes. If your route requires a user to be logged in or to have certain access rights, you should handle that within your route component yourself.
<Banner type="success">
For more information regarding the hooks that are available to you while you build custom
components, including the <strong>useField</strong> hook, [click here](/docs/admin/hooks).
</Banner>
#### Example
You can find examples of custom route views in the [Payload source code `/test/admin/components/views` folder](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/tree/master/test/admin/components/views). There, you'll find two custom routes:
1. A custom view that uses the `DefaultTemplate`, which is the built-in Payload template that displays the sidebar and "eyebrow nav"
1. A custom view that uses the `MinimalTemplate` - which is just a centered template used for things like logging in or out
To see how to pass in your custom views to create custom routes of your own, take a look at the `admin.components.routes` property of the [Payload test admin config](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/master/test/admin/config.ts).
## Custom providers
As your admin customizations gets more complex you may want to share state between fields or other components. You can add custom providers to do add your own context to any Payload app for use in other custom components within the admin panel. Within your config add `admin.components.providers`, these can be used to share context or provide other custom functionality. Read the [React context](https://reactjs.org/docs/context.html) docs to learn more.
<Banner type="warning"><strong>Reminder:</strong> Don't forget to pass the **children** prop through the provider component for the admin UI to show</Banner>
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Reminder:</strong> Don't forget to pass the **children** prop through the provider
component for the admin UI to show
</Banner>
### Styling Custom Components
@@ -222,25 +498,47 @@ To make use of Payload SCSS variables / mixins to use directly in your own compo
@import '~payload/scss';
```
### Getting the current locale
### Getting the current language
In any custom component you can get the selected locale with the `useLocale` hook. Here is a simple example:
When developing custom components you can support multiple languages to be consistent with Payload's i18n support. The best way to do this is to add your translation resources to the [i18n configuration](https://payloadcms.com/docs/configuration/i18n) and import `useTranslation` from `react-i18next` in your components.
For example:
```tsx
import { useLocale } from 'payload/components/utilities';
In any custom component you can get the selected locale with `useLocale` hook. `useLocale` returns the full locale object, consisting of a `label`, `rtl`(right-to-left) property, and then `code`. Here is a simple example:
```tsx
import { useLocale } from 'payload/components/utilities'
desc: Customize your Payload admin panel further by adding your own CSS or SCSS style sheet to the configuration, powerful theme and design options are waiting for you.
@@ -30,7 +31,7 @@ To make it as easy as possible for you to override our styles, Payload uses [BEM
In addition to adding your own style definitions, you can also override Payload's built-in CSS variables. We use as much as possible behind the scenes, and you can override any of them that you'd like to.
You can find the built-in Payload CSS variables within [`./src/admin/scss/app.scss`](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/master/src/admin/scss/app.scss) and [`./src/admin/scss/colors.scss`](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/master/src/admin/scss/colors.scss). The following variables are defined and can be overridden:
You can find the built-in Payload CSS variables within [`./src/admin/scss/app.scss`](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/packages/payload/src/admin/scss/app.scss) and [`./src/admin/scss/colors.scss`](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/packages/payload/src/admin/scss/colors.scss). The following variables are defined and can be overridden:
- Breakpoints
- Base color shades (white to black by default)
@@ -43,7 +44,8 @@ You can find the built-in Payload CSS variables within [`./src/admin/scss/app.sc
#### Dark mode
<Banner type="warning">
If you're overriding colors or theme elevations, make sure to consider how your changes will affect dark mode.
If you're overriding colors or theme elevations, make sure to consider how your changes will
affect dark mode.
</Banner>
By default, Payload automatically overrides all `--theme-elevation`s and inverts all success / warning / error shades to suit dark mode. We also update some base theme variables like `--theme-bg`, `--theme-text`, etc.
This key will automatically be made available to the Payload bundle and can be referenced in your Admin component code as `process.env.PAYLOAD_PUBLIC_STRIPE_PUBLISHABLE_KEY`.
desc: Learn how to exclude server-only code from the Payload Admin UI bundle
---
Because the Admin Panel browser bundle includes your Payload Config file, files using server-only modules need to be excluded.
It's common for your config to rely on server only modules to perform logic in access control functions, hooks, and other contexts.
Any file that imports a server-only module such as `fs`, `stripe`, `authorizenet`, `nodemailer`, etc. **cannot** be included in the browser bundle.
#### Example Scenario
Say we have a collection called `Subscriptions` that has a `beforeChange` hook that creates a Stripe subscription whenever a Subscription document is created in Payload.
**Collection config**:
```ts
// collections/Subscriptions/index.ts
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
import createStripeSubscription from './hooks/createStripeSubscription'
The above code is NOT production-ready and should not be referenced to create Stripe
subscriptions. Although creating a beforeChange hook is a completely valid spot to do things like
create subscriptions, the code above is incomplete and insecure, meant for explanation purposes
only.
</Banner>
**As-is, this collection will prevent your Admin panel from bundling or loading correctly, because Stripe relies on some Node-only packages.**
#### How to fix this
You need to make sure that you use `alias`es to tell your bundler to import "safe" files vs. attempting to import any server-side code that you need to get rid of. Depending on your bundler (Webpack, Vite, etc.) the steps involved may be slightly different.
The basic idea is to create a file that exports an empty object, and then alias import paths of any files that import server-only modules to that empty object file.
This way when your bundler goes to import a file that contains server-only modules, it will instead import the empty object file, which will not break the browser bundle.
### Aliasing server-only modules
To remove files that contain server-only modules from your bundle, you can use an `alias`.
First create new file that exports an empty object:
```js
// mocks/emptyObject.js
export default {}
```
Then, in your Payload config, you can alias the file containing the server-only module to the mock module. For example, here's how you'd do this in Webpack:
```ts
// payload.config.ts
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
import { webpackBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-webpack'
Payload provides a variety of powerful hooks that can be used within your own React components. With them, you can interface with Payload itself and build just about any type of complex customization you can think of—directly in familiar React code.
### useField
The `useField` hook is used internally within every applicable Payload field component, and it manages sending and receiving a field's state from its parent form.
Outside of internal use, its most common use-case is in custom `Field` components. When you build a custom React `Field` component, you'll be responsible for sending and receiving the field's `value` from the form itself. To do so, import the `useField` hook as follows:
```tsx
import { useField } from 'payload/components/forms'
The `useField` hook accepts an `args` object and sends back information and helpers for you to make use of:
```ts
const field = useField<string>({
path: 'fieldPathHere', // required
validate: myValidateFunc, // optional
disableFormData?: false, // if true, the field's data will be ignored
condition?: myConditionHere, // optional, used to skip validation if condition fails
})
// Here is what `useField` sends back
const {
showError, // whether or not the field should show as errored
errorMessage, // the error message to show, if showError
value, // the current value of the field from the form
formSubmitted, // if the form has been submitted
formProcessing, // if the form is currently processing
setValue, // method to set the field's value in form state
initialValue, // the initial value that the field mounted with
} = field;
// The rest of your component goes here
```
### useFormFields
There are times when a custom field component needs to have access to data from other fields, and you have a few options to do so. The `useFormFields` hook is a powerful and highly performant way to retrieve a form's field state, as well as to retrieve the `dispatchFields` method, which can be helpful for setting other fields' form states from anywhere within a form.
<Banner type="success">
<strong>This hook is great for retrieving only certain fields from form state</strong> because it
ensures that it will only cause a rerender when the items that you ask for change.
</Banner>
Thanks to the awesome package [`use-context-selector`](https://github.com/dai-shi/use-context-selector), you can retrieve a specific field's state easily. This is ideal because you can ensure you have an up-to-date field state, and your component will only re-render when _that field's state_ changes.
You can pass a Redux-like selector into the hook, which will ensure that you retrieve only the field that you want. The selector takes an argument with type of `[fields: Fields, dispatch: React.Dispatch<Action>]]`.
```tsx
import { useFormFields } from 'payload/components/forms'
const MyComponent: React.FC = () => {
// Get only the `amount` field state, and only cause a rerender when that field changes
return <span>The fee is ${(amount.value * feePercentage.value) / 100}</span>
}
}
```
### useAllFormFields
**To retrieve more than one field**, you can use the `useAllFormFields` hook. Your component will re-render when _any_ field changes, so use this hook only if you absolutely need to. Unlike the `useFormFields` hook, this hook does not accept a "selector", and it always returns an array with type of `[fields: Fields, dispatch: React.Dispatch<Action>]]`.
You can do lots of powerful stuff by retrieving the full form state, like using built-in helper functions to reduce field state to values only, or to retrieve sibling data by path.
```tsx
import { useAllFormFields, reduceFieldsToValues, getSiblingData } from 'payload/components/forms';
const ExampleComponent: React.FC = () => {
// the `fields` const will be equal to all fields' state,
// and the `dispatchFields` method is usable to send field state up to the form
If you are building a custom component, then you should use `setValue` which is returned from the `useField` hook to programmatically set your field's value. But if you're looking to update _another_ field's value, you can use `dispatchFields` returned from `useFormFields`.
You can send the following actions to the `dispatchFields` function.
| **`ADD_ROW`** | Adds a row of data (useful in array / block field data) |
| **`DUPLICATE_ROW`** | Duplicates a row of data (useful in array / block field data) |
| **`MODIFY_CONDITION`** | Updates a field's conditional logic result (true / false) |
| **`MOVE_ROW`** | Moves a row of data (useful in array / block field data) |
| **`REMOVE`** | Removes a field from form state |
| **`REMOVE_ROW`** | Removes a row of data from form state (useful in array / block field data) |
| **`REPLACE_STATE`** | Completely replaces form state |
| **`UPDATE`** | Update any property of a specific field's state |
To see types for each action supported within the `dispatchFields` hook, check out the Form types [here](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/packages/payload/src/admin/components/forms/Form/types.ts).
### useForm
The `useForm` hook can be used to interact with the form itself, and sends back many methods that can be used to reactively fetch form state without causing rerenders within your components each time a field is changed. This is useful if you have action-based callbacks that your components fire, and need to interact with form state _based on a user action_.
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Warning:</strong>
<br />
This hook is optimized to avoid causing rerenders when fields change, and as such, its `fields`
property will be out of date. You should only leverage this hook if you need to perform actions
against the form in response to your users' actions. Do not rely on its returned "fields" as being
up-to-date. They will be removed from this hook's response in an upcoming version.
</Banner>
The `useForm` hook returns an object with the following properties: |
<TableWithDrawers
columns={[
'Action',
'Description',
'Example',
]}
rows={[
[
{
value: <strong><code>fields</code></strong>,
},
{
value: "Deprecated. This property cannot be relied on as up-to-date.",
In any custom component you can get the selected locale object with the `useLocale` hook. `useLocale`gives you the full locale object, consisting of a `label`, `rtl`(right-to-left) property, and then `code`. Here is a simple example:
```tsx
import { useLocale } from 'payload/components/utilities'
const Greeting: React.FC = () => {
// highlight-start
const locale = useLocale()
// highlight-end
const trans = {
en: 'Hello',
es: 'Hola',
}
return <span> {trans[locale.code]} </span>
}
```
### useAuth
Useful to retrieve info about the currently logged in user as well as methods for interacting with it. It sends back an object with the following properties:
| **`logOut`** | A method to log out the currently logged in user |
| **`refreshCookie`** | A method to trigger the silent refreshing of a user's auth token |
| **`setToken`** | Set the token of the user, to be decoded and used to reset the user and token in memory |
| **`token`** | The logged in user's token (useful for creating preview links, etc.) |
| **`refreshPermissions`** | Load new permissions (useful when content that effects permissions has been changed) |
| **`permissions`** | The permissions of the current user |
```tsx
import { useAuth } from 'payload/components/utilities'
import { User } from '../payload-types.ts'
const Greeting: React.FC = () => {
// highlight-start
const { user } = useAuth<User>()
// highlight-end
return <span>Hi, {user.email}!</span>
}
```
### useConfig
Used to easily fetch the full Payload config.
```tsx
import { useConfig } from 'payload/components/utilities'
const MyComponent: React.FC = () => {
// highlight-start
const config = useConfig()
// highlight-end
return <span>{config.serverURL}</span>
}
```
### useEditDepth
Sends back how many editing levels "deep" the current component is. Edit depth is relevant while adding new documents / editing documents in modal windows and other cases.
```tsx
import { useEditDepth } from 'payload/components/utilities'
const MyComponent: React.FC = () => {
// highlight-start
const editDepth = useEditDepth()
// highlight-end
return <span>My component is {editDepth} levels deep</span>
}
```
### usePreferences
Returns methods to set and get user preferences. More info can be found [here](https://payloadcms.com/docs/admin/preferences).
Payload dynamically generates a beautiful, fully functional React admin panel to manage your data. It's extremely powerful and can be customized / extended upon easily by swapping in your own React components. You can add additional views, modify how built-in views look / work, swap out Payload branding for your client's, build your own field types and much more.
The Payload Admin panel is built with Webpack, code-split, highly performant (even with 100+ fields), and written fully in TypeScript.
The Payload Admin panel can be bundled with our officially supported [Vite](/docs/admin/vite) and [webpack](/docs/admin/webpack) bundlers or you can integrate another bundler following our adapter pattern approach.
When bundled, it is code-split, highly performant (even with 100+ fields), and written fully in TypeScript.
<Banner type="success">
The Admin panel is meant to be simple enough to give you a starting point but not bring too much complexity, so that you can easily customize it to suit the needs of your application and your editors.
The Admin panel is meant to be simple enough to give you a starting point but not bring too much
complexity, so that you can easily customize it to suit the needs of your application and your
editors.
</Banner>

*Screenshot of the Admin panel while editing a document from an example `AllFields` collection*
caption="Redesigned admin panel with a collapsible sidebar that's open by default, providing greater extensibility and enhanced horizontal real estate."
/>
## Admin Options
All options for the Admin panel are defined in your base Payload config file.
| Option | Description |
| -------------------- | -------------|
| `user` | The `slug` of a Collection that you want be used to log in to the Admin dashboard. [More](/docs/admin/overview#the-admin-user-collection) |
| `meta` | Base meta data to use for the Admin panel. Included properties are `titleSuffix`, `ogImage`, and `favicon`. |
| `disable` | If set to `true`, the entire Admin panel will be disabled. |
| `indexHTML` | Optionally replace the entirety of the `index.html` file used by the Admin panel. Reference the [base index.html file](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/master/src/admin/index.html) to ensure your replacement has the appropriate HTML elements. |
| `css` | Absolute path to a stylesheet that you can use to override / customize the Admin panel styling. [More](/docs/admin/customizing-css). |
| `scss` | Absolute path to a Sass variables / mixins stylesheet meant to override Payload styles to make for an easy re-skinning of the Admin panel. [More](/docs/admin/customizing-css#overriding-scss-variables). |
| `dateFormat` | Global date format that will be used for all dates in the Admin panel. Any valid [date-fns](https://date-fns.org/) format pattern can be used. |
| `avatar` | Set account profile picture. Options: `gravatar`, `default` or a custom React component. |
| `components` | Component overrides that affect the entirety of the Admin panel. [More](/docs/admin/components) |
| `webpack` | Customize the Webpack config that's used to generate the Admin panel. [More](/docs/admin/webpack) |
| `user` | The `slug` of a Collection that you want be used to log in to the Admin dashboard. [More](/docs/admin/overview#the-admin-user-collection) |
| `buildPath` | Specify an absolute path for where to store the built Admin panel bundle used in production. Defaults to `path.resolve(process.cwd(), 'build')`. |
| `meta` | Base meta data to use for the Admin panel. Included properties are `titleSuffix`, `ogImage`, and `favicon`. |
| `disable` | If set to `true`, the entire Admin panel will be disabled. |
| `indexHTML` | Optionally replace the entirety of the `index.html` file used by the Admin panel. Reference the [base index.html file](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/main/packages/payload/src/admin/index.html) to ensure your replacement has the appropriate HTML elements. |
| `css` | Absolute path to a stylesheet that you can use to override / customize the Admin panel styling. [More](/docs/admin/customizing-css). |
| `scss` | Absolute path to a Sass variables / mixins stylesheet meant to override Payload styles to make for an easy re-skinning of the Admin panel. [More](/docs/admin/customizing-css#overriding-scss-variables). |
| `dateFormat` | Global date format that will be used for all dates in the Admin panel. Any valid [date-fns](https://date-fns.org/) format pattern can be used. |
| `avatar` | Set account profile picture. Options: `gravatar`, `default` or a custom React component. |
| `autoLogin` | Used to automate admin log-in for dev and demonstration convenience. [More](/docs/authentication/config). |
| `livePreview` | Enable real-time editing for instant visual feedback of your front-end application. [More](/docs/live-preview/overview). |
| `components` | Component overrides that affect the entirety of the Admin panel. [More](/docs/admin/components) |
| `webpack` | Customize the Webpack config that's used to generate the Admin panel. [More](/docs/admin/webpack) |
| `vite` | Customize the Vite config that's used to generate the Admin panel. [More](/docs/admin/vite) |
| **`bundler`** | The bundler that you would like to use to bundle the admin panel. Officially supported bundlers: [Webpack](/docs/admin/webpack) and [Vite](/docs/admin/vite). |
| **`logoutRoute`** | The route for the `logout` page. |
| **`inactivityRoute`** | The route for the `logout` inactivity page. |
### The Admin User Collection
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Important:</strong><br />
The Payload Admin panel can only be used by one Collection that supports <a href="/docs/authentication/overview">Authentication</a>.
<strong>Important:</strong>
<br />
The Payload Admin panel can only be used by one Collection that supports
[Authentication](/docs/authentication/overview).
</Banner>
To specify which Collection to use to log in to the Admin panel, pass the `admin` options a `user` key equal to the slug of the Collection that you'd like to use.
`payload.config.js`:
```ts
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config';
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
const config = buildConfig({
admin: {
user: 'admins', // highlight-line
},
});
})
```
By default, if you have not specified a Collection, Payload will automatically provide you with a `User` Collection which will be used to access the Admin panel. You can customize or override the fields and settings of the default `User` Collection by passing your own collection using `users` as its `slug` to Payload. When this is done, Payload will use your provided `User` Collection instead of its default version.
@@ -15,8 +15,10 @@ Out of the box, Payload handles the persistence of your users' preferences in a
1. The "collapsed" state of blocks, on a document level, as users edit or interact with documents
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Important:</strong><br/>
All preferences are stored on an individual user basis. Payload automatically recognizes the user that is reading or setting a preference via all provided authentication methods.
<strong>Important:</strong>
<br />
All preferences are stored on an individual user basis. Payload automatically recognizes the user
that is reading or setting a preference via all provided authentication methods.
</Banner>
### Use cases
@@ -30,17 +32,17 @@ This API is used significantly for internal operations of the Admin panel, as me
### Database
Payload automatically creates an internally used `_preferences` collection that stores user preferences. Each document in the `_preferences` collection contains the following shape:
Payload automatically creates an internally used `payload-preferences` collection that stores user preferences. Each document in the `payload-preferences` collection contains the following shape:
| Key | Value |
| -------------------- | -------------|
| `id` | A unique ID for each preference stored. |
| `key` | A unique `key` that corresponds to the preference. |
| `user` | The ID of the `user` that is storing its preference. |
| `userCollection` | The `slug` of the collection that the `user` is logged in as. |
| `value` | The value of the preference. Can be any data shape that you need. |
| `createdAt` | A timestamp of when the preference was created. |
| `updatedAt` | A timestamp set to the last time the preference was updated.
Payload has a Vite bundler that you can install and bundle the Admin Panel with. This is an alternative to the [Webpack](/docs/admin/webpack) bundler and might give some performance boosts to your development workflow.
To use Vite as your bundler, first you need to install the package:
```bash
yarn add @payloadcms/bundler-vite
```
<Banner>
The Vite bundler is currently in beta. If you would like to help us test this package, we'd love to hear if you find any bugs or issues!
</Banner>
Vite works fundamentally differently than Webpack. In development mode, it will first pre-bundle any of your dependencies that are CommonJS-only, and then it'll leverage ESM directly in your browser for a better HMR experience.
It then uses Rollup to create production builds of your admin UI. With Vite, you should see a decent performance boost—especially after your first cold start. However, that first cold start might take a few more seconds.
<Banner type="warning">
In most cases, Vite should work out of the box. But existing Payload plugins may need to make compatibility changes to support Vite.
</Banner>
This is because Vite aliases work fundamentally differently than Webpack aliases, and Payload relies on aliasing server-only code out of the Payload config to ensure that the bundled admin JS works within your browser.
Here are the main differences between how Vite aliases work and how Webpack aliases work.
**Vite aliases do not work with absolute paths.**
In Vite, an alias will only match if the `find` property _exactly matches_ how you are importing your server-only file. So if you are importing a file with a relative path, i.e. `'../../my-module'`, and your alias is absolute, your alias will not work.
**Vite aliases do not get applied to pre-bundled dependencies.**
This especially affects plugins, as plugins will be pre-bundled by Vite using `esbuild`. To get around this and support Vite, plugin authors need to configure an alias to their plugin at the top level, so that the alias will work accordingly.
Here's an example. Say your plugin is called `payload-plugin-cool`. It's imported as follows:
```ts
import { myCoolPlugin } from 'payload-plugin-cool'
```
That plugin should create an alias to support Vite as follows:
This will effectively alias the entire plugin and work with Vite. If the plugin requires admin-specific code, then the `./my-admin-plugin.js` alias target file should reflect any changes necessary to the admin UI that the main server-side plugin performs.
### Extending the Vite config
The Payload config supports a new property for plugins to be able to extend the Vite config specifically. That property exists on the main Payload config under `admin.vite`.
It's a function that takes a Vite config, and returns an updated Vite config. Here's an example:
```ts
export const buildConfig({
collections: [],
admin: {
vite: (incomingViteConfig) => ({
...incomingViteConfig,
resolve: {
...incomingViteConfig.resolve,
// Do whatever you need here
}
})
}
})
```
Even though there is a new property for Vite configs specifically, we have implemented some "compatibility" between Webpack and Vite out-of-the-box.
If your config specifies Webpack aliases, we attempt to leverage them automatically within the Vite config. They are merged into the Vite alias configuration seamlessly and may work out-of-the-box.
desc: The Payload admin panel uses Webpack 5 and supports many common functionalities such as SCSS and Typescript out of the box to give you more freedom.
Payload uses Webpack 5 to build the Admin panel. It comes with support for many common functionalities such as SCSS and Typescript out of the box, but there are many cases where you may need to add support for additional functionalities.
Payload has a Webpack (v5) bundler that you can build the Admin panel with. For now, we recommended using it because it is stable. If you are feeling a bit more adventurous you can give the [Vite](/docs/admin/vite) bundler a shot.
To extend the Webpack config, add the `webpack` key to your base Payload config, and provide a function that accepts the default Webpack config as its only argument:
Out of the box, the Webpack bundler supports common functionalities such as SCSS and Typescript, but there are many cases where you may need to add support for additional functionalities.
`payload.config.ts`
```ts
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config';
#### Installation
export default buildConfig({
admin: {
// highlight-start
webpack: (config) => {
// Do something with the config here
return config;
}
// highlight-end
}
});
```bash
yarn add @payloadcms/bundler-webpack
```
### Aliasing server-only modules
#### Import the bundler
A common use case for extending the Payload config is to alias server-only modules, thus preventing them from inclusion into the browser JavaScript bundle.
```ts
// payload.config.ts
As the Payload config is used in both server **and** client contexts, you may find yourself writing code in your Payloadconfig that may be incompatible with browser environments.
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
import { webpackBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-webpack'
Examples of **non** browser-friendly packages:
export default buildConfig({
// highlight-start
admin: {
bundler: webpackBundler()
},
// highlight-end
})
```
- `fs`
- `stripe`
- `authorizenet`
- `nodemailer`
### Extending Webpack
You may rely on server-only packages such as the above to perform logic in access control functions, hooks, and other contexts (which is great!) but when you boot up your Payload app and try to view it in the browser, you'll likely run into missing dependency issues or other general incompatibilities.
If you need to extend the Webpack config, you can do so by passing a function to the `admin.webpack` property on your Payload config.
The function will receive the Webpack config as an argument and should return the modified config.
```ts
// payload.config.ts
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
import { webpackBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-webpack'
export default buildConfig({
admin: {
bundler: webpackBundler()
// highlight-start
webpack: (config) => {
// full control of the Webpack config
return config
},
// highlight-end
},
})
```
<Banner type="success">
<strong>Tip:</strong><br/>
To avoid problems with server code making it to your Webpack bundle, you can use the <strong>alias</strong> Webpack feature to tell Webpack to avoid importing the modules you want to restrict to server-only.
<strong>Tip:</strong>
<br />
If changes to your Webpack aliases are not surfacing, they might be
[cached](https://webpack.js.org/configuration/cache/) in `node_modules/.cache/webpack`. Try
deleting that folder and restarting your server.
</Banner>
<strong>For example, let's say that you have a Collection called `Subscriptions` which relies on Stripe:</strong>
<br/><br/>
`collections/Subscriptions/index.js`
```ts
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types';
import createStripeSubscription from './hooks/createStripeSubscription';
const Subscription: CollectionConfig = {
slug: 'subscriptions',
hooks: {
beforeChange: [
createStripeSubscription,
]
},
fields: [
{
name: 'stripeSubscriptionID',
type: 'text',
required: true,
}
]
};
export default Subscription;
```
The collection above features a `beforeChange` hook that creates a Stripe subscription whenever a Subscription document is created in Payload.
<strong>That hook might look something like this:</strong>
The above code is NOT production-ready and should not be referenced to create Stripe subscriptions. Although creating a beforeChange hook is a completely valid spot to do things like create subscriptions, the code above is incomplete and insecure, meant for explanation purposes only.
</Banner>
**As-is, this collection will prevent your Admin panel from bundling or loading correctly, because Stripe relies on some Node-only packages.**
To remedy this issue you can extend the Payload Webpack config to alias your entire `createStripeSubscription` hook to a separate, empty mock file.
Example in `payload.config.js`:
```js
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config';
import path from 'path';
import Subscription from './collections/Subscription';
The above code will alias the file at path `createStripeSubscriptionPath` to a mocked module, which might look like this:
`mocks/emptyObject.js`
```js
export default {};
```
Now, when Webpack sees that you're attempting to import your `createStripeSubscriptionPath` file, it'll disregard that actual file and load your mock file instead. Not only will your Admin panel now bundle successfully, you will have optimized its filesize by removing unnecessary code! And you might have learned something about Webpack, too.
## Admin environment vars
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Important:</strong><br />
Be careful about what variables you provide to your client-side code. Analyze every single one to make sure that you're not accidentally leaking anything that an attacker could exploit. Only keys that are safe to be available to everyone in plain text should be provided to your Admin panel.
</Banner>
By default, `env` variables are **not** provided to the Admin panel for security and safety reasons. But, Payload provides you with a way to still provide `env` vars to your frontend code.
**Payload will automatically supply any present `env` variables that are prefixed with `PAYLOAD_PUBLIC_` directly to the Admin panel.**
For example, if you've got the following environment variable:
This key will automatically be made available to the Payload bundle and can be referenced in your Admin component code as `process.env.PAYLOAD_PUBLIC_STRIPE_PUBLISHABLE_KEY`.
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ To enable Authentication on a collection, define an `auth` property and set it t
| **`useAPIKey`** | Payload Authentication provides for API keys to be set on each user within an Authentication-enabled Collection. [More](/docs/authentication/config#api-keys) |
| **`tokenExpiration`** | How long (in seconds) to keep the user logged in. JWTs and HTTP-only cookies will both expire at the same time. |
| **`maxLoginAttempts`** | Only allow a user to attempt logging in X amount of times. Automatically locks out a user from authenticating if this limit is passed. Set to `0` to disable. |
| **`lockTime`** | Set the time that a user should be locked out if they fail authentication more times than `maxLoginAttempts` allows for. |
| **`lockTime`** | Set the time (in milliseconds) that a user should be locked out if they fail authentication more times than `maxLoginAttempts` allows for. |
| **`depth`** | How many levels deep a `user` document should be populated when creating the JWT and binding the `user` to the express `req`. Defaults to `0` and should only be modified if absolutely necessary, as this will affect performance. |
| **`cookies`** | Set cookie options, including `secure`, `sameSite`, and `domain`. For advanced users. |
| **`forgotPassword`** | Customize the way that the `forgotPassword` operation functions. [More](/docs/authentication/config#forgot-password) |
@@ -29,32 +29,54 @@ To enable Authentication on a collection, define an `auth` property and set it t
To integrate with third-party APIs or services, you might need the ability to generate API keys that can be used to identify as a certain user within Payload.
In Payload, users are essentially documents within a collection. Just like you can authenticate as a user with an email and password, which is considered as our default local auth strategy, you can also authenticate as a user with an API key. API keys are generated on a user-by-user basis, similar to email and passwords, and are meant to represent a single user.
For example, if you have a third-party service or external app that needs to be able to perform protected actions at its discretion, you have two options:
1. Create a user for the third-party app, and log in each time to receive a token before you attempt to access any protected actions
1. Enable API key support for the Collection, where you can generate a non-expiring API key per user in the collection
1. Enable API key support for the Collection, where you can generate a non-expiring API key per user in the collection. This is particularly useful as you can create a "user" that reflects an integration with a specific external service and assign a "role" or specific access only needed by that service/integration. Alternatively, you could create a "super admin" user and assign an API key to that user so that any requests made with that API key are considered as being made by that super user.
Technically, both of these options will work for third-party integrations but the second option with API key is simpler, because it reduces the amount of work that your integrations need to do to be authenticated properly.
To enable API keys on a collection, set the `useAPIKey` auth option to `true`. From there, a new interface will appear in the Admin panel for each document within the collection that allows you to generate an API key for each user in the Collection.
<Banner type="success">
User API keys are encrypted within the database, meaning that if your database
is compromised, your API keys will not be.
User API keys are encrypted within the database, meaning that if your database is compromised,
your API keys will not be.
</Banner>
##### Authenticating via API Key
#### Authenticating via API Key
To utilize your API key while interacting with the REST or GraphQL API, add the `Authorization` header.
To authenticate REST or GraphQL API requests using an API key, set the `Authorization` header. The header is case-sensitive and needs the slug of the `auth.useAPIKey` enabled collection, then " API-Key ", followed by the `apiKey` that has been assigned. Payload's built-in middleware will then assign the user document to `req.user` and handle requests with the proper access control. By doing this, Payload recognizes the request being made as a request by the user associated with that API key.
Payload ensures that the same, uniform access control is used across all authentication strategies. This enables you to utilize your existing access control configurations with both API keys and the standard email/password authentication. This consistency can aid in maintaining granular control over your API keys.
#### API Key _Only_ Authentication
If you want to use API keys as the only authentication method for a collection, you can disable the default local strategy by setting `disableLocalStrategy` to `true` on the collection's `auth` property. This will disable the ability to authenticate with email and password, and will only allow for authentication via API key.
```ts
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
export const Customers: CollectionConfig = {
slug: 'customers',
auth: {
useAPIKey: true,
disableLocalStrategy: true,
},
}
```
### Forgot Password
@@ -68,26 +90,25 @@ Function that accepts one argument, containing `{ req, token, user }`, that allo
<Banner type="success">
<strong>Tip:</strong>
<br />
HTML templating can be used to create custom email templates, inline CSS
automatically, and more. You can make a reusable function that standardizes
all email sent from Payload, which makes sending custom emails more DRY.
Payload doesn't ship with an HTML templating engine, so you are free to choose
your own.
HTML templating can be used to create custom email templates, inline CSS automatically, and more.
You can make a reusable function that standardizes all email sent from Payload, which makes
sending custom emails more DRY. Payload doesn't ship with an HTML templating engine, so you are
free to choose your own.
</Banner>
Example:
```ts
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types';
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
const Customers: CollectionConfig = {
export const Customers: CollectionConfig = {
slug: 'customers',
auth: {
forgotPassword: {
// highlight-start
generateEmailHTML: ({ req, token, user }) => {
// Use the token provided to allow your user to reset their password
return `Hey ${user.email}, verify your email by clicking here: ${url}`;
}
return `Hey ${user.email}, verify your email by clicking here: ${url}`
},
// highlight-end
}
}
};
},
},
}
```
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Important:</strong>
<br />
If you specify a different URL to send your users to for email verification,
such as a page on the frontend of your app or similar, you need to handle
making the call to the Payload REST or GraphQL verification operation yourself
on your frontend, using the token that was provided for you. Above, it was
passed via query parameter.
If you specify a different URL to send your users to for email verification, such as a page on the
frontend of your app or similar, you need to handle making the call to the Payload REST or GraphQL
verification operation yourself on your frontend, using the token that was provided for you.
Above, it was passed via query parameter.
</Banner>
**`generateEmailSubject`**
@@ -209,9 +227,8 @@ As of Payload `1.0.0`, you can add additional authentication strategies to Paylo
Behind the scenes, Payload uses PassportJS to power its local authentication strategy, so most strategies listed on the PassportJS website will work seamlessly. Combined with adding custom components to the admin panel's `Login` view, you can create advanced authentication strategies directly within Payload.
<Banner type="warning">
This is an advanced feature, so only attempt this if you are an experienced
developer. Otherwise, just let Payload's built-in authentication handle user
auth for you.
This is an advanced feature, so only attempt this if you are an experienced developer. Otherwise,
just let Payload's built-in authentication handle user auth for you.
</Banner>
The `strategies` property is an array that takes objects with the following properties:
@@ -227,3 +244,42 @@ If you pass a strategy to the `strategy` property directly, the `name` property
However, if you pass a function to `strategy`, `name` is a required property.
In either case, Payload will prefix the strategy name with the collection `slug` that the strategy is passed to.
### Admin autologin
For testing and demo purposes you may want to skip forcing the admin user to login in order to access the panel.
The `admin.autologin` property is used to configure the how visitors are handled when accessing the admin panel.
The default is that all users will have to login and this should not be enabled for environments where data needs to protected.
@@ -17,6 +17,7 @@ The Access operation returns what a logged in user can and can't do with the col
`GET http://localhost:3000/api/access`
Example response:
```ts
{
canAccessAdmin: true,
@@ -66,6 +67,8 @@ query {
}
```
Document access can also be queried on a collection/global basis. Access on a global can queried like `http://localhost:3000/api/global-slug/access`, Collection document access can be queried like `http://localhost:3000/api/collection-slug/access/:id`.
### Me
Returns either a logged in user with token or null when there is no logged in user.
@@ -75,6 +78,7 @@ Returns either a logged in user with token or null when there is no logged in us
user: { // The JWT "payload" ;) from the logged in user
@@ -92,7 +96,7 @@ Example response:
```graphql
query {
Me[collection-singular-label] {
me[collection-singular-label] {
user {
email
}
@@ -106,6 +110,7 @@ query {
Accepts an `email` and `password`. On success, it will return the logged in user as well as a token that can be used to authenticate. In the GraphQL and REST APIs, this operation also automatically sets an HTTP-only cookie including the user's token. If you pass an Express `res` to the Local API operation, Payload will set a cookie there as well.
**Example REST API login**:
```ts
const res = await fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/[collection-slug]/login', {
method: 'POST',
@@ -115,10 +120,10 @@ const res = await fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/[collection-slug]/login', {
body: JSON.stringify({
email: 'dev@payloadcms.com',
password: 'this-is-not-our-password...or-is-it?',
})
}),
})
const json = await res.json();
const json = await res.json()
// JSON will be equal to the following:
/*
@@ -166,6 +171,7 @@ const result = await payload.login({
As Payload sets HTTP-only cookies, logging out cannot be done by just removing a cookie in JavaScript, as HTTP-only cookies are inaccessible by JS within the browser. So, Payload exposes a `logout` operation to delete the token in a safe way.
**Example REST API logout**:
```ts
const res = await fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/[collection-slug]/logout', {
method: 'POST',
@@ -192,6 +198,7 @@ This operation requires a non-expired token to send back a new one. If the user'
If successful, this operation will automatically renew the user's HTTP-only cookie and will send back the updated token in JSON.
**Example REST API token refresh**:
```ts
const res = await fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/[collection-slug]/refresh-token', {
method: 'POST',
@@ -200,7 +207,7 @@ const res = await fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/[collection-slug]/refresh-tok
},
})
const json = await res.json();
const json = await res.json()
// JSON will be equal to the following:
/*
@@ -231,7 +238,10 @@ mutation {
```
<Banner type="success">
The Refresh operation will automatically find the user's token in either a JWT header or the HTTP-only cookie. But, you can specify the token you're looking to refresh by providing the REST API with a `token` within the JSON body of the request, or by providing the GraphQL resolver a `token` arg.
The Refresh operation will automatically find the user's token in either a JWT header or the
HTTP-only cookie. But, you can specify the token you're looking to refresh by providing the REST
API with a `token` within the JSON body of the request, or by providing the GraphQL resolver a
`token` arg.
</Banner>
### Verify by Email
@@ -239,13 +249,14 @@ mutation {
If your collection supports email verification, the Verify operation will be exposed which accepts a verification token and sets the user's `_verified` property to `true`, thereby allowing the user to authenticate with the Payload API.
**Example REST API user verification**:
```ts
const res = await fetch(`http://localhost:3000/api/[collection-slug]/verify/${TOKEN_HERE}`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
});
})
```
**Example GraphQL Mutation**:
@@ -272,6 +283,7 @@ If a user locks themselves out and you wish to deliberately unlock them, you can
To restrict who is allowed to unlock users, you can utilize the [`unlock`](/docs/access-control/overview#unlock) access control function.
**Example REST API unlock**:
```ts
const res = await fetch(`http://localhost:3000/api/[collection-slug]/unlock`, {
method: 'POST',
@@ -306,6 +318,7 @@ The link to reset the user's password contains a token which is what allows the
By default, the Forgot Password operations send users to the Payload Admin panel to reset their password, but you can customize the generated email to send users to the frontend of your app instead by [overriding the email HTML](/docs/authentication/config#forgot-password).
**Example REST API Forgot Password**:
```ts
const res = await fetch(`http://localhost:3000/api/[collection-slug]/forgot-password`, {
method: 'POST',
@@ -315,7 +328,7 @@ const res = await fetch(`http://localhost:3000/api/[collection-slug]/forgot-pass
disableEmail: false // you can disable the auto-generation of email via local API
});
disableEmail: false, // you can disable the auto-generation of email via local API
})
```
<Banner type="success">
<strong>Tip:</strong><br/>
You can stop the reset-password email from being sent via using the local API. This is helpful if you need to create user accounts programmatically, but not set their password for them. This effectively generates a reset password token which you can then use to send to a page you create, allowing a user to "complete" their account by setting their password. In the background, you'd use the token to "reset" their password.
<strong>Tip:</strong>
<br />
You can stop the reset-password email from being sent via using the local API. This is helpful if
you need to create user accounts programmatically, but not set their password for them. This
effectively generates a reset password token which you can then use to send to a page you create,
allowing a user to "complete" their account by setting their password. In the background, you'd
After a user has "forgotten" their password and a token is generated, that token can be used to send to the reset password operation along with a new password which will allow the user to reset their password securely.
**Example REST API Reset Password**:
```ts
const res = await fetch(`http://localhost:3000/api/[collection-slug]/reset-password`, {
@@ -78,9 +84,14 @@ Once enabled, each document that is created within the Collection can be thought
Successfully logging in returns a `JWT` (JSON web token) which is how a user will identify themselves to Payload. By providing this JWT via either an HTTP-only cookie or an `Authorization` header, Payload will automatically identify the user and add its user JWT data to the Express `req`, which is available throughout Payload including within access control, hooks, and more.
You can specify what data gets encoded to the JWT token by setting `saveToJWT` to true in your auth collection fields. If you wish to use a different key other than the field `name`, you can provide it to `saveToJWT` as a string. It is also possible to use `saveToJWT` on fields that are nested in inside groups and tabs. If a group has a `saveToJWT` set it will include the object with all sub-fields in the token. You can set `saveToJWT: false` for any fields you wish to omit. If a field inside a group has `saveToJWT` set, but the group does not, the field will be included at the top level of the token.
<Banner type="success">
<strong>Tip:</strong><br/>
You can access the logged in user from access control functions and hooks via the Express <strong>req</strong>. The logged in user is automatically added as the <strong>user</strong> property.
<strong>Tip:</strong>
<br />
You can access the logged-in user from access control functions and hooks via the Express{' '}
<strong>req</strong>. The logged-in user is automatically added as the <strong>user</strong>{' '}
property.
</Banner>
### HTTP-only cookies
@@ -100,16 +111,19 @@ Fetch example, including credentials:
For more about how to automatically include cookies in requests from your app to your Payload API, [click here](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Fetch_API/Using_Fetch#Sending_a_request_with_credentials_included).
<Banner type="success">
<strong>Tip:</strong><br/>
To make sure you have a Payload cookie set properly in your browser after logging in, you can use Chrome's Developer Tools - Application - Cookies - [your-domain-here]. The Chrome Developer tools will still show HTTP-only cookies, even when JavaScript running on the page can't.
<strong>Tip:</strong>
<br />
To make sure you have a Payload cookie set properly in your browser after logging in, you can use
Chrome's Developer Tools - Application - Cookies - [your-domain-here]. The Chrome Developer tools
will still show HTTP-only cookies, even when JavaScript running on the page can't.
</Banner>
### CSRF Protection
@@ -121,28 +135,33 @@ For example, let's say you have a very popular app running at coolsite.com. This
So, if a user of coolsite.com is logged in and just browsing around on the internet, they might stumble onto a page with bad intentions. That bad page might automatically make requests to all sorts of sites to see if they can find one that they can log into - and coolsite.com might be on their list. If your user was logged in while they visited that evil site, the attacker could do whatever they wanted as if they were your coolsite.com user by just sending requests to the coolsite API (which would automatically include the auth cookie). They could send themselves a bunch of money from your user's account, change the user's password, etc. This is what a CSRF attack is.
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>To protect against CSRF attacks, Payload only accepts cookie-based authentication from domains that you explicitly whitelist.</strong>
<strong>
To protect against CSRF attacks, Payload only accepts cookie-based authentication from domains
that you explicitly whitelist.
</strong>
</Banner>
To define domains that should allow users to identify themselves via the Payload HTTP-only cookie, use the `csrf` option on the base Payload config to whitelist domains that you trust.
`payload.config.ts`:
```ts
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config';
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
const config = buildConfig({
collections: [
// collections here
],
// highlight-start
csrf: [ // whitelist of domains to allow cookie auth from
csrf: [
// whitelist of domains to allow cookie auth from
'https://your-frontend-app.com',
'https://your-other-frontend-app.com',
],
// highlight-end
});
})
export default config;
export default config
```
### Identifying users via the Authorization Header
@@ -150,11 +169,12 @@ export default config;
In addition to authenticating via an HTTP-only cookie, you can also identify users via the `Authorization` header on an HTTP request.
@@ -11,38 +11,46 @@ Because Payload uses your existing Express server, you are free to add whatever
This approach has a ton of benefits - it's great for isolation of concerns and limiting scope, but it also means that your additional routes won't have access to Payload's user authentication.
<Banner type="success">
You can make full use of Payload's built-in authentication within your own custom Express endpoints by adding Payload's authentication middleware.
You can make full use of Payload's built-in authentication within your own custom Express
endpoints by adding Payload's authentication middleware.
</Banner>
<Banner type="warning">
Payload must be initialized before the `payload.authenticate` middleware can be used. This is done
by calling `payload.init()` prior to adding the middleware.
Once you have created a project, you will need to select your plan. This will determine the resources that are allocated to your project and the features that are available to you.
<Banner type="success">
Note: All Payload Cloud teams that deploy a project require a card on file. This helps us prevent
fraud and abuse on our platform. If you select a plan with a free trial, you will not be charged
until your trial period is over. We’ll remind you 7 days before your trial ends and you can cancel
| **Region** | Select the region closest to your audience. This will ensure the fastest communication between your data and your client. |
| **Project Name** | A name for your project. You can change this at any time. |
| **Project Slug** | Choose a unique slug to identify your project. This needs to be unique for your team and you can change it any time. |
| **Team** | Select the team you want to create the project under. If this is your first project, a personal team will be created for you automatically. You can modify your team settings and invite new members at any time from the Team Settings page. |
### Build Settings
If you are deploying a new project from a template, the following settings will be automatically configured for you. If you are using your own repository, you need to make sure your build settings are accurate for your project to deploy correctly.
| **Root Directory** | The folder where your `package.json` file lives. |
| **Install Command** | The command used to install your modules, for example: `yarn install` or `npm install` |
| **Build Command** | The command used to build your application, for example: `yarn build` or `npm run build` |
| **Serve Command** | The command used to serve your application, for example: `yarn serve` or `npm run serve` |
| **Branch to Deploy** | Select the branch of your repository that you want to deploy from. This is the branch that will be used to build your project when you commit new changes. |
| **Default Domain** | Set a default domain for your project. This must be unique and you will not able to change it. You can always add a custom domain later in your project settings. |
### Environment Variables
Any of the features in Payload Cloud that require environment variables will automatically be provided to your application. If your app requires any custom environment variables, you can set them here.
<Banner type="warning">
Note: For security reasons, any variables you wish to provide to the Admin panel must be prefixed
Payment methods can be set per project and can be updated any time. You can use team’s default payment method, or add a new one. Modify your payment methods in your Project settings / Team settings.
<Banner type="success">
<strong>Note:</strong> All Payload Cloud teams that deploy a project require a card on file. This
helps us prevent fraud and abuse on our platform. If you select a plan with a free trial, you will
not be charged until your trial period is over. We’ll remind you 7 days before your trial ends and
A deployment solution specifically designed for Node.js + MongoDB applications, offering seamless deployment of your entire stack in one place. You can get started in minutes with a one-click template or bring your own codebase with you.
Payload Cloud offers various plans tailored to meet your specific needs, including a MongoDB Atlas database, S3 file storage, and email delivery powered by [Resend](https://resend.com). To see a full breakdown of features and plans, see our [Cloud Pricing page](https://payloadcms.com/cloud-pricing).
To get started, you first need to create an account. Head over to [the login screen](https://payloadcms.com/login) and **Register for Free**.
<Banner type="success">
To create your first project, you can either select [a template](#starting-from-a-template) or
[import an existing project](#importing-from-an-existing-codebase) from GitHub.
</Banner>
## Starting from a Template
Templates come preconfigured and provide a one-click solution to quickly deploy a new application.
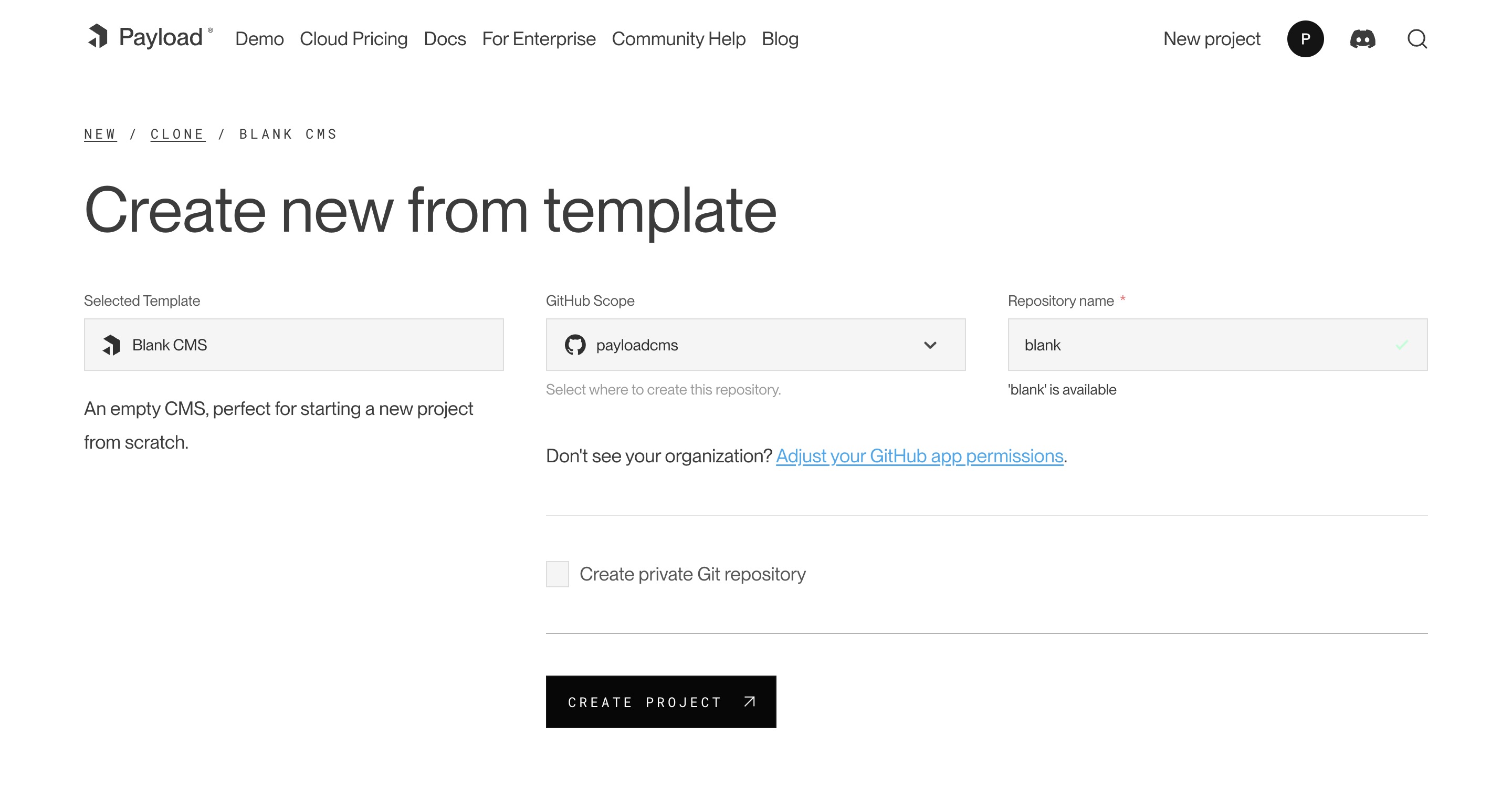
_Creating a new project from a template._
After creating an account, select your desired template from the Projects page. At this point, you need to connect to authorize the Payload Cloud application with your GitHub account. Click Continue with GitHub and follow the prompts to authorize the app.
Next, select your `GitHub Scope`. If you belong to multiple organizations, they will show up here. If you do not see the organization you are looking for, you may need to adjust your GitHub app permissions.
After selecting your scope, create a unique `repository name` and select whether you want your repository to be public or private on GitHub.
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Note:</strong> Public repositories can be accessed by anyone online, while private
repositories grant access only to you and anyone you explicitly authorize.
</Banner>
Once you are ready, click **Create Project**. This will clone the selected template to a new repository in your GitHub account, and take you to the configuration page to set up your project for deployment.
## Importing from an Existing Codebase
Payload Cloud works for any Node.js + MongoDB app. From the New Project page, select **import an existing Git codebase**. Choose the organization and select the repository you want to import. From here, you will be taken to the configuration page to set up your project for deployment.
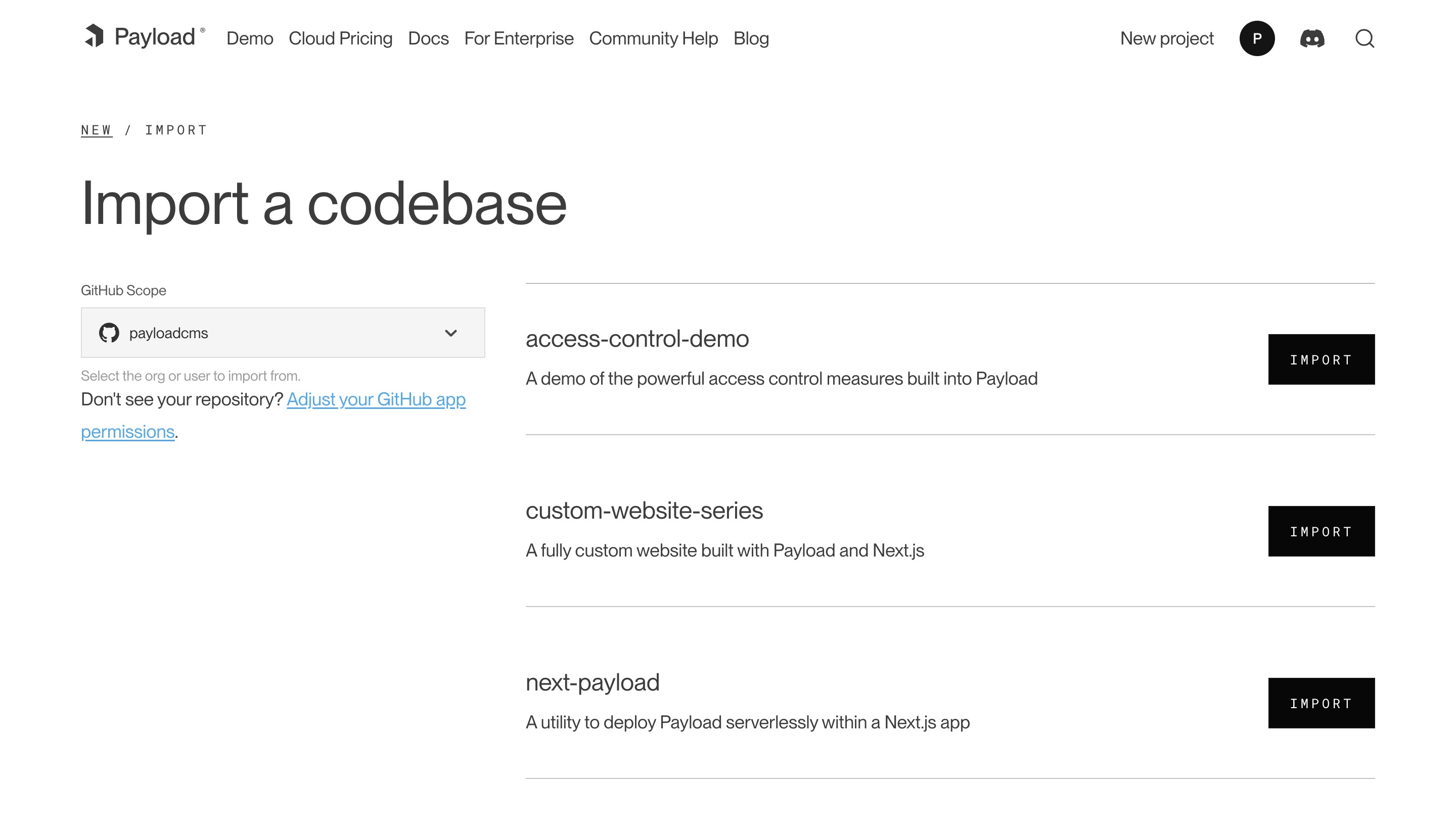
_Creating a new project from an existing repository._
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Note:</strong> In order to make use of the features of Payload Cloud in your own codebase,
you will need to add the [Cloud Plugin](https://github.com/payloadcms/plugin-cloud) to your
_A screenshot of the Overview page for a Cloud project._
### Database
Your Payload Cloud project comes with a MongoDB serverless Atlas DB instance or a Dedicated Atlas cluster, depending on your plan. To interact with your cloud database, you will be provided with a MongoDB connection string. This can be found under the **Database** tab of your project.
`mongodb+srv://your_connection_string`
### File Storage
Payload Cloud gives you S3 file storage backed by Cloudflare as a CDN, and this plugin extends Payload so that all of your media will be stored in S3 rather than locally.
AWS Cognito is used for authentication to your S3 bucket. The[Payload Cloud Plugin](https://github.com/payloadcms/plugin-cloud)will automatically pick up these values. These values are only if you'd like to access your files directly, outside of Payload Cloud.
### Build Settings
You can update settings from your Project’s Settings tab. Changes to your build settings will trigger a redeployment of your project.
### Environment Variables
From the Environment Variables page of the Settings tab, you can add, update and delete variables for use in your project. Like build settings, these changes will trigger a redeployment of your project.
<Banner>
Note: For security reasons, any variables you wish to provide to the Admin panel must be prefixed
With Payload Cloud, you can add custom domain names to your project. To do so, first go to the Domains page of the Settings tab of your project. Here you can see your default domain. To add a new domain, type in the domain name you wish to use.
<Banner>
Note: do not include the protocol (http:// or https://) or any paths (/page). Only include the
domain name and extension, and optionally a subdomain. - your-domain.com - backend.your-domain.com
</Banner>
Once you click save, a DNS record will be generated for your domain name to point to your live project. Add this record into your DNS provider’s records, and once the records are resolving properly (this can take 1hr to 48hrs in some cases), your domain will now to point to your live project.
You will also need to configure your Payload project to use your specified domain. In your `payload.config.ts` file, specify your `serverURL` with your domain:
```ts
export default buildConfig({
serverURL: 'https://example.com',
// the rest of your config,
})
```
### Email
Powered by [Resend](https://resend.com), Payload Cloud comes with integrated email support out of the box. No configuration is needed, and you can use `payload.sendEmail()` to send email right from your Payload app. To learn more about sending email with Payload, checkout the [Email Configuration](https://payloadcms.com/docs/email/overview) overview.
If you are on the Pro or Enterprise plan, you can add your own custom Email domain name. From the Email page of your project’s Settings, add the domain you wish to use for email delivery. This will generate a set of DNS records. Add these records to your DNS provider and click verify to check that your records are resolving properly. Once verified, your emails will now be sent from your custom domain name.
### Developing Locally
To make changes to your project, you will need to clone the repository defined in your project settings to your local machine. In order to run your project locally, you will need configure your local environment first. Refer to your repository’s `README.md` file to see the steps needed for your specific template.
From there, you are ready to make updates to your project. When you are ready to make your changes live, commit your changes to the branch you specified in your Project settings, and your application will automatically trigger a redeploy and build from your latest commit.
### Cloud Plugin
Projects generated from a template will come pre-configured with the official Cloud Plugin, but if you are using your own repository you will need to add this into your project. To do so, add the plugin to your Payload config:
`yarn add @payloadcms/plugin-cloud`
```js
import { payloadCloud } from '@payloadcms/plugin-cloud'
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
export default buildConfig({
plugins: [payloadCloud()],
// rest of config
})
```
<Banner type="warning">
**Note:** If your Payload config already has an email with transport, this will take precedence
over Payload Cloud's email service.
</Banner>
##### **Optional configuration**
If you wish to opt-out of any Payload cloud features, the plugin also accepts options to do so.
Within Payload Cloud, the team management feature offers you the ability to manage your
organization, team members, billing, and subscription settings.
</Banner>
_A screenshot of the Team Settings page._
### Members
Each team has members that can interact with your projects. You can invite multiple people to your team and each individual can belong to more than one team. You can assign them either `owner` or `user` permissions. Owners are able to make admin-only changes, such as deleting projects, and editing billing information.
### Adding Members
To add a new member to your team, visit your Team’s Settings page, and click “Invite Teammate”. You can then add their email address, and assign their role. Press “Save” to send the invitations, which will send an email to the invited team member where they can create a new account.
### Billing
Users can update billing settings and subscriptions for any teams where they are designated as an `owner`. To make updates to the team’s payment methods, visit the Billing page under the Team Settings tab. You can add new cards, delete cards, and set a payment method as a default. The default payment method will be used in the event that another payment method fails.
### Subscriptions
From the Subscriptions page, a team owner can see all current plans for their team. From here, you can see the price of each plan, if there is an active trial, and when you will be billed next.
### Invoices
The Invoices page will you show you the invoices for your account, as well as the status on their payment.
Payload Collections are defined through configs of their own, and you can define as many as your application needs. Each Collection will scaffold a MongoDB collection automatically based on fields that you define.
Payload Collections are defined through configs of their own, and you can define as many as your application needs. Each
Collection will scaffold a new collection automatically in your database of choice, based on fields that you define.
It's often best practice to write your Collections in separate files and then import them into the main Payload config.
## Options
| Option | Description |
|---------------- | -------------|
| **`slug`** * | Unique, URL-friendly string that will act as an identifier for this Collection. |
| **`fields`** * | Array of field types that will determine the structure and functionality of the data stored within this Collection. [Click here](/docs/fields/overview) for a full list of field types as well as how to configure them. |
| **`labels`** | Singular and plural labels for use in identifying this Collection throughout Payload. Auto-generated from slug if not defined. |
| **`admin`** | Admin-specific configuration. See below for [more detail](#admin-options). |
| **`hooks`** | Entry points to "tie in" to Collection actions at specific points. [More](/docs/hooks/overview#collection-hooks) |
| **`access`** | Provide access control functions to define exactly who should be able to do what with Documents in this Collection. [More](/docs/access-control/overview/#collections) |
| **`auth`** | Specify options if you would like this Collection to feature authentication. For more, consult the [Authentication](/docs/authentication/config) documentation. |
| **`upload`** | Specify options if you would like this Collection to support file uploads. For more, consult the [Uploads](/docs/upload/overview) documentation. |
| **`timestamps`** | Set to false to disable documents' automatically generated `createdAt` and `updatedAt` timestamps. |
| **`versions`** | Set to true to enable default options, or configure with object properties. [More](/docs/versions/overview#collection-config)|
| **`endpoints`** | Add custom routes to the REST API. [More](/docs/rest-api/overview#custom-endpoints) |
| **`slug`** \* | Unique, URL-friendly string that will act as an identifier for this Collection. |
| **`fields`** \* | Array of field types that will determine the structure and functionality of the data stored within this Collection. [Click here](/docs/fields/overview) for a full list of field types as well as how to configure them. |
| **`labels`** | Singular and plural labels for use in identifying this Collection throughout Payload. Auto-generated from slug if not defined. |
| **`admin`** | Admin-specific configuration. See below for [more detail](#admin-options). |
| **`hooks`** | Entry points to "tie in" to Collection actions at specific points. [More](/docs/hooks/overview#collection-hooks) |
| **`access`** | Provide access control functions to define exactly who should be able to do what with Documents in this Collection. [More](/docs/access-control/overview/#collections) |
| **`auth`** | Specify options if you would like this Collection to feature authentication. For more, consult the [Authentication](/docs/authentication/config) documentation. |
| **`upload`** | Specify options if you would like this Collection to support file uploads. For more, consult the [Uploads](/docs/upload/overview) documentation. |
| **`timestamps`** | Set to false to disable documents' automatically generated `createdAt` and `updatedAt` timestamps. |
| **`versions`** | Set to true to enable default options, or configure with object properties. [More](/docs/versions/overview#collection-config)|
| **`endpoints`** | Add custom routes to the REST API. Set to `false` to disable routes. [More](/docs/rest-api/overview#custom-endpoints) |
| **`graphQL`** | An object with `singularName` and `pluralName` strings used in schema generation. Auto-generated from slug if not defined. Set to `false` to disable GraphQL. |
| **`typescript`** | An object with property `interface` as the text used in schema generation. Auto-generated from slug if not defined. |
| **`defaultSort`** | Pass a top-level field to sort by default in the collection List view. Prefix the name of the field with a minus symbol ("-") to sort in descending order. |
| **`custom`** | Extension point for adding custom data (e.g. for plugins) |
*\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required.*
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
#### Simple collection example
```ts
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types';
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
const Orders: CollectionConfig = {
slug: 'orders',
fields: [
{
name: 'total',
type: 'number',
required: true,
},
{
name: 'placedBy',
type: 'relationship',
relationTo: 'customers',
required: true,
}
]
};
export const Orders: CollectionConfig = {
slug: 'orders',
fields: [
{
name: 'total',
type: 'number',
required: true,
},
{
name: 'placedBy',
type: 'relationship',
relationTo: 'customers',
required: true,
},
],
}
```
#### More collection config examples
You can find an assortment of [example collection configs](https://github.com/payloadcms/public-demo/tree/master/src/collections) in the Public Demo source code on GitHub.
You can find an assortment
of [example collection configs](https://github.com/payloadcms/public-demo/tree/master/src/collections) in the Public
Demo source code on GitHub.
### Admin options
You can customize the way that the Admin panel behaves on a collection-by-collection basis by defining the `admin` property on a collection's config.
You can customize the way that the Admin panel behaves on a collection-by-collection basis by defining the `admin`
property on a collection's config.
| Option | Description |
|---------------------------- | -------------|
| `group` | Text used as a label for grouping collection links together in the navigation. |
| `useAsTitle` | Specify a top-level field to use for a document title throughout the Admin panel. If no field is defined, the ID of the document is used as the title. |
| `description`| Text or React component to display below the Collection label in the List view to give editors more information. |
| `defaultColumns` | Array of field names that correspond to which columns to show by default in this collection's List view. |
| `disableDuplicate ` | Disables the "Duplicate" button while editing documents within this collection. |
| `group` | Text used as a label for grouping collection and global links together in the navigation. |
| `hidden` | Set to true or a function, called with the current user, returning true to exclude this collection from navigation and admin routing. |
| `hooks` | Admin-specific hooks for this collection. [More](#admin-hooks) |
| `useAsTitle` | Specify a top-level field to use for a document title throughout the Admin panel. If no field is defined, the ID of the document is used as the title. |
| `description` | Text or React component to display below the Collection label in the List view to give editors more information. |
| `defaultColumns` | Array of field names that correspond to which columns to show by default in this collection's List view. |
| `disableDuplicate ` | Disables the "Duplicate" button while editing documents within this collection. |
| `hideAPIURL` | Hides the "API URL" meta field while editing documents within this collection. |
| `enableRichTextLink` | The [Rich Text](/docs/fields/rich-text) field features a `Link` element which allows for users to automatically reference related documents within their rich text. Set to `true` by default. |
| `enableRichTextRelationship` | The [Rich Text](/docs/fields/rich-text) field features a `Relationship` element which allows for users to automatically reference related documents within their rich text. Set to `true` by default. |
| `preview` | Function to generate preview URLS within the Admin panel that can point to your app. [More](#preview). |
| `components` | Swap in your own React components to be used within this collection. [More](/docs/admin/components#collections) |
| `listSearchableFields ` | Specify which fields should be searched in the List search view. [More](/docs/configuration/collections#list-searchable-fields) |
| `preview` | Function to generate preview URLS within the Admin panel that can point to your app. [More](#preview). |
| `livePreview` | Enable real-time editing for instant visual feedback of your front-end application. [More](/docs/live-preview/overview). |
| `components` | Swap in your own React components to be used within this collection. [More](/docs/admin/components#collections) |
| `listSearchableFields` | Specify which fields should be searched in the List search view. [More](#list-searchable-fields) |
| **`pagination`** | Set pagination-specific options for this collection. [More](#pagination) |
### Preview
Collection `admin` options can accept a `preview` function that will be used to generate a link pointing to the frontend of your app to preview data.
Collection `admin` options can accept a `preview` function that will be used to generate a link pointing to the frontend
of your app to preview data.
If the function is specified, a Preview button will automatically appear in the corresponding collection's Edit view. Clicking the Preview button will link to the URL that is generated by the function.
If the function is specified, a Preview button will automatically appear in the corresponding collection's Edit view.
Clicking the Preview button will link to the URL that is generated by the function.
**The preview function accepts two arguments:**
@@ -85,65 +101,132 @@ If the function is specified, a Preview button will automatically appear in the
| `defaultLimit` | Integer that specifies the default per-page limit that should be used. Defaults to 10. |
| `limits` | Provide an array of integers to use as per-page options for admins to choose from in the List view. |
### Access control
You can specify extremely granular access control (what users can do with documents in a collection) on a collection by collection basis. To learn more, go to the [Access Control](/docs/access-control/overview) docs.
You can specify extremely granular access control (what users can do with documents in a collection) on a collection by
collection basis. To learn more, go to the [Access Control](/docs/access-control/overview) docs.
### Hooks
Hooks are a powerful way to extend collection functionality and execute your own logic, and can be defined on a collection by collection basis. To learn more, go to the [Hooks](/docs/hooks/overview) documentation.
Hooks are a powerful way to extend collection functionality and execute your own logic, and can be defined on a
collection by collection basis. To learn more, go to the [Hooks](/docs/hooks/overview) documentation.
### Field types
Collections support all field types that Payload has to offer—including simple fields like text and checkboxes all the way to more complicated layout-building field groups like Blocks. [Click here](/docs/fields/overview) to learn more about field types.
Collections support all field types that Payload has to offer—including simple fields like text and checkboxes all the
way to more complicated layout-building field groups like Blocks. [Click here](/docs/fields/overview) to learn more
about field types.
#### List Searchable Fields
### List Searchable Fields
In the List view, there is a "search" box that allows you to quickly find a document with a search. By default, it searches on the ID field. If you have `admin.useAsTitle` defined, the list search will use that field. However, you can define more than one field to search to make it easier on your admin editors to find the data they need.
In the List view, there is a "search" box that allows you to quickly find a document with a search. By default, it
searches on the ID field. If you have `admin.useAsTitle` defined, the list search will use that field. However, you can
define more than one field to search to make it easier on your admin editors to find the data they need.
For example, let's say you have a Posts collection with `title`, `metaDescription`, and `tags` fields - and you want all three of those fields to be searchable in the List view. You can simply add `admin.listSearchableFields: ['title', 'metaDescription', 'tags']` - and the admin UI will automatically search on those three fields plus the ID field.
For example, let's say you have a Posts collection with `title`, `metaDescription`, and `tags` fields - and you want all
three of those fields to be searchable in the List view. You can simply
add `admin.listSearchableFields: ['title', 'metaDescription', 'tags']` - and the admin UI will automatically search on
those three fields plus the ID field.
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Note:</strong><br/>
If you are adding <strong>listSearchableFields</strong>, make sure you index each of these fields so your admin queries can remain performant.
<strong>Note:</strong>
<br />
If you are adding <strong>listSearchableFields</strong>, make sure you index each of these fields
so your admin queries can remain performant.
</Banner>
### Admin Hooks
In addition to collection hooks themselves, Payload provides for admin UI-specific hooks that you can leverage.
**`beforeDuplicate`**
The `beforeDuplicate` hook is an async function that accepts an object containing the data to duplicate, as well as the
locale of the doc to duplicate. Within this hook, you can modify the data to be duplicated, which is useful in cases
where you have unique fields that need to be incremented or similar, as well as if you want to automatically modify a
document's `title`.
Example:
```ts
import { BeforeDuplicate, CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
// Your auto-generated Page type
import { Page } from '../payload-types.ts'
const beforeDuplicate: BeforeDuplicate<Page> = ({ data }) => {
Payload utilizes a few Express-specific middleware packages within its own routers. You can customize how they work by passing in configuration options to the main Payload config's `express` property.
### Custom Middleware
Payload allows you to pass in custom Express middleware to be used on all of the routes it opens. This is useful for adding logging or any other custom functionality to your endpoints.
There are 2 exposed properties. Each property is an array of middleware functions.
- `preMiddleware` - runs before any of the Payload middleware
- `postMiddleware` - runs after all of the Payload middleware
`express.json()` is used to parse JSON body content into JavaScript objects accessible on the Express `req`. Payload allows you to customize all of the `json` method's options. Common examples of customization use-cases are increasing the max allowed JSON body size which defaults to `2MB`.
@@ -36,11 +70,11 @@ To customize compression options, pass an object to the Payload config's `expres
Global configs are in many ways similar to [Collections](/docs/configuration/collections). The big difference is that Collections will potentially contain *many* documents, while a Global is a "one-off". Globals are perfect for things like header nav, site-wide banner alerts, app-wide localized strings, and other "global" data that your site or app might rely on.
Global configs are in many ways similar to [Collections](/docs/configuration/collections). The big difference is that Collections will potentially contain _many_ documents, while a Global is a "one-off". Globals are perfect for things like header nav, site-wide banner alerts, app-wide localized strings, and other "global" data that your site or app might rely on.
As with Collection configs, it's often best practice to write your Globals in separate files and then import them into the main Payload config.
## Options
| Option | Description |
| ---------------- | -------------|
| **`slug`** * | Unique, URL-friendly string that will act as an identifier for this Global. |
| **`fields`** * | Array of field types that will determine the structure and functionality of the data stored within this Global. [Click here](/docs/fields/overview) for a full list of field types as well as how to configure them. |
| **`label`** | Singular label for use in identifying this Global throughout Payload. Auto-generated from slug if not defined. |
| **`description`**| Text or React component to display below the Global header to give editors more information. |
| **`admin`** | Admin-specific configuration. See below for [more detail](/docs/configuration/globals#admin-options). |
| **`hooks`** | Entry points to "tie in" to collection actions at specific points. [More](/docs/hooks/overview#global-hooks) |
| **`access`** | Provide access control functions to define exactly who should be able to do what with this Global. [More](/docs/access-control/overview/#globals) |
| **`versions`** | Set to true to enable default options, or configure with object properties. [More](/docs/versions/overview#globals-config)|
| **`endpoints`** | Add custom routes to the REST API. [More](/docs/rest-api/overview#custom-endpoints)|
| **`slug`** \* | Unique, URL-friendly string that will act as an identifier for this Global. |
| **`fields`** \* | Array of field types that will determine the structure and functionality of the data stored within this Global. [Click here](/docs/fields/overview) for a full list of field types as well as how to configure them. |
| **`label`** | Text for the name in the Admin panel or an object with keys for each language. Auto-generated from slug if not defined. |
| **`description`**| Text or React component to display below the Global header to give editors more information. |
| **`admin`** | Admin-specific configuration. See below for [more detail](/docs/configuration/globals#admin-options). |
| **`hooks`** | Entry points to "tie in" to collection actions at specific points. [More](/docs/hooks/overview#global-hooks) |
| **`access`** | Provide access control functions to define exactly who should be able to do what with this Global. [More](/docs/access-control/overview/#globals) |
| **`versions`** | Set to true to enable default options, or configure with object properties. [More](/docs/versions/overview#globals-config)|
| **`endpoints`** | Add custom routes to the REST API. [More](/docs/rest-api/overview#custom-endpoints)|
| **`graphQL.name`** | Text used in schema generation. Auto-generated from slug if not defined. |
| **`typescript`** | An object with property `interface` as the text used in schema generation. Auto-generated from slug if not defined. |
| **`custom`** | Extension point for adding custom data (e.g. for plugins) |
*\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required.*
_\* An asterisk denotes that a property is required._
#### Simple Global example
```ts
import { GlobalConfig } from 'payload/types';
import { GlobalConfig } from 'payload/types'
const Nav: GlobalConfig = {
slug: 'nav',
fields: [
{
name: 'items',
type: 'array',
required: true,
maxRows: 8,
fields: [
{
name: 'page',
type: 'relationship',
relationTo: 'pages', // "pages" is the slug of an existing collection
required: true,
}
]
},
]
};
slug: 'nav',
fields: [
{
name: 'items',
type: 'array',
required: true,
maxRows: 8,
fields: [
{
name: 'page',
type: 'relationship',
relationTo: 'pages', // "pages" is the slug of an existing collection
required: true,
},
],
},
],
}
export default Nav;
export default Nav
```
#### Global config example
@@ -62,9 +65,51 @@ You can find an [example Global config](https://github.com/payloadcms/public-dem
You can customize the way that the Admin panel behaves on a Global-by-Global basis by defining the `admin` property on a Global's config.
| Option | Description |
| ---------------------------- | -------------|
| `components` | Swap in your own React components to be used within this Global. [More](/docs/admin/components#globals) |
| `group` | Text used as a label for grouping collection and global links together in the navigation. |
| `hidden` | Set to true or a function, called with the current user, returning true to exclude this global from navigation and admin routing. |
| `components` | Swap in your own React components to be used within this Global. [More](/docs/admin/components#globals) |
| `preview` | Function to generate a preview URL within the Admin panel for this global that can point to your app. [More](#preview). |
| `livePreview`| Enable real-time editing for instant visual feedback of your front-end application. [More](/docs/live-preview/overview). |
| `hideAPIURL` | Hides the "API URL" meta field while editing documents within this collection. |
### Preview
Global `admin` options can accept a `preview` function that will be used to generate a link pointing to the frontend of your app to preview data.
If the function is specified, a Preview button will automatically appear in the corresponding global's Edit view. Clicking the Preview button will link to the URL that is generated by the function.
**The preview function accepts two arguments:**
1. The document being edited
1. An `options` object, containing `locale` and `token` properties. The `token` is the currently logged-in user's JWT.
Not only does Payload support managing localized content, it also has internationalization support so that admin users can work in their preferred language. Payload's i18n support is built on top of [i18next](https://www.i18next.com). It comes included by default and can be extended in your config.
While Payload's built-in features come translated, you may want to also translate parts of your project's configuration too. This is possible in places like collections and globals labels and groups, field labels, descriptions and input placeholder text. The admin UI will display all the correct translations you provide based on the user's language.
Here is an example of a simple collection supporting both English and Spanish editors:
```ts
import { CollectionConfig } from 'payload/types'
export const Articles: CollectionConfig = {
slug: 'articles',
labels: {
singular: {
en: 'Article',
es: 'Artículo',
},
plural: {
en: 'Articles',
es: 'Artículos',
},
},
admin: {
group: { en: 'Content', es: 'Contenido' },
},
fields: [
{
name: 'title',
type: 'text',
label: {
en: 'Title',
es: 'Título',
},
admin: {
placeholder: { en: 'Enter title', es: 'Introduce el título' },
},
},
{
name: 'type',
type: 'radio',
options: [
{
value: 'news',
label: { en: 'News', es: 'Noticias' },
}, // etc...
],
},
],
}
```
### Admin UI
The Payload admin panel reads the language settings of a user's browser and display all text in that language, or will fall back to English if the user's language is not yet supported.
After a user logs in, they can change their language selection in the `/account` view.
<Banner>
<strong>Note:</strong>
<br />
If there is a language that Payload does not yet support, we accept code
Payload's backend uses express middleware to set the language on incoming requests before they are handled. This allows backend validation to return error messages in the user's own language or system generated emails to be sent using the correct translation. You can make HTTP requests with the `accept-language` header and Payload will use that language.
Anywhere in your Payload app that you have access to the `req` object, you can access i18next's extensive internationalization features assigned to `req.i18n`. To access text translations you can use `req.t('namespace:key')`.
Read the i18next [API documentation](https://www.i18next.com/overview/api) to learn more.
### Configuration Options
In your Payload config, you can add translations and customize the settings in `i18n`. Payload will use your custom options and merge it with the default, allowing you to override the settings Payload provides.
**Example Payload config extending i18n:**
```ts
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
export default buildConfig({
//...
i18n: {
fallbackLng: 'en', // default
debug: false, // default
resources: {
en: {
custom: {
// namespace can be anything you want
key1: 'Translation with {{variable}}', // translation
},
// override existing translation keys
general: {
dashboard: 'Home',
},
},
},
},
//...
})
```
See the i18next [configuration options](https://www.i18next.com/overview/configuration-options) to learn more.
@@ -17,31 +17,55 @@ Add the `localization` property to your Payload config to enable localization pr
```ts
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
export default buildConfig({
collections: [
// collections go here
],
localization: {
locales: ['en', 'es', 'de'],
defaultLocale: 'en',
fallback: true,
},
})
```
**Example Payload config set up for localization with full locales objects:**
```ts
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
export default buildConfig({
collections: [
// collections go here
],
localization: {
locales: [
'en',
'es',
'de',
{
label: 'English',
code: 'en',
},
{
label: 'Arabic',
code: 'ar',
// opt-in to setting default text-alignment on Input fields to rtl (right-to-left) when current locale is rtl
rtl: true,
},
],
defaultLocale: 'en',
fallback: true,
},
});
})
```
**Here is a brief explanation of each of the options available within the `localization` property:**
**`locales`**
Array-based list of all locales that you would like to support. These strings do not need to be in any specific format. It's up to you to define how to represent your locales. Common patterns are to use two-letter ISO 639 language codes or four-letter language and country codes (ISO 3166‑1) such as `en-US`, `en-UK`, `es-MX`, etc.
Array-based list of all locales that you would like to support. These can be strings of locale codes or objects with a `label`, a locale `code`, and the `rtl` (right-to-left) property. The locale codes do not need to be in any specific format. It's up to you to define how to represent your locales. Common patterns are to use two-letter ISO 639 language codes or four-letter language and country codes (ISO 3166‑1) such as `en-US`, `en-UK`, `es-MX`, etc.
**`defaultLocale`**
Required string that matches one of the locales from the array provided. By default, if no locale is specified, documents will be returned in this locale.
Required string that matches one of the locale codes from the array provided. By default, if no locale is specified, documents will be returned in this locale.
**`fallback`**
@@ -68,8 +92,21 @@ With the above configuration, the `title` field will now be saved in the databas
All field types with a `name` property support the `localized` property—even the more complex field types like `array`s and `block`s.
<Banner>
<strong>Note:</strong><br/>
Enabling localization for field types that support nested fields will automatically create localized "sets" of all fields contained within the field. For example, if you have a page layout using a blocks field type, you have the choice of either localizing the full layout, by enabling localization on the top-level blocks field, or only certain fields within the layout.
<strong>Note:</strong>
<br />
Enabling localization for field types that support nested fields will automatically create
localized "sets" of all fields contained within the field. For example, if you have a page layout
using a blocks field type, you have the choice of either localizing the full layout, by enabling
localization on the top-level blocks field, or only certain fields within the layout.
</Banner>
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Important:</strong>
<br />
When converting an existing field to or from `localized: true` the data structure in the document
will change for this field and so existing data for this field will be lost. Before changing the
localization setting on fields with existing data, you may need to consider a field migration
strategy.
</Banner>
### Retrieving localized docs
@@ -115,7 +152,9 @@ query {
```
<Banner>
In GraphQL, specifying the locale at the top level of a query will automatically apply it throughout all nested relationship fields. You can override this behavior by re-specifying locale arguments in nested related document queries.
In GraphQL, specifying the locale at the top level of a query will automatically apply it
throughout all nested relationship fields. You can override this behavior by re-specifying locale
<strong>Tip:</strong><br/>The REST and Local APIs can return all localization data in one request by passing 'all' or '*' as the <strong>locale</strong> parameter. The response will be structured so that field values come back as the full objects keyed for each locale instead of the single, translated value.
<strong>Tip:</strong>
<br />
The REST and Local APIs can return all localization data in one request by passing 'all' or '*' as
the <strong>locale</strong> parameter. The response will be structured so that field values come
back as the full objects keyed for each locale instead of the single, translated value.
Payload is a *config-based*, code-first CMS and application framework. The Payload config is central to everything that Payload does. It scaffolds the data that Payload stores as well as maintains custom React components, hook logic, custom validations, and much more. The config itself and all of its dependencies are run through Babel, so you can take full advantage of newer JavaScript features and even directly import React components containing JSX.
Payload is a _config-based_, code-first CMS and application framework. The Payload config is central to everything that Payload does. It scaffolds the data that Payload stores as well as maintains custom React components, hook logic, custom validations, and much more.
<strong>Also, because the Payload source code is fully written in TypeScript, its configs are strongly typed—meaning that even if you aren't using TypeScript to build your project, your IDE (such as VSCode) may still provide helpful information like type-ahead suggestions while you write your config.</strong>
**Also, because the Payload source code is fully written in TypeScript, its configs are strongly typed—meaning that even if you aren't using TypeScript, your IDE (such as VSCode) may still provide helpful information like type-ahead suggestions while you write your config.**
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Important:</strong><br />This file is included in the Payload admin bundle, so make sure you do not embed any sensitive information.
<strong>Important:</strong>
<br />
This file is included in the Payload admin bundle, so make sure you do not embed any sensitive
information.
</Banner>
## Options
| Option | Description |
| -------------------- | -------------|
| `serverURL` | A string used to define the absolute URL of your app including the protocol, for example `https://example.com`. No paths allowed, only protocol, domain and (optionally) port |
| `collections` | An array of all Collections that Payload will manage. To read more about how to define your collection configs, [click here](/docs/configuration/collections). |
| `cors` | Either a whitelist array of URLS to allow CORS requests from, or a wildcard string (`'*'`) to accept incoming requests from any domain. |
| `globals` | An array of all Globals that Payload will manage. For more on Globals and their configs, [click here](/docs/configuration/globals). |
| `admin` | Base Payload admin configuration. Specify custom components, control metadata, set the Admin user collection, and [more](/docs/admin/overview#admin-options). |
| `localization` | Opt-in and control how Payload handles the translation of your content into multiple locales. [More](/docs/configuration/localization) |
| `graphQL` | Manage GraphQL-specific functionality here. Define your own queries and mutations, manage query complexity limits, and [more](/docs/graphql/overview#graphql-options). |
| `cookiePrefix` | A string that will be prefixed to all cookies that Payload sets. |
| `csrf` | A whitelist array of URLs to allow Payload cookies to be accepted from as a form of CSRF protection. [More](/docs/authentication/overview#csrf-protection) |
| `defaultDepth` | If a user does not specify `depth` while requesting a resource, this depth will be used. [More](/docs/getting-started/concepts#depth) |
| `maxDepth` | The maximum allowed depth to be permitted application-wide. This setting helps prevent against malicious queries. Defaults to `10`. |
| `indexSortableFields`| Automatically index all sortable top-level fields in the database to improve sort performance and add database compatibility for Azure Cosmos and similar. |
| `upload` | Base Payload upload configuration. [More](/docs/upload/overview#payload-wide-upload-options). |
| `routes` | Control the routing structure that Payload binds itself to. Specify `admin`, `api`, `graphQL`, and `graphQLPlayground`. |
| `email` | Base email settings to allow Payload to generate email such as Forgot Password requests and other requirements. [More](/docs/email/overview#configuration) |
| `express`| Express-specific middleware options such as compression and JSON parsing. [More](/docs/configuration/express) |
| `debug` | Enable to expose more detailed error information. |
| `rateLimit` | Control IP-based rate limiting for all Payload resources. Used to prevent DDoS attacks and [more](/docs/production/preventing-abuse#rate-limiting-requests). |
| `hooks` | Tap into Payload-wide hooks. [More](/docs/hooks/overview) |
| `plugins` | An array of Payload plugins. [More](/docs/plugins/overview) |
| `endpoints` | An array of custom API endpoints added to the Payload router. [More](/docs/rest-api/overview#custom-endpoints) |
| `serverURL` | A string used to define the absolute URL of your app including the protocol, for example `https://example.com`. No paths allowed, only protocol, domain and (optionally) port |
| `collections` | An array of all Collections that Payload will manage. To read more about how to define your collection configs, [click here](/docs/configuration/collections). |
| `cors` | Either a whitelist array of URLS to allow CORS requests from, or a wildcard string (`'*'`) to accept incoming requests from any domain. |
| `globals` | An array of all Globals that Payload will manage. For more on Globals and their configs, [click here](/docs/configuration/globals). |
| `admin` | Base Payload admin configuration. Specify custom components, control metadata, set the Admin user collection, and [more](/docs/admin/overview#admin-options). |
| `editor` | Default richText editor which will be used by richText fields. |
| `localization` | Opt-in and control how Payload handles the translation of your content into multiple locales. [More](/docs/configuration/localization) |
| `graphQL` | Manage GraphQL-specific functionality here. Define your own queries and mutations, manage query complexity limits, and [more](/docs/graphql/overview#graphql-options). |
| `cookiePrefix` | A string that will be prefixed to all cookies that Payload sets. |
| `csrf` | A whitelist array of URLs to allow Payload cookies to be accepted from as a form of CSRF protection. [More](/docs/authentication/overview#csrf-protection) |
| `defaultDepth` | If a user does not specify `depth` while requesting a resource, this depth will be used. [More](/docs/getting-started/concepts#depth) |
| `maxDepth` | The maximum allowed depth to be permitted application-wide. This setting helps prevent against malicious queries. Defaults to `10`. |
| `indexSortableFields` | Automatically index all sortable top-level fields in the database to improve sort performance and add database compatibility for Azure Cosmos and similar. |
| `upload` | Base Payload upload configuration. [More](/docs/upload/overview#payload-wide-upload-options). |
| `routes` | Control the routing structure that Payload binds itself to. Specify `admin`, `api`, `graphQL`, and `graphQLPlayground`. |
| `email` | Base email settings to allow Payload to generate email such as Forgot Password requests and other requirements. [More](/docs/email/overview#configuration) |
| `express` | Express-specific middleware options such as compression and JSON parsing. [More](/docs/configuration/express) |
| `debug` | Enable to expose more detailed error information. |
| `rateLimit` | Control IP-based rate limiting for all Payload resources. Used to prevent DDoS attacks and [more](/docs/production/preventing-abuse#rate-limiting-requests). |
| `hooks` | Tap into Payload-wide hooks. [More](/docs/hooks/overview) |
| `plugins` | An array of Payload plugins. [More](/docs/plugins/overview) |
| `endpoints` | An array of custom API endpoints added to the Payload router. [More](/docs/rest-api/overview#custom-endpoints) |
| `custom` | Extension point for adding custom data (e.g. for plugins) |
#### Simple example
```ts
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config';
import { buildConfig } from 'payload/config'
import { mongooseAdapter } from '@payloadcms/db-mongodb'
import { postgresAdapter } from '@payloadcms/db-postgres'
import { viteBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-vite'
import { webpackBundler } from '@payloadcms/bundler-webpack'
import { lexicalEditor } from '@payloadcms/richtext-lexical'
import { slateEditor } from '@payloadcms/richtext-slate'
export default buildConfig({
collections: [
{
slug: 'pages',
fields: [
{
name: 'title',
type: 'text',
required: true,
},
{
name: 'content',
type: 'richText',
required: true,
}
]
}
],
globals: [
{
slug: 'header',
fields: [
{
name: 'nav',
type: 'array',
fields: [
{
name: 'page',
type: 'relationship',
relationTo: 'pages',
},
]
}
]
}
]
});
bundler: webpackBundler() // or viteBundler(),
db: mongooseAdapter({}) // or postgresAdapter({}),
editor: lexicalEditor({}) // or slateEditor({})
collections: [
{
slug: 'pages',
fields: [
{
name: 'title',
type: 'text',
required: true,
},
{
name: 'content',
type: 'richText',
required: true,
},
],
},
],
globals: [
{
slug: 'header',
fields: [
{
name: 'nav',
type: 'array',
fields: [
{
name: 'page',
type: 'relationship',
relationTo: 'pages',
},
],
},
],
},
],
})
```
#### Full example config
@@ -94,12 +110,15 @@ You can see a full [example config](https://github.com/payloadcms/public-demo/bl
We suggest using the `dotenv` package to handle environment variables alongside of Payload. All that's necessary to do is to require the package as high up in your application as possible (for example, at the top of your `server.js` file), and ensure that it can find an `.env` file that you create.
**Add this line to the top of your server:**
```
require('dotenv').config()
// ...
// the rest of your `server.js` file goes here
```
Note that if you rely on any environment variables in your config itself, you should also call `dotenv()` at the top of your config itself as well. There's no harm in calling it in both your server and your config itself!
**Here is an example project structure w/ `dotenv` and an `.env` file:**
```
@@ -111,75 +130,56 @@ project-name
```
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Important:</strong><br />
If you use an environment variable to configure any properties that are required for the Admin panel to function (ex. serverURL or any routes), you need to make sure that your Admin panel code can access it. <a href="/docs/admin/webpack#admin-environment-vars">Click here</a> for more info.
<strong>Important:</strong>
<br />
If you use an environment variable to configure any properties that are required for the Admin
panel to function (ex. serverURL or any routes), you need to make sure that your Admin panel code
can access it. [Click here](/docs/admin/webpack#admin-environment-vars) for more info.
By default, the Payload config must be in the root of your current working directory and named either `payload.config.js` or `payload.config.ts` if you're using TypeScript.
Payload is designed to automatically locate your configuration file. By default, it will first look in the root of your current working directory for a file named `payload.config.js` or `payload.config.ts` if you're using TypeScript.
But, you can specify where your Payload config is located as well as what it's named by using the environment variable `PAYLOAD_CONFIG_PATH`. The path you provide via this environment variable can either be absolute or relative to your current working directory.
In development mode, if the configurationfile is not found at the root, Payload will attempt to read your `tsconfig.json`, and search in the directory specified in `compilerOptions.rootDir` (typically "src").
In production mode, Payload will first attempt to find the config file in the output directory specified in `compilerOptions.outDir` of your `tsconfig.json`, then fallback to the source directory (`compilerOptions.rootDir`), and finally will check the 'dist' directory.
Please ensure your `tsconfig.json` is properly configured if you want Payload to accurately auto-detect your configuration file location. If `tsconfig.json` does not exist or doesn't specify `rootDir` or `outDir`, Payload will default to the current working directory.
#### Overriding the Config Location
In addition to the above automated detection, you can specify your own location for the Payload config file. This is done by using the environment variable `PAYLOAD_CONFIG_PATH`. The path you provide via this environment variable can either be absolute or relative to your current working directory. This can be useful in situations where your Payload config is not in a standard location, or you wish to switch between multiple configurations.
When `PAYLOAD_CONFIG_PATH` is set, Payload will use this path to load the configuration, bypassing all automated detection.
### Developing within the Config
The Payload config itself, as well as all files that it requires or imports, are run through Babel. TypeScript and all common ES6 features are fully supported. To see the Babel config that is used to parse Payload configs, check out the Payload source code [here](https://github.com/payloadcms/payload/blob/master/src/babel.config.js).
Payload comes with `isomorphic-fetch` installed which means that even in Node, you can use the `fetch` API just as you would within the browser. No need to import `axios` or similar, unless you want to!
#### Payload Config and Babel
The entire Payload config is transpiled automatically by Payload via `babel`.
If for any reason you need to re-use the built-in Payload `babel.config.js`, you can do so by importing it as follows:
```
import { config } from 'payload/babel';
```
<Banner type="warning">
<strong>Note:</strong><br/>
Because the Payload config is transpiled internally, if you want to import it to share or reuse any of its properties within your own Node server's code, you need to make sure that <em>you manually transpile it</em> using <strong>babel-register</strong> or similar. For example, if you try to import your config directly into your server, your Node process will likely crash because the Payload config supports React components, TypeScript, and new ES6+ features.
</Banner>
However, you can share code, like for example your config's `serverURL` property by "hoisting" your shared properties above your config and writing any "shared" code in a module that is compatible with your Node environment.
For example, to share your `serverURL`, you could create a file like the following:
`serverURL.js`:
```js
const serverURL = 'http://localhost:3000';
module.exports = serverURL;
```
Then, you could import this file into both your Payload config and your server, in an effort to avoid importing your full Payload config directly into your server.
### TypeScript
You can import config types as follows:
```ts
import { Config } from 'payload/config';
import { Config } from 'payload/config'
// This is the type used for an incoming Payload config.
// Only the bare minimum properties are marked as required.
```
```ts
import { SanitizedConfig } from 'payload/config';
import { SanitizedConfig } from 'payload/config'
// This is the type used after an incoming Payload config is fully sanitized.
// Generally, this is only used internally by Payload.
desc: Payload features first-party database migrations all done in TypeScript.
---
Payload exposes a full suite of migration controls available for your use. Migration commands are accessible via the `npm run payload` command in your project directory.
Ensure you have an npm script called "payload" in your `package.json` file.
Note that you need to run Payload migrations through the package manager that you are using, because Payload should not be globally installed on your system.
</Banner>
### Migration file contents
Payload stores all created migrations in a folder that you can specify. By default, migrations are stored in `./src/migrations`.
A migration file has two exports - an `up` function, which is called when a migration is executed, and a `down` function that will be called if for some reason the migration fails to complete successfully. The `up` function should contain all changes that you attempt to make within the migration, and the `down` should ideally revert any changes you make.
For an added level of safety, migrations should leverage Payload [transactions](/docs/database/transactions).
Here is an example migration file:
```ts
import { MigrateUpArgs, MigrateDownArgs } from '@payloadcms/your-db-adapter'
export async function up({ payload }: MigrateUpArgs): Promise<void> {
// Perform changes to your database here.
// You have access to `payload` as an argument, and
// everything is done in TypeScript.
};
export async function down({ payload }: MigrateDownArgs): Promise<void> {
// Do whatever you need to revert changes if the `up` function fails
};
```
All database adapters should implement similar migration patterns, but there will be small differences based on the adapter and its specific needs. Below is a list of all migration commands that should be supported by your database adapter.
### Migrate
The `migrate` command will run any migrations that have not yet been run.
```text
npm run payload migrate
```
### Create
Create a new migration file in the migrations directory. You can optionally name the migration that will be created. By default, migrations will be named using a timestamp.
```text
npm run payload migrate:create optional-name-here
```
### Status
The `migrate:status` command will check the status of migrations and output a table of which migrations have been run, and which migrations have not yet run.
`payload migrate:status`
```text
npm run payload migrate:status
```
### Down
Roll back the last batch of migrations.
```text
npm run payload migrate:down
```
### Refresh
Roll back all migrations that have been run, and run them again.
```text
npm run payload migrate:refresh
```
### Reset
Roll back all migrations.
```text
npm run payload migrate:reset
```
### Fresh
Drops all entities from the database and re-runs all migrations from scratch.
To use Payload with MongoDB, install the package `@payloadcms/db-mongodb`. It will come with everything you need to store your Payload data in MongoDB.
Then from there, pass it to your Payload config as follows:
```ts
import { mongooseAdapter } from '@payloadcms/db-mongodb'
| `autoPluralization` | Tell Mongoose to auto-pluralize any collection names if it encounters any singular words used as collection `slug`s. |
| `connectOptions` | Customize MongoDB connection options. Payload will connect to your MongoDB database using default options which you can override and extend to include all the [options](https://mongoosejs.com/docs/connections.html#options) available to mongoose. |
| `migrationDir` | Customize the directory that migrations are stored. |
### Access to Mongoose models
After Payload is initialized, this adapter exposes all of your Mongoose models and they are available for you to work with directly.
We will be adding support for SQLite and MySQL in the near future using Drizzle ORM.
To use a specific database adapter, you need to install it and configure it according to its own specifications. Visit the documentation for your applicable database adapter to learn more.
## Selecting a database
There are several factors to consider when choosing which database technology and hosting option is right for your project and workload. Payload can theoretically support any database, but it's up to you to decide which database to use.
#### When to use MongoDB
If your project has a lot of dynamic fields, and you are comfortable with allowing Payload to enforce data integrity across your documents, MongoDB is a great choice. With it, your Payload documents are stored as _one_ document in your database—no matter if you have localization enabled, how many block or array fields you have, etc. This means that the shape of your data in your database will very closely reflect your field schema, and there is minimal complexity involved in storing or retrieving your data.
You should prefer MongoDB if:
- You prefer simplicity within your database
- You don't want to deal with keeping production / staging databases in sync via [DDL changes](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_definition_language)
- Most (or everything) in your project is localized
- You leverage a lot of array fields, block fields, or `hasMany` select fields and similar
#### When to use a relational DB
Many projects might call for more rigid database architecture where the shape of your data is strongly enforced at the database level. For example, if you know the shape of your data and it's relatively "flat", and you don't anticipate it to change often, your workload might suit relational databases like Postgres very well.
You should prefer a relational DB like Postgres if:
- You are comfortable with migration workflows
- You require enforced data consistency at the database level
- You have a lot of relationships between collections and require relationships to be enforced
#### Differences in Payload features
It's important to note that almost everything Payload does is available in all of our officially supported database adapters, including localization, arrays, blocks, etc.
The only thing that is not supported in Postgres yet is the [Point field](/docs/fields/point), but that should be added soon.
It's up to you to choose which database you would like to use.
## Configuration
To configure the database for your Payload application, an adapter can be assigned to `config.db`. This property is required within your Payload config.
Here's an example:
```ts
import { postgresAdapter } from '@payloadcms/db-postgres'
export default buildConfig({
// Your config goes here
collections: [
// Collections go here
],
// Here is where you pass your database adapter
// and the adapter will require options specific to itself
db: postgresAdapter({
pool: {
connectionString: process.env.DATABASE_URI,
}
}),
})
```
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff
Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user
Blocking a user prevents them from interacting with repositories, such as opening or commenting on pull requests or issues. Learn more about blocking a user.